Broken links are hyperlinks leading to non-existent pages, caused by deleted content, URL changes, typos, server issues, and redirect problems. They damage search engine optimization (SEO), harm user experience, and hurt brand credibility.
Fix broken links by using audit tools like OTTO SEO and Google Search Console (GSC) to detect issues, then prioritize repairs based on traffic impact. Solutions include removing unnecessary links, implementing 301 redirects, replacing missing content, and contacting external site owners. Prevent future problems through consistent URL structures, thorough link testing before publishing, regular audits, and systematic maintenance processes.
What Are Broken Links?

Broken or dead links are hyperlinks that lead to non-existent internal or external pages.
Broken links result from deleted, moved, or renamed pages. Users who click on broken links reach an error page. The most common error is 404 (not found), although others cause broken links, too. Broken links harm SEO and user experience.
What Types of Broken Links Are There?
There are 3 types of broken links. The types of broken links are listed below.
- Broken internal links. They direct users to another piece of content on the same site.
- Broken external links. They direct users to a piece of content on a different site.
- Broken backlinks. They appear in content on another site and direct users to your content.
What Causes Broken Links?

There are 7 common causes of broken links. We explain them in detail below.
1. Deleted or moved content. Site owners remove old blog posts, landing pages, or product listings. In other cases, they relocate pages during redesigns or server changes. Users encounter 404 errors if links still point to these missing pages. For example, a page about a past webinar gets removed, but footer links still reference it.
2. Changes in URL structure. Teams restructure websites to improve SEO or user flow. They update folder names or add new hierarchy levels to URLs. Those paths break if internal links use the outdated URLs. For example, changing /services to /solutions/services breaks any navigation menu item that still uses the older format.
3. Misspelled URLs. Writers accidentally enter incorrect paths while linking. One misplaced letter or missing symbol breaks the link. For example, writing www.site.com/blogg instead of www.site.com/blog stops the page from loading. These mistakes lead to bad requests or missing page errors that confuse users.
4. External content removal. External sites update content or shut down entire pages. Links to those resources stop working without warning. For example, a case study on a partner website gets removed, but your blog post still links to it. Over time, more of these outdated links build up due to link rot.
5. Server and protocol issues. Web servers sometimes return 500 internal server errors or 503 service unavailable messages when content exists but technical problems prevent access. Mixed protocol problems also create broken experiences when HTTPS sites link to HTTP resources that browsers block for security reasons.
6. Redirect chains and loops. Multiple redirects in sequence slow page loading and sometimes fail entirely. Redirect loops occur when Page A redirects to Page B, which redirects back to Page A. These circular references prevent users from reaching any destination.
7. Soft 404 errors. Some pages return a successful 200 status code but display “page not found” content. Search engines and users expect error codes to match page content. These inconsistencies confuse crawlers and waste indexing resources.
How Do Broken Links Impact Your Website?
Broken links harm your website’s SEO, user experience (UX), and brand reputation. Search engines expect to see a certain number of broken backlinks, but too many send a signal that the website is neglected. We explain how broken links harm your website in more detail below.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Broken links damage SEO in 4 direct ways. The ways broken links damage SEO are listed below.
- Waste crawl equity. Googlebot crawls a limited number of pages per visit. When broken links lead to 404 errors, the bot spends time on dead ends instead of valuable pages. This waste reduces the chances of Google indexing and ranking important content.
- Stop link equity transfer. Internal links help distribute SEO value from strong pages to others. When those links break, the target page receives no benefit. For example, if a blog post links to another post that no longer exists, the flow of link equity ends, weakening both user navigation and ranking potential.
- Disrupt crawlability. Broken links interrupt the structure Googlebot uses to understand site architecture. Crawlers depend on consistent links to move across pages. Dead ends confuse the bot and make it harder to map relationships between content. This confusion affects how pages rank or even appear in search results.
