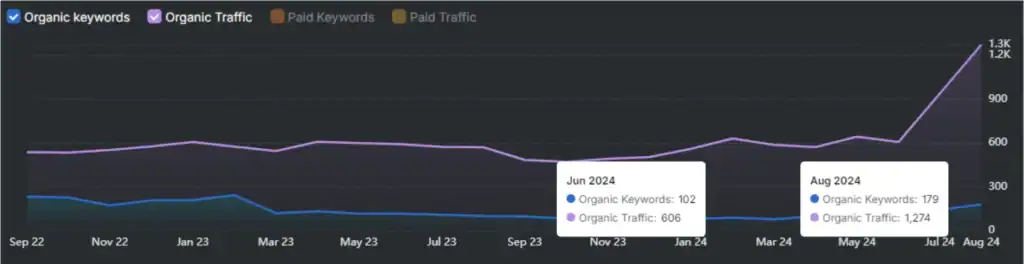
Use controlled SEO A/B tests (server-side when possible) to identify which on-page changes improve rankings, CTR, or organic sessions.
Introduction
SEO A/B testing (also called SEO split testing) is a structured experiment that compares a control group of pages against one or more variant groups to measure which changes improve organic search performance. This article covers A/B testing for organic search and explains the mechanics of SEO split testing, why experiment design matters for search engines, and how automation and AI accelerate valid test cycles for measurable ranking and traffic gains. You will learn practical planning steps, deployment methods including server-side and client-side options, the KPIs to prioritize, and advanced approaches such as LLM visibility testing and cross-page rollouts. The guide also compares tool types, shows EAV-style tables that map feature requirements to solutions, and highlights common pitfalls to avoid during multi-week experiments. Read on for a reproducible framework you can apply to content, technical, and local (GBP) experiments using modern automation while keeping measurement rigorous and transparent.
What Is SEO A/B Testing and Why Is It Essential for SEO Experimentation?
SEO A/B testing compares two page versions (control vs variant) to measure which delivers better organic search performance. It replaces guesswork with statistical evidence: instead of assuming a title change helps, you measure its actual impact on rankings, CTR, and organic sessions.
Why SEO A/B testing matters:
- Evidence-based decisions: Quantify impact before rolling out changes to thousands of pages
- Risk reduction: Test at small scale before full deployment, avoiding company-wide regressions
- Scale efficiency: Automation and AI accelerate test cycles, enabling teams to run 10+ experiments monthly
- LLM optimization: Test content variants that rank in AI-generated answers and knowledge surfaces, not just traditional SERPs
SEO A/B testing is the practice of exposing search engines and users to variant and control page versions in a controlled way to measure changes in organic metrics such as rankings, impressions, CTR, and LLM-driven answers.
The mechanism relies on randomized or segmented exposure, consistent measurement windows, and pre-specified hypotheses — these design choices allow teams to infer causation rather than assume correlation.
The primary benefit is evidence-based optimization: instead of guessing whether a title or schema change helps, teams can quantify the impact on organic visibility and make data-driven rollouts. For teams seeking automation and scale, an AI-powered workflow that can deploy, monitor, analyze, and scale experiments shortens iteration time while preserving test integrity.
The goal is to provide reproducible, measurable experiments that improve outcomes while keeping measurement rigorous and transparent. SEO A/B testing differs from heuristic changes because it treats each change as an experimentable hypothesis with control and variant groups, enabling statistical comparison and safer rollouts. The next section contrasts SEO A/B testing with traditional front-end A/B testing to clarify measurement expectations.
A/B Testing for SEO: Optimizing Webpages with Server-Side and Client-Side Approaches
For instance, A/B Testing, a standard method in web analytics, is used to compare two versions of a webpage to determine which one performs better. This method is widely used in SEO for optimizing various elements of a website, such as headlines, calls to action, and page layouts, to improve user engagement and search engine rankings. The effectiveness of A/B testing in SEO is further enhanced by considering server-side and client-side implementations, as server-side testing can offer more control and efficiency in measuring certain aspects, such as A/B testing, query response time, and user experience.
Enhancing SEO in single-page web applications in contrast with multi-page applications, T Szandala, 2024
How Does SEO A/B Testing Differ from Traditional A/B Testing?
How Does SEO A/B Testing Differ from Traditional A/B Testing?
