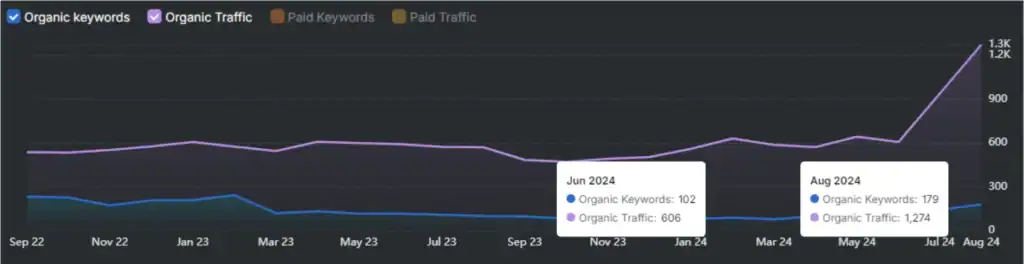
Google Discover is a personalized content feed that recommends articles, videos, and updates based on user activity. Google Discover is a part of Google Search, available on Android and iOS. Google Discover uses machine learning to deliver content related to a user’s interests, recent behavior, and engagement signals without a search query.
With over 800 million monthly active users, Google Discover represents a huge opportunity for publishers to increase visibility. Google Discover SEO content must be timely, visually rich, and relevant to topics a user already follows. Google Discover optimization includes using large images, demonstrating clear E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), and maintaining high performance on mobile. Two effective strategies include reinforcing semantic relevance with structured data and creating content around emerging trends.
What is Google Discover?
Google Discover is a queryless content recommendation system developed by Google. Google Discover delivers personalized results to users based on predictive interest modeling, not keyword input. Discover appears on the Google app homepage, Chrome’s new tab page on mobile devices, and the Google.com homepage on mobile browsers, as a discovery engine that introduces users to content they might not actively search for.
Google Discover uses machine learning models to analyze user behavior, such as previous searches, location history, content engagement, and interactions across Google services. These behavioral signals are mapped to entities, which represent real-world topics or objects. Based on this mapping, Google surfaces articles, videos, and other media that match the user’s current interest graph.
The Discover feed consists of content cards featuring large images or thumbnails, headlines, publisher information, and publication dates. Each card represents content that Google’s algorithms have determined might interest the specific user based on their digital footprint across Google services.
Content appearing in Google Discover is filtered through systems that assess topical relevance, visual richness, freshness, and quality guidelines. There is no fixed ranking position. Visibility is personalized and recalculated in real-time for each user session. Discover is governed by separate content policies from traditional Search, and inclusion is subject to compliance with Google’s Discover content rules.
What is Google Discover Optimization in Overall SEO?
Google Discover optimization refers to increasing the likelihood that content appears in the Discover feed by aligning with Google’s predictive content delivery systems. While traditional SEO targets specific search queries, Discover optimization focuses on matching user interests through behavioral modeling and semantic content relevance.
In the overall SEO ecosystem, Google Discover represents a separate traffic channel built on interest forecasting instead of query matching. While ranking in Search depends on factors like keyword relevance and backlink strength, SEO for Google Discover is driven by visual appeal, content quality, mobile usability, and topical relevance to user interests.
Unlike Google Search, Discover does not return a ranked list of pages. Instead, it selects pages that match current interest profiles tied to named entities and their contextual relationships.
If you want to optimize for Google Discover, you need to produce content that satisfies four primary requirements, which are relevance to recurring or trending entities, clear authorship and trust signals, mobile-first technical structure, and large, engaging images. Pages eligible for Discover inclusion must comply with Discover-specific content policies, which differ from traditional SEO guidelines.
What is the Importance of Google Discover for Website Owners?
Google Discover offers website owners a way to reach users who aren’t actively searching but are likely to engage based on their interests. Discover creates substantial traffic volumes and an opportunity to appear earlier in the user journey, before traditional SEO would even apply.
Users accessing content through Discover typically have a genuine interest in the topic instead of seeking specific information, which can result in longer session durations and higher page views per session. The heightened engagement provides publishers with opportunities to introduce readers to additional content, capture email subscribers, or move users through marketing funnels.
SEO Google Discover visibility helps build topic recognition over time. When users see content from the same source in Discover often, it can lead to stronger brand recall and direct return visits. Discover surfaces content that aligns with long-term interests as well, not just trending topics, which allows evergreen articles to stay visible longer.