- Create JavaScript rendering problems. Single-page applications and dynamic websites often generate links through JavaScript. When these scripts fail or load incorrectly, users and crawlers encounter broken navigation paths that traditional link checkers miss.
Broken links create technical and strategic problems for SEO. Regular audits and updates ensure crawlers are able to access, understand, and rank every important page.
User Experience (UX)
Broken links disrupt user experience in different ways. How the broken links disrupt user experience are listed below.
- Create dead ends. Users expect to reach helpful or relevant content when they click a link. A broken link leads to an error page instead, stopping their journey. For example, the user receives no guidance and leaves the site immediately because a product page links to a missing size chart.
- Increase bounce rates. Visitors leave when they encounter broken links, especially early in a session. These quick exits raise the bounce rate, signaling that the site fails to meet user expectations. A user is likely to exit and search elsewhere if they land on a blog post and click a broken link within the first few seconds.
- Hurt user satisfaction. Visitors want smooth, intuitive navigation. Broken links interrupt that flow and make content hard to access. Users view the site as unprofessional and unhelpful if this happens regularly.
- Affect mobile users differently. Mobile devices often display different error messages or loading behaviors than desktop computers. It is possible for a link that works on desktop to fail on mobile due to protocol restrictions or responsive design issues.
Reputation
Broken links weaken a website’s reputation for the audience, reduce perceived professionalism, and signal neglect to users and partners. How broken links weaken a website’s credibility is listed below.
- Damage brand perception. Visitors associate broken links with poor quality and lack of care. If users encounter multiple errors during a visit, they question the site’s reliability. For example, a missing link on a service page suggests that the company doesn’t maintain its own content.
- Create a negative impression. Professionals, journalists, or collaborators who cite or reference your content expect stable, accessible links. A broken link in shared content reflects poorly and potentially discourages future mentions or partnerships. For example, the linked page no longer exists so the journalist removes it as a reference.
- Signal neglect to search engines and users. A site filled with broken links looks outdated or abandoned. This impression lowers trust and discourages return visits. Nonprofit organizations that link to expired campaign pages year after year tend to turn away donors.
- Affect international audiences. Multilingual websites face additional reputation risks when broken links appear in specific language versions. Visitors often assume the organization doesn’t prioritize their market or language community.
How to Check For Broken Links
There are several ways to check for broken links. We will analyze them in more detail in this section.
Find Broken Backlinks with OTTO SEO
OTTO SEO applies changes directly to websites, unlike tools that only provide suggestions. This eliminates the need for manual implementation.
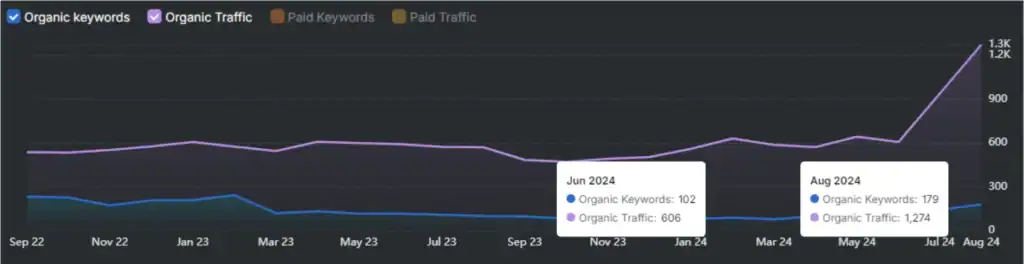
It identifies redirects and broken links, then recommends replacing them with final URLs. This preserves crawl budget and improves link equity transfer to the target page.