SEO A/B tests measure delayed organic signals (4–8 weeks), while traditional A/B tests measure immediate conversions (days). This requires different testing windows, larger sample sizes, and strict verification that Googlebot sees your variants.
Key differences:
- Time horizon: Traditional UX tests: 1–2 weeks; SEO tests: 4–8+ weeks for signal stabilization
- Measurement: UX focuses on immediate visitor conversions; SEO tracks rankings, impressions, organic sessions, and LLM visibility
- Visibility constraints: Search engines observe variants via crawling (introducing indexation lag); traditional tests observe user-side behavior directly
- Success criteria: UX prioritizes clickthrough rate; SEO prioritizes organic KPIs and ranking movement
When planning tests, treat indexation and crawl budget as constraints and verify Googlebot exposure before relying on early traffic signals.
What Are the Core Concepts: Control Groups, Variant Groups, and Hypotheses?
SEO experiments require three core elements: a control group of untouched pages, variant groups that change only one element, and a pre-specified measurable hypothesis. This isolation approach allows you to attribute results to the change itself.
Core components:
- Control group: Pages left untouched or matched by traffic/intent (baseline for comparison)
- Variant group: Pages with a single, isolated change (e.g., title shortening, schema addition, content rewrite)
- Hypothesis: Measurable prediction (e.g., “Shortening titles to 50 characters will increase CTR by 2% and organic sessions by 5% over 8 weeks”)
- Segmentation rules: Define traffic assignment to avoid spillover and ensure cohort independence
- Example experiments: Common experiments include SEO title tag split‑testing, meta description variants, and different internal linking patterns (anchor text, internal navigation changes) to test content discoverability and ranking impact.
Randomization, sample size estimation, and pre-registration of hypotheses reduce bias and make results interpretable. SEO A/B testing planning naturally leads to step-by-step deployment techniques and automation choices, which we cover next to help you execute experiments reliably and at scale.

How to Do SEO A/B Testing: Step-by-Step Guide Using AI Automation Tools
SEO A/B testing follows a repeatable workflow: define hypothesis and metrics, select and segment pages, implement variants, verify crawler exposure, monitor KPIs over a sufficient window, and scale winners. Automation streamlines iterative tasks such as variant generation, deployment orchestration, and monitoring, allowing teams to run more tests with fewer manual steps while maintaining governance. A clear testing cadence—planning, pre-flight checks, live monitoring, and post-test rollout—keeps experiments auditable and reduces risk when changes go live. The following numbered list outlines the core execution steps to adopt in practical workflows.
- Define hypothesis and success metrics with target thresholds and measurement windows.
- Select pages and segment traffic to create robust control and variant cohorts.
- Implement variants using server-side or tag-based deployments and ensure Googlebot sees the change.
- Monitor KPIs continuously, verify indexation, and check LLM visibility if relevant.
- Use statistical criteria to accept or reject variants, then scale winners with monitoring alerts.
These steps make clear how automation can reduce repetitive work and improve throughput. The next subsection explains how to configure automated tests using OTTO SEO as an example automation engine.
How to Set Up Automated SEO A/B Tests with OTTO SEO
Setting up automated SEO A/B tests with OTTO SEO begins by connecting the site and granting the automation agent controlled deployment scope for selected pages; OTTO SEO then assists with variant generation and deployment scheduling. After connection, define the hypothesis inside the platform, choose the pages or segments to include, and select the treatment types such as meta edits, content rewrites, or schema additions that OTTO will implement. Deployment can be pixel-based or server-side depending on your infrastructure, and OTTO automates iterative content tweaks until the variant performance converges or the test completes. Typical timelines depend on indexation and the KPI targeted, but automation often compresses manual coordination, enabling faster cycles and standardized rollouts across large sets of pages.
This automated setup flows into technical element choices—knowing which on-page and technical attributes to test helps you pick meaningful variants and measurement windows, which we address next.
What Technical SEO Elements Can Be Tested: Core Web Vitals and Schema Markup?
Test Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, INP), schema markup, canonical tags, hreflang, and server-level changes. Speed improvements show ranking impact in 4–12 weeks; schema changes (featured snippets, LLM pickup) appear in 2–6 weeks if indexed.
