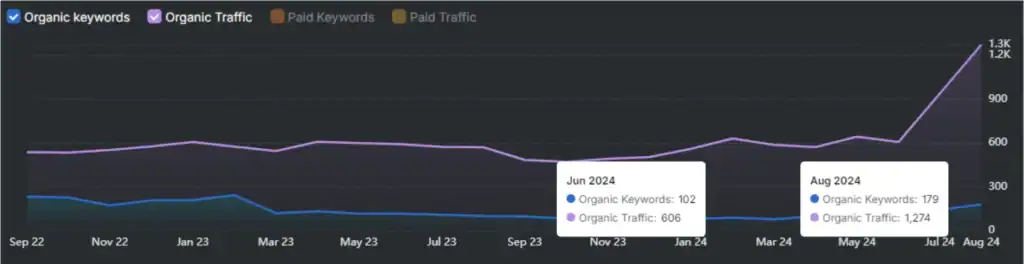
Modern SEO has evolved beyond traditional tactics like simple keyword optimization and link building. Google now employs a sophisticated two-phase ranking system that evaluates content through Initial Document Ranking and Re-ranking phases, while simultaneously using AI Overview to handle complex queries that standard results can’t satisfy.
Contemporary SEO success depends on understanding how user engagement metrics like click-through rates and dwell time influence rankings, despite Google’s public denials. Proper image optimization directly impacts Core Web Vitals and search performance, while topical dominance (covering subjects comprehensively across related keywords) has become more influential than backlink quantity alone in establishing domain authority.
5 SEO Secrets That Actually Work
We are going to explore 5 less-known SEO secrets that actually bring results. The 5 secrets are explained in detail below.

1. Google Ranks You Twice
Google evaluates your content through two distinct ranking phases that determine your final search position.
Initial Document Ranking (IDR)
Google assigns provisional rankings to newly published or updated pages during the Initial Document Ranking (IDR) phase. This preliminary evaluation occurs before Google fully assesses all content signals and determines your page’s initial search position based on immediate available data.
You maximize your initial ranking potential with the 3 practices listed below.
- Optimize for Immediate Crawlability. Google needs to understand your content from publication. Proper headings, structured data, and clear, relevant content create positive first impressions that influence initial positioning.
- Leverage Immediate Signals. Google prioritizes metadata quality, early user interactions, content relevance, topical authority, and overall site credibility during this phase. These factors heavily influence your starting position.
- Plan for Ongoing Adjustments. Google continuously refines rankings as additional signals accumulate. User engagement data, link acquisition, and deeper content analysis cause position fluctuations after the initial phase.
The IDR phase establishes your starting position rather than your final ranking, but this foundation significantly impacts your long-term search performance.
Re-rankings Phase
Re-rankings represent Google’s refined evaluation after initial quality and relevance assessments. This process enhances SERP efficiency, quality, and sustainability through advanced filtering and source evaluation.
Your initial ranking score heavily influences re-ranking outcomes, making strong IDR performance crucial for sustained success. Google applies additional criteria during re-rankings. The additional criteria are listed below.
- Duplicate content filtering
- Audience segmentation analysis
- Topical familiarity assessment
- Commercial intent evaluation
- User activity and click-through analysis
- Community endorsement signals
- Source trust verification
- Search demand fluctuation response
Navigation Impact: NavBoost and Twiddlers
Google’s NavBoost system uses user click patterns to enhance, lower, or stabilize search rankings. This system ranks among Google’s most influential ranking signals, which makes user engagement optimization critical for sustained visibility.
Twiddlers function as fine-tuning mechanisms that adjust search results immediately before display. These re-ranking tools optimize final result presentation based on real-time user behavior data and query context.
Effective site navigation helps users and search engines discover content efficiently. Site navigation impacts both ranking phases through improved user experience (UX) signals and crawlability optimization.