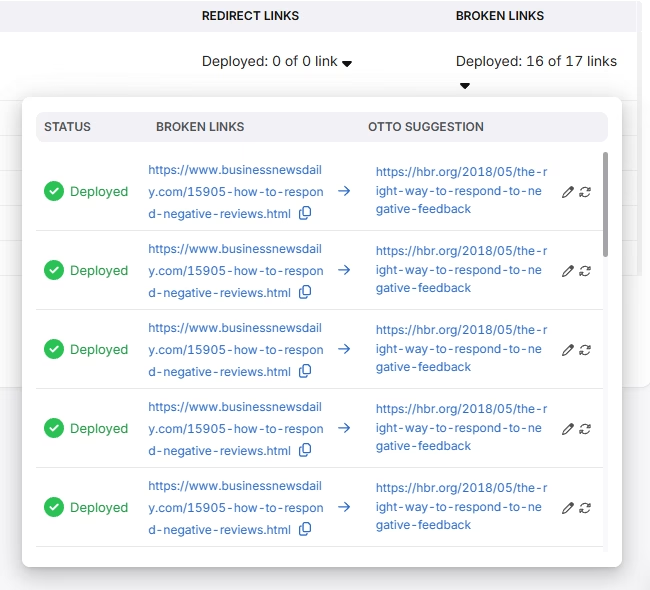
OTTO SEO handles tasks across content, on-page, off-page and technical SEO areas. It updates meta tags, discovers issues with the sitemap, indexing, and other aspects of technical SEO.
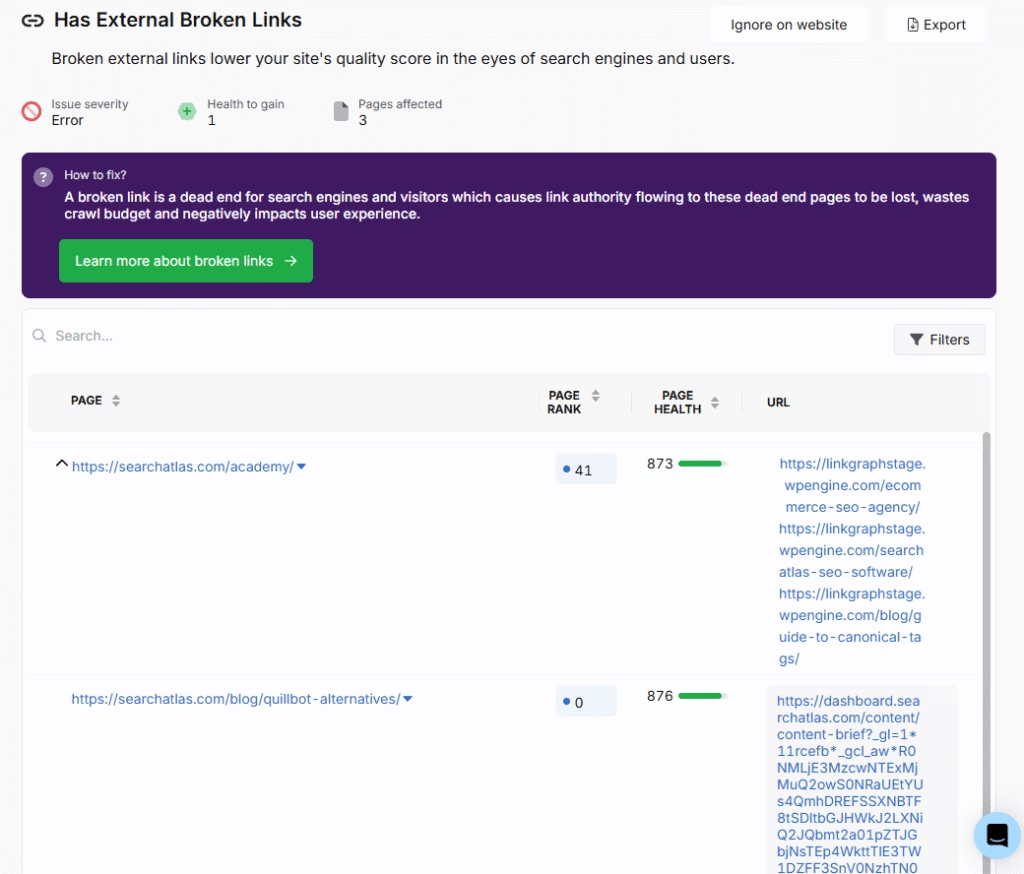
Find Broken External Links With the Site Audit Tool
The site audit tool scans a website and generates a detailed report on technical SEO performance. It uses automated crawlers to evaluate page speed, broken links, metadata, indexability, and content layout.