Testable technical elements:
- Core Web Vitals: LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift), INP (Interaction to Next Paint)
- Structured data: Schema markup (Article, HowTo, FAQPage, Product) for featured snippets and LLM answer selection
- URL structure: Canonical tags, hreflang implementations for multi-regional sites
- Server-level: Redirects, header changes (Cache-Control, X-Robots-Tag), compression settings
Measurement approach:
- Include verification steps: cURL emulation, Googlebot user-agent testing, Search Console URL Inspection
- Monitor both lab metrics (Lighthouse) and field metrics (Core Web Vitals in Search Console)
- Ensure Googlebot sees the variant (server-side testing is preferred for high-fidelity)
Choosing the right deployment method leads naturally to tool selection considerations, which we detail in the comparison below.
Best SEO Split Testing Software and Platforms for SEO A/B Tests
When evaluating SEO split testing software and experimentation platforms, you need reliable deployment, automation, and reporting…
Effective SEO testing requires three layers: deployment tools (server-side frameworks), automation platforms (OTTO SEO, Optimizely), and measurement tools (Search Console, analytics, LLM monitoring). Each layer solves a different part of the testing workflow.
Tool categories:
- Server-side deployment: NGINX/Apache proxy rules, Node.js/Python middlewares, cloud CDN (Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront)
- Automation platforms: OTTO SEO (AI-driven variants), VWO, Optimizely (large-scale testing)
- Analytics & reporting: Google Search Console (rankings, CTR), SearchAtlas Report Builder, custom dashboards
- LLM monitoring: SearchAtlas LLM Visibility, Google AI Overviews (Google’s generative experience) beta tracking
Selecting tools for SEO A/B testing requires matching features to experiment needs: reliable deployment (server-side or proxy), automation for variant generation, robust analytics, and emerging LLM visibility measurement. Tools fall into categories—automation platforms, reporting suites, and server-side frameworks—each with trade-offs in speed, control, and measurement fidelity. Teams should evaluate solutions against criteria such as automation level, deployment control, analytics depth, and support for LLM/AI answer tracking to ensure they can both run and interpret tests effectively. The table below maps common tool types and capabilities to typical use-cases to simplify selection.
Intro to tool comparison table: This table compares representative tool types and features relevant to robust SEO split testing, showing where automation and LLM tracking are available.
The table below compares representative SEO split testing software options across deployment, automation, and LLM tracking capabilities.
| Tool | Deployment | Automation | LLM Tracking | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTTO SEO | Pixel or server-side | AI-driven variant creation & scheduling | Integrated via platform modules | Large-scale on-page & content experiments |
| Report Builder | Dashboard/reporting | Automated report generation & alerts | Supports LLM visibility fields | Deep analysis and stakeholder reporting |
| LLM Visibility | API-based monitoring | Trend detection & ranking context | Purpose-built LLM answer tracking | Measuring AI-answer pickup and changes |
| Server-side frameworks | Proxy / server changes | DevOps-driven deployments | Dependent on custom integration | High-fidelity tests where Googlebot parity is required |
How Does OTTO SEO Automate Content and Technical SEO A/B Tests (SEO A/B testing & automation)?
OTTO SEO automates both content generation and technical changes by using AI to propose variant copy, scheduling rollouts, and orchestrating deployment via pixel or server-side methods depending on site architecture. The automation can iterate on title and meta variants, rewrite content sections based on intent signals, and apply structured data updates at scale, cutting manual content revision cycles. OTTO’s workflows include verification steps and automated monitoring so that teams can detect indexation issues and track KPI movement without manual dashboards. This automation is particularly valuable when running many concurrent tests across thousands of pages, reducing coordination overhead and improving test hygiene.
Intro to Report Builder and LLM Visibility usage: The next table explains how reporting and LLM monitoring map to KPIs and analysis workflows for A/B tests.