2. You Can Use Google’s AI Mode to Your Advantage
Google includes a feature in Search called AI Overview. AI Overview appears when users ask complex or open-ended questions which standard results do not answer well. Google designed AI Mode to step in when traditional search does not meet user expectations. This creates a more advanced search experience, but it comes with a hidden cost.
AI Mode runs on Gemini 2.0, which uses more computational power than standard search. This makes AI Mode expensive for Google to operate. It does not pull from indexed pages quickly like regular results. It requires heavy resources and slows down delivery. Google avoids using AI Mode by default because of this high cost. It only appears when no other content fits the query well.
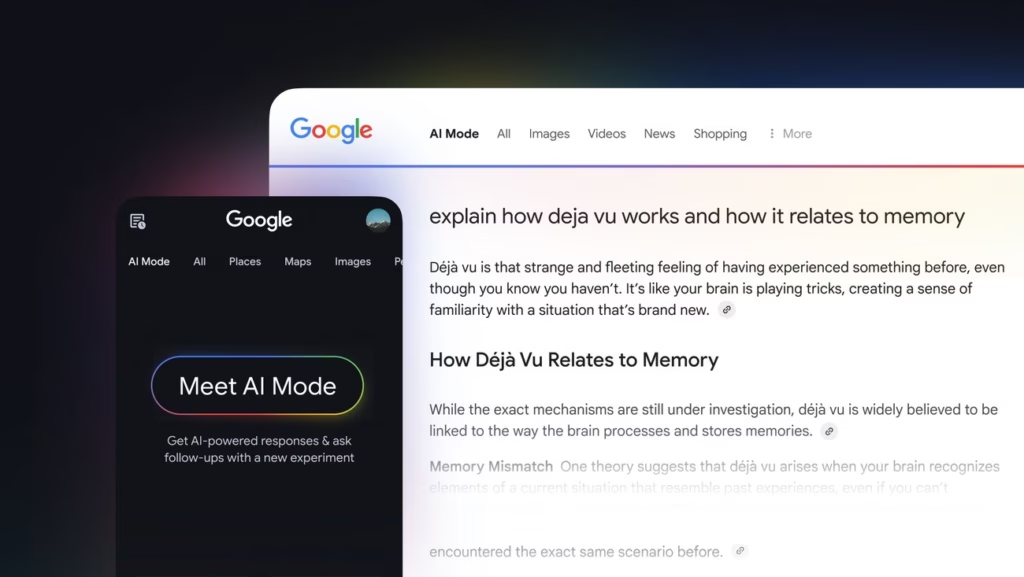
This creates an opportunity for SEOs. Google does not need to trigger AI Mode when a page answers complex questions instead. A page that gives clear, structured, and complete answers helps Google serve search results faster and more cheaply. Google often shows pages that fit that role higher in the results.
To reduce Google’s reliance on AI Mode, a page needs to complete certain conditions. The conditions are listed below.
- Giving complete and specific answers
- Handling nuanced topics which users often search
- Comparing options when possible
- Using a clear format
- Including information which users typically look for next
These signals help Google avoid AI Mode and choose your content instead.
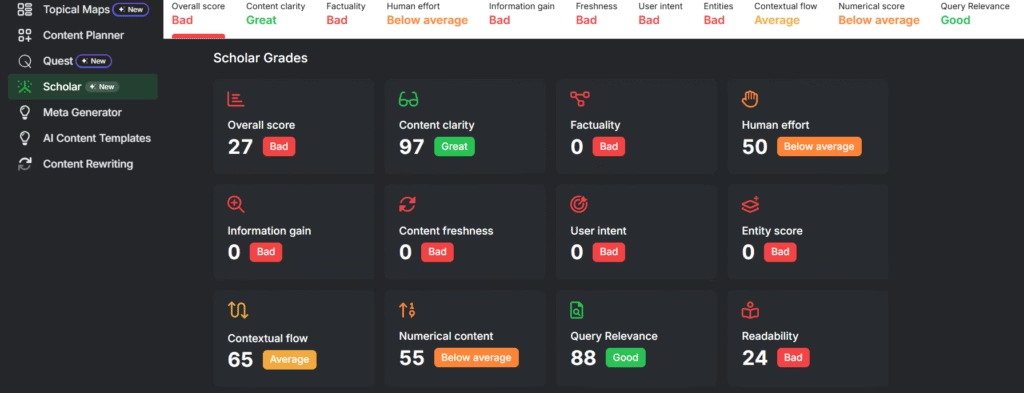
Search Atlas includes a tool called Scholar which measures how well a page meets this standard. Each page receives exact feedback which shows what to improve. Scholar scores content from 0 to 100 using metrics which reflect Google’s ranking signals. These metrics are listed below.