The crawl simulates how search engine bots navigate the site and flags issues that harm visibility or disrupt user experience. The report organizes findings into categories such as crawlability, mobile usability, on-page content, and link errors.
Run a site audit on any domain to identify SEO strengths and uncover weak points. The tool lists broken external links under the Issues with Links section.
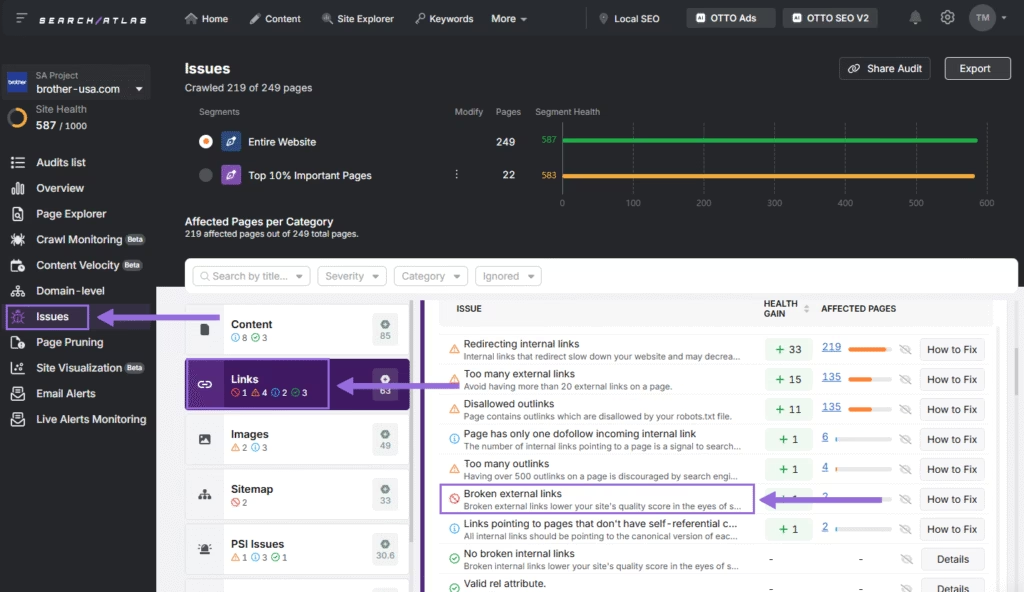
Click the Broken External Links option to discover issues of this type.
Identify 404 Errors With Site the Audit Tool
The Site Audit Tool monitors your website around the clock and alerts you to any issues affecting site health. It displays pages by HTTP status in a clear pie chart, which makes it easy to track changes.
Use it to quickly find and fix 404 pages. Replace broken URLs. After that, internal links will stop pointing to dead ends and start guiding users and crawlers to live, relevant pages.
Alternative Link Checking Tools
Several other tools help identify broken links across different scenarios and website types.
Online broken link checkers scan individual pages or entire sites through web interfaces. These tools work well for smaller websites or quick spot checks without requiring software installation.
Browser extensions detect broken links as you browse your site manually. They highlight problematic links in real-time and help identify issues during content review processes.
Command-line tools integrate broken link detection into development workflows. Technical teams use these tools to check links before deploying website updates or during automated testing.
How Often Should You Check For Broken Links?
Link checking frequency depends on website size, update frequency, and business priorities.