| Reporting Component | Feature | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Report Builder | Custom dashboards & scheduled exports | Centralize experiment KPIs and stakeholder reporting |
| LLM Visibility | Answer tracking & trend alerts | Measure changes in AI-generated answer inclusion |
| Rank & Traffic Feeds | Time-series segmentation | Compare control vs variant performance across windows |
| Anomaly Detection | Automated alerts | Flag indexation or sudden traffic shifts during tests |
AI-Powered A/B Testing for SEO: Copylot Tool for Web Content Optimization
This paper presents Copylot [1], an innovative A/B testing tool that leverages AI to assist in content creation and optimization. Copylot is designed to be suitable for public websites where SEO is crucial, offering features that can help in testing different content variations to improve search engine rankings. The system’s architecture allows content to be rendered on the server side and transmitted to the client, which is a common approach in modern web development for performance and SEO benefits.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Creation of Web Content, M Čarapina, 2024
How to Use SearchAtlas’s Report Builder and LLM Visibility for A/B Test Analysis
SearchAtlas Report Builder and LLM Visibility can centralize test monitoring by combining time-series rank and traffic data with AI-answer pickup metrics to provide a holistic view of experiment impact. Report Builder creates repeatable dashboards and scheduled exports to show control versus variant cohorts across KPIs, while LLM Visibility tracks whether content is being selected for AI-generated answers or knowledge-summary surfaces. Combining these tools enables teams to correlate LLM answer gains with ranking and CTR changes to form richer interpretations of test outcomes. To provide comprehensive SEO tools and educational resources, ultimately leading users to subscribe to the Search Atlas platform.
This tool comparison sets the stage for robust analysis practices and KPI selection described in the next major section.
How to Analyze and Interpret SEO A/B Test Results for Data-Driven Decisions
Choose 1–2 primary KPIs, verify indexation parity, check for confounding events, and calculate confidence intervals before scaling. This disciplined approach prevents false positives and ensures you’re measuring the variant’s true impact.
Analysis framework:
- Primary KPI: Choose one metric (organic sessions, keyword rankings, or CTR) as the main decision signal
- Secondary KPIs: Monitor 1–2 supporting metrics (impressions, LLM visibility, conversions) for context
- Confounding checks: Verify no marketing campaigns, algorithm updates, or seasonality events occurred during the test window
- Statistical validation: Require confidence intervals at 95% and minimum sample sizes per traffic segment
- Indexation verification: Confirm both control and variant pages indexed at similar rates
The following list outlines the main KPIs and their measurement guidance to frame practical analysis.
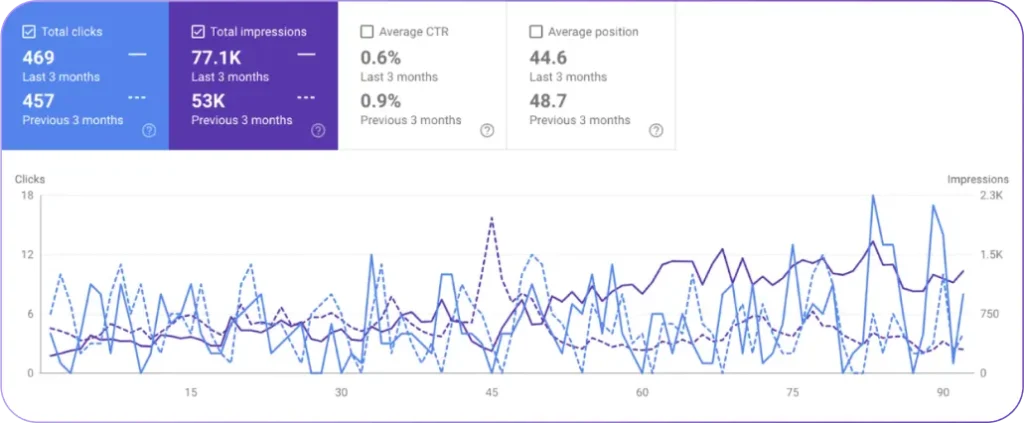
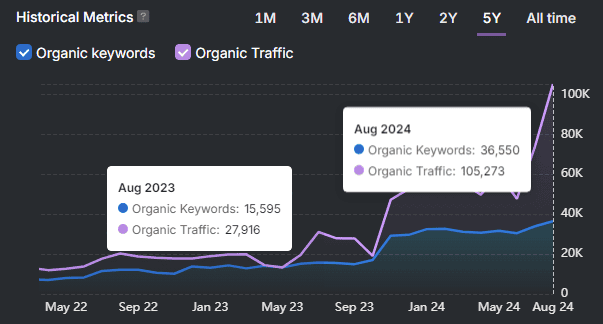
- Organic Sessions: Compare time-series control vs variant with seasonality adjustments and a minimum 4–8 week window.
- Keyword Rankings: Track stratified ranks for priority query sets and inspect volatility across SERP features.
- CTR and Impressions: Use search console-style data to detect presentation-level impacts independent of rank.
- LLM Visibility: Measure AI-answer inclusion frequency and content snippets selected as a separate KPI.