- Clarity
- Factuality
- Human Effort
- Information Gain
- Freshness
- Search Intent Alignment
- Entity Coverage
- Contextual Flow
A page that earns a higher Scholar score meets more of Google’s quality criteria. Pages meet the criteria through high content quality. A page that replaces the need for AI responses becomes more valuable to Google and more visible to users.
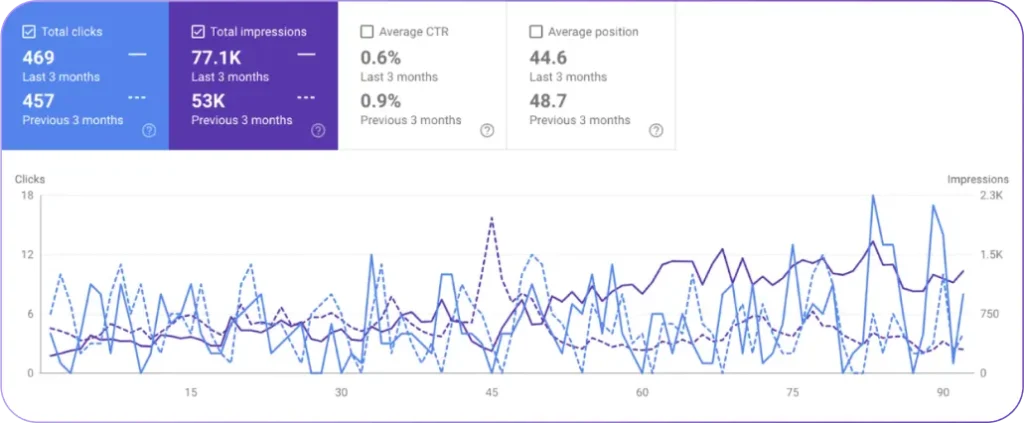
3. Clicks and Dwell Time Matter for Rankings
Google has repeatedly stated that it does not use click-through rates (CTR) or dwell time as ranking factors. Official documentation and public statements claim that search rankings do not consider how users interact with results. Leaked documents, however, confirm that Google does track user clicks and time spent on pages. This data helps Google evaluate the quality of search results and adjust rankings accordingly. These findings contradict Google’s long-standing public position.
What Is Click-Through Rate (CTR)?
CTR measures how often users click a result after seeing it in search. It reflects how appealing your title and description are. A high CTR shows that users find your result relevant to their query. A low CTR suggests that your snippet does not match the search intent or lacks clarity. We briefly list ways to improve CTR below.
- Use clear, descriptive titles which match the search query
- Write meta descriptions which preview the content accurately
- Include numbers, brackets, or specific terms which signal value (e.g., “7 Ways to Improve Site Speed”)
- Avoid misleading or vague headlines
- Use schema markup to show extra details in the snippet
What Is Dwell Time?
Dwell time tracks how long users stay on a page after clicking a result, before returning to search. A longer dwell time often means that the content satisfies the query. A short dwell time suggests that the user did not find what they needed. Improved dwell time helps you boost Google rankings. We explain ways to improve dwell time below.
- Start with a strong opening that confirms the user is in the right place
- Structure content with headings, subheadings, lists, and visuals which keep users engaged
- Answer the main query early, then offer related insights
- Avoid fluff or off-topic information
- Improve readability by using short paragraphs and simple language. Use readability tools.