Large websites with frequent content updates need weekly or bi-weekly broken link audits. E-commerce sites, news websites, and blogs that publish daily generate more opportunities for broken links through rapid content changes.
Smaller websites benefit from monthly link checks. Corporate websites, portfolios, and service-based businesses that update content less frequently face fewer broken link risks.
Schedule comprehensive quarterly audits regardless of website size. These deep reviews discover issues that regular scans miss and provide opportunities to optimize link strategies. Run immediate checks after major website changes. Site migrations, redesigns, and large content updates create the highest risk for broken links. Check all links within 48 hours of deploying significant changes.
How to Fix Broken Links
We explain how to prioritize link fixes and how to fix different broken link issues.
Prioritize Link Fixes by Impact
Fix broken links systematically by focusing on the most important issues first.
Start with high-traffic pages that contain broken links. These pages affect more users and carry greater SEO weight than low-traffic content. Use analytics data to identify which pages receive the most visitors.
Address broken links in conversion-critical content next. Product pages, service descriptions, and contact forms that contain broken links directly impact business results. Fix these issues before they reduce sales or lead generation.
Focus on broken internal links before external links. You control internal link destinations and fixes happen immediately. External link fixes require outreach or alternative sources that take more time.
Remove the Broken Link
Delete broken internal or external links when no suitable replacement exists. Remove links that lead to pages without current value. This action clears dead ends and improves user navigation.
Redirect the Link
Apply a 301 redirect to send users and crawlers to a live, relevant URL. Redirect the link to another page after the original content becomes unavailable. This method preserves authority and traffic. Use server-side redirects or HTML meta tags depending on your setup.
Replace the Page
Restore the missing page with content that meets the original intent. Publish new content under the same URL after identifying what users expected. This step protects existing inbound links and supports long-term rankings.
Contact the Site Owner to Replace a Broken Backlink
Request a fix from the referring site after discovering a broken backlink. Suggest a working URL with similar relevance. This outreach helps recover lost link equity and creates potential backlink opportunities.
Substitute the Source or Remove It
Replace a dead external link with a valid source when the original site no longer exists. Remove the link entirely when no reliable substitute is available. This improves SEO content quality and user trust.
Measure Link Fix Impact
Track improvements after fixing broken links to demonstrate SEO and user experience value. The recommended metrics and reports are listed below.
- Crawl Error Reports. Monitor crawl error reports in Google Search Console before and after link fixes. Successful repairs reduce 404 errors and improve site health scores.
- Bounce Rates. Compare bounce rates on pages where you fixed broken links. Users stay longer on pages with working navigation paths.
- Organic Traffic. Track organic search traffic to pages that previously contained broken links. Fixed internal linking often improves rankings and visibility.
- Ranking Performance. Measure link equity recovery by monitoring the ranking performance of pages that received new internal links through redirect fixes.
How to Prevent Broken Links
Broken links reduce site credibility, waste crawl budget, and disrupt navigation. You prevent these issues through consistent structure, routine checks, and well-managed redirects.
Use a Consistent URL Structure
Write URLs that describe the page content in simple, direct terms. Apply the same structure across your entire website. You will reduce errors when URL formats remain consistent from one section to another.
Check All Links Before Publishing
Manually open every link after you add it to content. Confirm that it loads the correct page and follows the expected format. This lets you catch typos and formatting mistakes before users do.
Run Regular Link Checks
Use Google Search Console or Search Atlas to detect broken links across your site. Fix them early to avoid problems with indexing and user flow. Use automated tools like OTTO SEO to speed up the process.
Set Up Redirects Thoughtfully
Use 301 redirects to move old URLs to new destinations when content changes. Choose redirect targets that match the original intent. Consider long-term content plans before applying permanent redirects.
Monitor Redirects and Update as Needed
Check redirect performance in Search Atlas or Google Search Console. Replace or remove old redirects when they no longer serve their purpose. Redirection must stay aligned with both user intent and site goals.