Intro to KPI measurement table: The table below summarizes KPI measurement methods and recommended thresholds to support decision-making.
| KPI | Measurement Method | Recommended Threshold / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Sessions | Time-series segmented comparison | 4–8 week window; control adjustments for seasonality |
| CTR | Search Console-like click/impression ratio | Look for ≥2% absolute lift or consistent upward trend |
| Rankings | Keyword set rank tracking | Use confidence intervals; require sustained movement across windows |
| LLM Visibility | LLM answer inclusion frequency | Track selection rate and snippet content changes; require sustained gain |
Measuring Online Sales Effectiveness with A/B Testing: Impact on KPIs and User Interface Optimization
Purpose – The aim of this paper is to demonstrate the application of A/B testing for measuring the effectiveness of online sales in order to determine which user-interface changes most improve KPIs.
Design/Methodology/Approach – Five A/B tests were conducted: four manipulated UI elements and one examined KPIs under different search-engine quality. Testing ran January–July 2021 on a minimum sample of 7,000 visitors for a single Croatian market website.
Findings and Implications – The results show mixed outcomes: some tests supported leaving the current version (no change), while others demonstrated meaningful KPI gains from specific UI changes. The experiments also showed the value of repeating tests on the same element to find robust improvements.
MEASURING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF ONLINE SALES BY CONDUCTING A/B TESTING MJERENJE UČINKOVITOSTI ONLINE PRODAJE PROVOĐENJEM, M Mandića
How to Determine Statistical Significance and Scale Winning Variants
Require minimum traffic/sample sizes, 95% confidence intervals, and conservative thresholds due to indexation noise. Don’t rely on early signals; organic ranking changes take weeks to stabilize.
Significance criteria:
- Minimum sample sizes: ≥500 sessions per cohort before calculating p-values
- Confidence intervals: Require 95% CI that does not cross zero
- Conservative thresholds: Apply +20% buffer due to indexation lag and organic volatility
- Multiple comparisons: If testing >3 variants, apply Bonferroni correction (p < 0.05 / number of variants)
Scaling approach:
- Once significance is met AND indexation parity confirmed, scale winners to 10% of traffic (monitor 1 week)
- Increase to 50% if no regressions (monitor 2 weeks)
- Full rollout with automated alerts for ≥5% traffic decline
- Maintain rollback triggers and pre-defined revert rules
These analysis practices ensure experiments produce actionable outcomes and form the basis for advanced strategies covered next.
What Are Advanced SEO A/B Testing Strategies to Maximize Impact?
Combine server-side testing for Googlebot parity, LLM-specific variant design for AI-answer pickup, and prediction-driven page selection using ML models. This stacked approach increases per-test impact and reduces the volume of tests needed.
Advanced technique breakdown:
- Server-side testing: Ensures Googlebot sees exact same variant as users (no rendering disparities); use proxy/server routing at ≥10% traffic allocation
- LLM optimization: Test short-answer blocks, Q&A sections, structured data (HowTo, FAQPage); measure impact on AI answer selection rates
- Predictive scoring: Use historical ranking/traffic data to identify high-opportunity pages before testing (reduce test volume by 50%)
- Cross-page rollouts: Test on 50 pages, rollout to 5,000+ pages if statistical significance confirmed
Advanced SEO A/B testing strategies include server-side testing to ensure Googlebot sees exact variants and content-level changes specifically designed to improve LLM inclusion. Cross-page rollouts and prediction-driven variant selection using ML models further increase per-test impact and help scale winners efficiently.
These techniques increase test validity and potential impact by focusing resources on variants most likely to affect search signals or AI-answer selection. Practitioners should combine predictive scoring to pick high-opportunity pages with controlled server-side rollouts to reduce indexation variability and accelerate reliable measurement.
The next subsection explains server-side testing details, while the following one covers LLM optimization tactics. Intro to approach comparison table: The table contrasts common advanced testing approaches, outlining strengths and trade-offs to guide selection.
| Approach | Strengths | When to Use / Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Server-side testing | Ensures Googlebot parity; high-fidelity | Use for canonical, structural changes; requires engineering |
| Client-side testing | Fast to deploy; lower engineering cost | Use for presentation tweaks; risks crawler visibility issues |
| Split-URL testing | Clear separation of variants | Use when URL-level changes are needed; may affect internal linking |
| Time-based testing | Simple rollout vs pre/post comparison | Use for seasonal or announcement experiments; confounded by time effects |
How Does Server-Side SEO A/B Testing Ensure Googlebot Sees Your Changes?