Google treats your content as helpful when it sees that users click your result and stay on the page. This increases the chance of ranking high in the SERPs.
4. Image Optimization Affects Rankings More Than You Think
Images improve user experience, but they often cause performance issues. Large files increase load times, which hurts Core Web Vitals and SEO. Google considers speed in its rankings, so optimizing images plays a direct role in visibility. Poor image optimization is one of the most common SEO mistakes.
Image optimization matters because heavy images delay page loading. Delayed page loading leads to higher bounce rates on mobile or slow connections. As a result, search engines detect poor engagement and reduce rankings. Optimized visuals support better scores, faster loading, and stronger user signals. Clean, fast-loading images improve site performance. Search engines respond with better rankings.
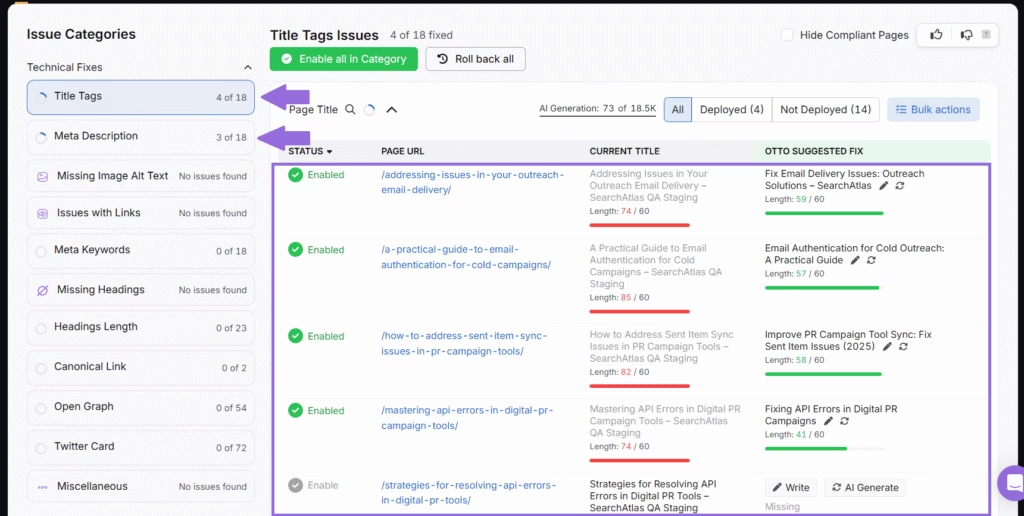
To optimize images properly, use formats that balance quality and size. The wrong type inflates files or distorts visuals. Different formats are discussed below.
- WebP. High-quality visuals with strong compression. Works well for general web use.
- AVIF. Superior compression. Produces smaller files while preserving quality.
- JPEG. Ideal for photos. Keeps detail at reduced sizes but degrades with heavy compression.
- PNG. Best for transparency and graphics. Maintains quality but increases file size.
- GIF. Used for short animations. Keep files small to avoid performance issues.
- SVG. Perfect for scalable icons and vectors. Supports animation and CSS interaction.
There are several ways to improve image performance.
- Convert large files to AVIF when supported.
- Fall back to WebP or JPEG if needed
- Apply lazy loading to delay image rendering until users scroll.
- Compress files with tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh.
- Remove visuals that add no content value.
- Add descriptive alt text for accessibility and indexing.
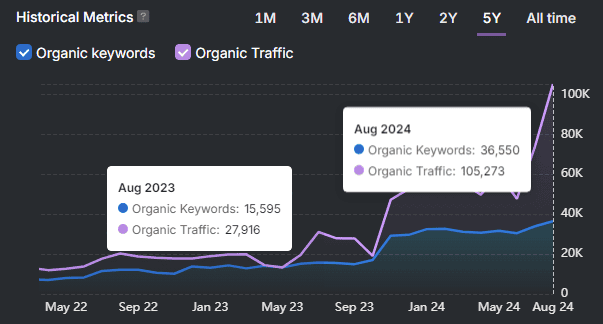
5. Authority Depends on Topical Dominance, Not Just Backlinks
Google no longer focuses only on backlinks. Instead, it evaluates how deeply and consistently a website covers a specific topic. This shift marks the rise of a new metric called Topical Dominance.