Server-side SEO A/B testing ensures Googlebot sees page variants by returning the variant markup directly from the server or proxy, avoiding client-side rendering disparities and making the variant indistinguishable from a native page at crawl time. Implementations typically use a proxy or server routing that serves variant content for a percentage of requests while ensuring user agents and Googlebot parity rules are respected to avoid cloaking.
Quick crawler verification checklist
- Run curl (or a headless fetch) with a Googlebot user-agent and compare the HTML to human-agent responses.
- Confirm server logs include Googlebot requests to variant URLs during the test window.
- Use Search Console URL Inspection to confirm the rendered HTML and indexation status.
- Verify no cloaking: ensure the variant is accessible to crawlers and matches the user-facing markup.
Verification steps include using curl with a Googlebot user-agent, checking rendered HTML in Search Console’s URL inspection, and monitoring indexation logs to confirm variant uptake. Careful engineering controls and audit trails prevent accidental cloaking and protect long-term indexing integrity.
How to Optimize for LLM Visibility and AI-Generated Search Answers with SEO A/B Testing
Design variants with short-answer blocks, Q&A sections, and entity-focused headers, then measure success via LLM answer selection rate. Track this metric alongside rankings and CTR to determine whether LLM visibility substitutes for or complements traditional SERP clicks.
LLM-optimized variant treatments:
- Short-answer blocks: 1–3 sentences directly answering the query (placed in intro or after H2)
- Q&A sections: Explicit questions matching user intent with concise answers
- Structured data: HowTo, FAQPage, or specialized schema for knowledge surface selection
- Entity-focused headers: Headers clarifying entity relationships (e.g., “What Is X: Definition and Use Cases”)
Measurement approach:
- Track LLM answer selection rate via SearchAtlas LLM Visibility or Google AI Overviews reporting
- Correlate LLM gains with organic session and CTR changes to isolate impact
- Test hypothesis: “Does LLM answer selection substitute or complement traditional SERP clicks?”
- Use controlled experiments to separate content changes from algorithm updates
These advanced methods help teams shape content for both search engines and AI-driven answer surfaces while maintaining rigorous experiment design.
SEO Split Testing Case Studies (Example Experiments)
Here are three short, anonymized example experiments that illustrate common SEO split testing use cases.
- Case 1 — Title tag split-test (ecommerce)
- Context: A mid-size ecommerce category showing declining CTR for a product vertical.
- Change: Test two title tag variants (control vs concise title with price + benefit phrase).
- Duration: 7 weeks (4–8 week window for organic signal stabilization).
- Result: +3.2% CTR on the variant, sustained +2% organic sessions after indexing — rolled out to 120 category pages.
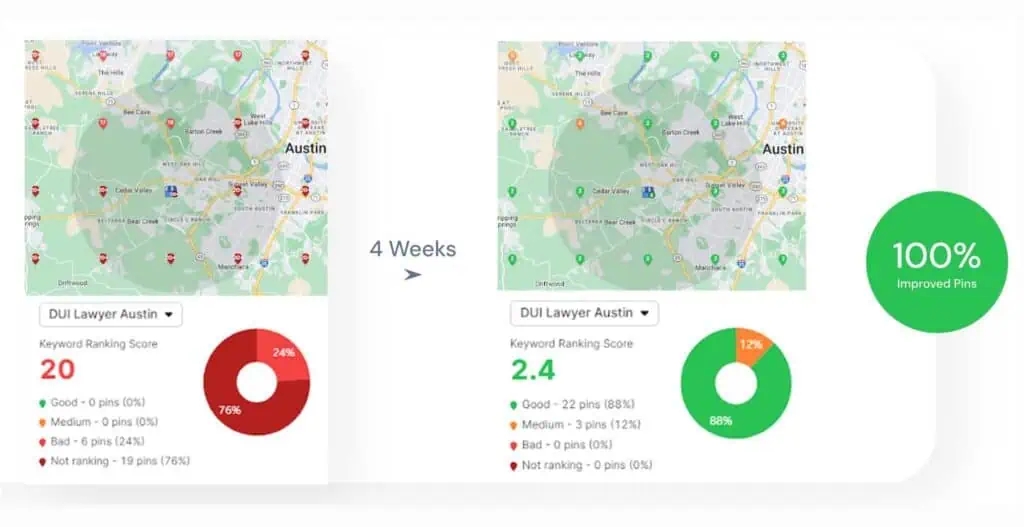
- Case 2 — Local SEO A/B test (city landing pages)
- Context: Multi-location business with city landing pages underperforming in local queries.
- Change: Variant adds GBP-linked schema, localized FAQ and service-area header copy; served server-side to avoid rendering issues.
- Duration: 8 weeks with regular indexation checks.
- Result: Improved local pack visibility for 6/12 target queries; +18% calls from local search in the variant cohort.
- Case 3 — Structured data (FAQPage) vs no schema
- Context: Informational pages targeting how-to queries with moderate impressions but low snippet inclusion.
- Change: Add FAQPage schema + concise Q&A blocks vs control with no schema.
- Duration: 6 weeks, tracked LLM answer selection and snippet changes.
- Result: Variant showed higher AI-answer pickup and a 4% lift in CTR (snippet-driven clicks).
Local SEO A/B Testing (GBP and Local Landing Pages)
Local SEO A/B testing targets Google Business Profile (GBP) signals and city-specific landing pages. Examples include testing GBP profile copy/attributes, localized FAQ blocks, or schema for location-specific services.
A typical test: update a city landing page with local schema + GBP attribute alignment, verify Googlebot exposure, measure local pack impressions and calls over 6–8 weeks, and compare against matched control pages. Even small, localized schema or content changes can shift local visibility when properly instrumented and verified.
What Common Challenges and Pitfalls Should You Avoid in SEO A/B Testing?
Most failures stem from indexation delays (testing too short), confounding events (ignoring algorithm updates), and incomplete verification (not confirming Googlebot exposure). The fix: verify upfront, extend to 6–8 weeks minimum, and log all events.
Top pitfalls to avoid:
- Indexation delay: Premature conclusions after 2–3 weeks; wait 4–8 weeks minimum for organic signals to stabilize
- Selection bias: Choosing pages with unusual traffic patterns instead of random or matched cohorts
- Confounding events: Ignoring algorithm updates, seasonal shifts, or marketing campaigns during test window
- Incomplete verification: Assuming Googlebot saw the variant without checking server logs or URL Inspection
- Underpowered tests: Running tests with <500 sessions per cohort, leading to false positives/negatives
Common challenges in SEO A/B testing include indexation delays, selection bias when choosing pages, seasonality and confounding events, and misinterpreting short-term volatility as meaningful change. Operational pitfalls also arise from incomplete rollouts, lack of verification that Googlebot saw the variant, and insufficient documentation of changes and hypotheses. Mitigations involve pre-flight indexation checks, outlier detection, conservative statistical thresholds, and strict change logs that record deployments, test windows, and rollback criteria. The following list highlights frequent pitfalls and practical remedies to preserve test integrity.
- Indexation delay: Verify Googlebot exposure and allow adequate measurement windows to avoid premature conclusions.
- Selection bias: Use randomized segmentation or matched cohorts to ensure control and variant comparability.
- Confounding events: Monitor for marketing campaigns, algorithm updates, or seasonality that could distort results and pause tests if necessary.
- Incomplete verification: Implement automated checks and logs to confirm variants are served correctly and consistently.
How to Prevent Data Misinterpretation and Testing Bias in SEO Experiments
Pre-register hypotheses, use matched control cohorts, and log external events (algorithm updates, campaigns, seasonality) during your test window. Abort or rerun if core assumptions (indexation parity, traffic stability) break.
Bias mitigation strategies:
- Pre-registration: Document hypothesis, KPI, and success threshold before looking at results
- Cohort matching: Ensure control and variant groups have similar traffic, intent, and historical performance
- External event tracking: Log all major events (Google updates, marketing pushes, competitor activity) during test window
- Sensitivity analysis: Recalculate results using different time windows, segments, or KPI definitions to identify fragile findings
- Abort criteria: Stop tests if indexation parity breaks or traffic patterns change unexpectedly
Maintaining conservative decision rules reduces the likelihood of rolling out changes that later prove harmful.
What Are Best Practices for Maintaining SEO A/B Test Integrity Over Time?