What Is Topical Dominance?
Topical dominance is a metric that shows how well a website covers a subject across multiple related keywords. Google sees ranking for a large set of interconnected search terms as a sign of authority. Sites that do this are able to outperform bigger competitors, even ones with higher Domain Authority (DA) or more backlinks.
Why Keyword Difficulty Misses the Full Picture
Keyword difficulty estimates how hard it is to rank for a term, based mainly on backlinks to top-ranking pages. Keyword difficulty ignores how much content you publish or how closely your topics relate. That creates a blind spot. You miss the opportunity to build authority through content when you rely on keyword difficulty alone.
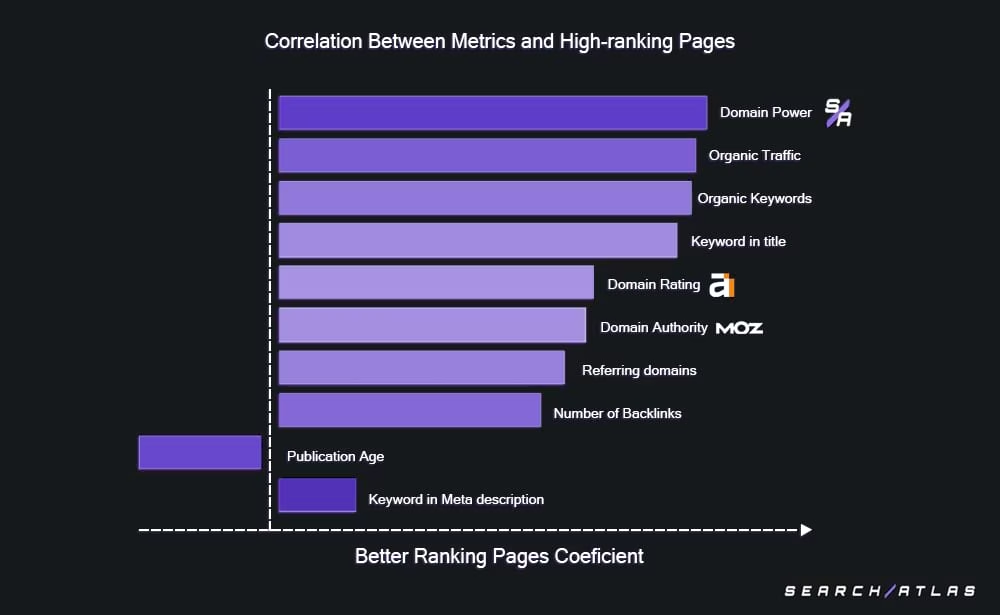
Search Atlas ran correlation studies comparing keyword rankings to topical dominance scores. The findings show a stronger connection between rankings and topical dominance than between rankings and backlinks. This proves that Google favors subject coverage and depth over link volume.
Content Beats Links
Backlinks still matter but they no longer define site authority on their own. At a recent SEO event, only 15% of attendees said they still prioritize link building. Over 60% now focus on publishing high-quality, topic-aligned content. You build topical authority when your content forms a tight, consistent network of related pages. Having a tight, consistent network of related pages gives Google a strong reason to favor your site even in competitive verticals (finance, law, health).
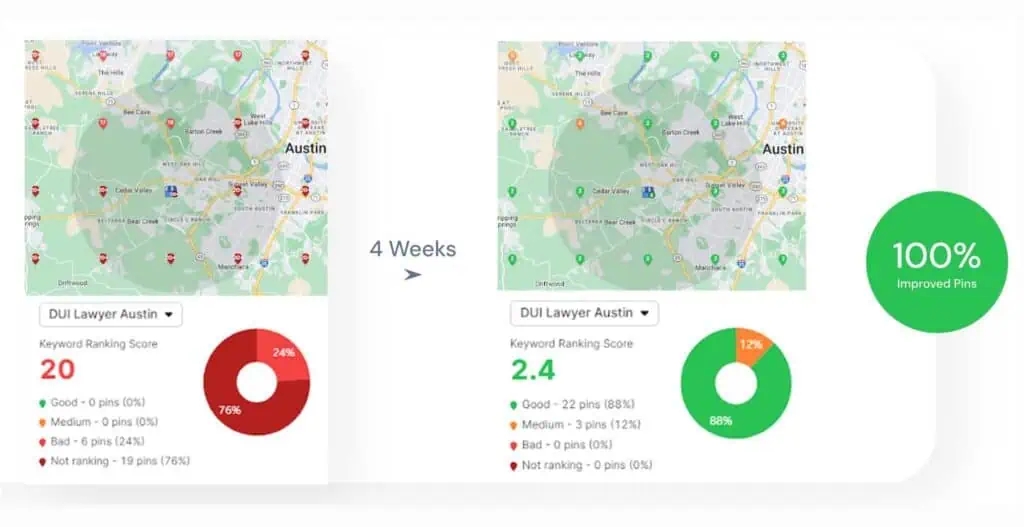
Search Atlas created a full-featured Topical Dominance tool. It evaluates how well a site covers a topic, a niche, or even an entire knowledge domain. You enter your website, analyze competitors, and see where your strengths or gaps lie.
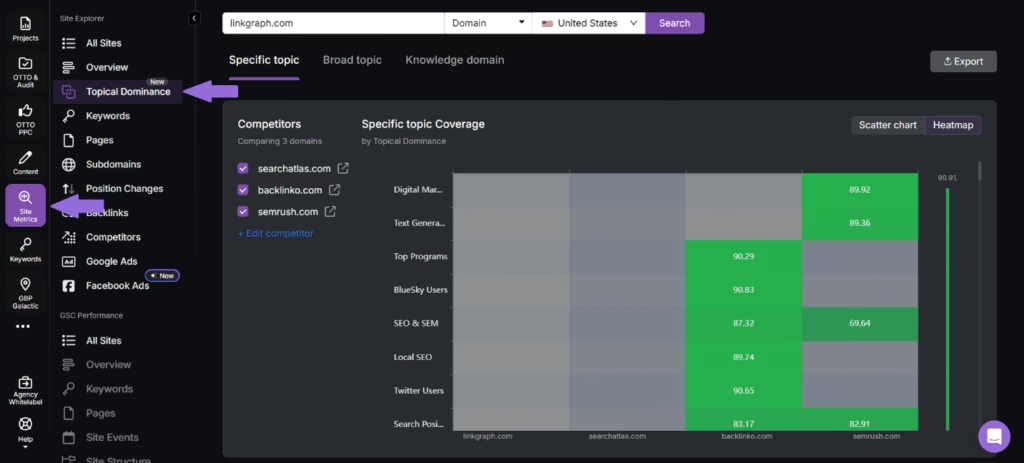
The Topical Dominance metric is a key part of Domain Power (DP). Domain Power is a new authority metric that relies on organic traffic and keyword rankings to assess the authority of a site. Domain Power is useful for authority building and predicting SERP rankings because it relies on relevance and performance over just raw backlink count.
Change the Way You Do SEO
These five secrets represent fundamental shifts in how Google evaluates content quality and relevance. Websites that adapt to these evolved ranking factors will outperform competitors still relying on outdated SEO practices focused solely on keywords and backlinks.
Search Atlas is an AI SEO platform that leads with new SEO insights, metrics and tools. Test these tools and refresh your strategy with a 7-day FREE trial. Cancel anytime.