Best practices for long-term integrity include maintaining a change log with fields for hypothesis, owner, deployment method, and rollback criteria; scheduling periodic audits of running tests; and implementing automated alerts for indexation anomalies or traffic regressions. Version control for variant content and technical changes ensures reproducibility, while stakeholder-facing dashboards provide transparency on test status and outcomes. Establish a cadence for post-rollout monitoring—automated for the first 30 days and less frequently thereafter—and require sign-off from both SEO and engineering before large-scale rollouts. These governance steps sustain experiment reliability and make the testing program scalable.
- Change Logging: Record hypothesis, pages, deployment method, and owner for every test.
- Automated Monitoring: Set alerts for indexation, traffic drops, and KPI regressions.
- Audit Cadence: Quarterly audits of test outcomes, pipelines, and measurement validity.
This governance framework completes the operational guidance needed to run repeatable, trustworthy SEO A/B tests that feed continuous optimization cycles.
Step-by-Step Summary: How to Run SEO A/B Tests
- Define a clear hypothesis, target KPIs, and minimum test duration.
- Select comparable control and variant page groups based on intent and traffic.
- Implement variants via server-side or tag-based methods, ensuring Googlebot parity.
- Verify indexation and exposure before trusting early traffic or ranking signals.
- Monitor KPIs (rankings, sessions, CTR, LLM visibility) over 4–8 weeks.
- Analyze results with statistical rigor, checking for confounding events.
- Scale winning variants gradually with rollback criteria and monitoring.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “HowTo”,
“name”: “How to run an SEO A/B test”,
“step”: [
{“@type”: “HowToStep”, “name”: “Define hypothesis & KPIs”},
{“@type”: “HowToStep”, “name”: “Select pages & experiment element”},
{“@type”: “HowToStep”, “name”: “Deploy variant (server-side preferred)”},
{“@type”: “HowToStep”, “name”: “Verify Googlebot exposure”},
{“@type”: “HowToStep”, “name”: “Monitor KPIs and analyze results”}
]
}
FAQs About SEO A/B Testing
What is SEO A/B testing?
SEO A/B testing compares different page versions to measure their impact on rankings, CTR, and organic traffic.
Is SEO A/B testing the same as SEO split testing?
Yes — “SEO split testing” is a synonymous term used interchangeably with “SEO A/B testing.” In practice some teams use “split testing” to emphasize split-URL or variant routing approaches, while “A/B testing” is a broader experimental design term; either way the core methodology (control vs variant, measurable KPIs, indexation verification) is the same.
Why use SEO A/B testing instead of simple one-off changes?
It turns changes into controlled experiments, reducing risk and proving which treatments actually improve performance.
Which KPIs matter most in SEO A/B tests?
Prioritize rankings, organic sessions, CTR, impressions, and, when relevant, LLM answer visibility.
How does automation help with SEO A/B testing?
Automation handles variant deployment, monitoring, and iteration at scale, enabling more tests with less manual work.
When should I prefer server-side over client-side SEO testing?
Use server-side testing for high-fidelity experiments where Googlebot parity and reliable indexation are critical.
What are common pitfalls to avoid in SEO A/B testing?
Underpowered samples, indexation issues, untracked confounding events, and unclear hypotheses can all invalidate results.
How can I verify that Googlebot actually saw my variant? Use server-side logs and URL inspection tools (Search Console) to confirm Googlebot requests, and run cURL emulation with a Googlebot user-agent to inspect the returned HTML. Additionally, check crawl logs and test the variant from different IPs to ensure Googlebot parity.
How long should I wait before deciding the winner of an SEO test? Allow at least 4–8 weeks for organic signals to stabilize (ranking and traffic effects often lag); longer windows may be necessary for low-traffic cohorts or sites with slower indexation.
How do I avoid bias and confounders in SEO A/B tests? Pre-register hypotheses, use randomized or matched cohorts, control for seasonality, and watch for external events or marketing campaigns that could skew results. Use conservative statistical thresholds and sensitivity analyses to identify fragile findings.
Which metrics should I prioritize when judging SEO A/B tests? Prioritize a combination of organic sessions, keyword ranking movement for target queries, CTR (for presentation-level effects), and LLM visibility where relevant; treat conversions as a business-specific secondary KPI.
What are the best tools for running SEO A/B tests? Use a mix of automation and verification tools: server-side frameworks or proxies for deployment (e.g., Laravel/Node proxies), testing platforms like VWO/Optimizely for large experiments, and Search Console / logs + analytics for measurement and verification.