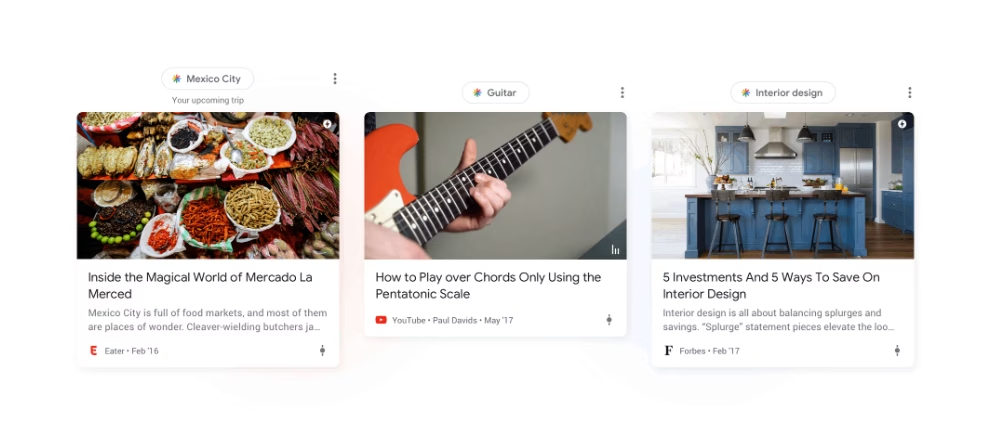
Since Google actively personalizes feeds based on user engagement, consistently appearing in Discover can create a positive feedback loop where engaged readers receive more of your content over time.
When users interact with content through clicks, reads, shares, or dismissals, the system refines its understanding of their preferences. The feedback loop strengthens audience connections and builds a loyal readership base.
How Does Google Discover Work?
Google Discover works by predicting which content a user is most likely to engage with based on their behavior across Google services. Instead of responding to search queries, Discover uses an interest-based ranking model that analyzes signals such as browsing history, location data, app usage, past search interactions, YouTube viewing activity, and Chrome behavior. These signals are processed by the Google Discover algorithm, which assigns relevance scores to pages mapped to known entities and topics.
The system creates a dynamic, personalized feed that updates in real time. Each content card is selected based on semantic similarity to a user’s current interest graph, which is constantly refined. Unlike Google Search, which returns a fixed set of ranked results for a query, Discover recalculates visibility on a per-user, per-session basis.
Content eligibility is determined by Google Discover content policies, which are distinct from general Search guidelines. Pages that rely on clickbait headlines, misleading preview images, or lack transparency in authorship are excluded. Discover prioritizes content that demonstrates clarity, accuracy, freshness, and topic authority, and penalizes manipulation or low-quality engagement strategies.
How is Google Discover Feed Generated?
The Google Discover feed is generated in real time whenever a user opens the Google app, visits Google.com on mobile, or starts a new tab in Chrome. The system pulls from the user’s interest profile, based on recent search behavior, location context, app usage, and content interactions. The user profile is matched against a dynamic index of eligible content mapped to named entities and topic clusters.
Each item in the feed, called a content card, is selected for its predicted alignment with the user’s preferences at that moment.
The algorithm Google Discover filters content by freshness, format, and engagement probability, favoring recently published articles that are semantically specific and visually complete.
Since the feed is generated per session, it can vary across devices, users, and time intervals, reflecting Google’s real-time recalculation of the most relevant signals and content index updates.
What are the Types of Google Discover Content?

Google Discover supports a range of content types, depending on the user’s interest profile and the entity associations of the content. While the format may vary by vertical, all content selected for the feed must meet technical and editorial standards. Discover favors self-contained pages that respond to a recurring interest without requiring a query.
The types of content most commonly shown in Google Discover are listed below.
- News and Current Events. Timely coverage of breaking stories, trending developments, and updates in politics, business, technology, and entertainment. News articles typically appear in Discover within hours of publication and follow short visibility cycles.
- Evergreen Articles. Informational guides, tutorials, and explanatory content that remain relevant over time. High-performing evergreen pieces align with recurring user interests and maintain visibility beyond the initial publication window.
- Lifestyle Content. Articles focused on food, health, fitness, travel, home, and personal development. These topics consistently perform well across user segments and often lead to repeated engagement.
- Blog Posts. Written posts published on websites across industries, covering informational, opinion-based, or topical content. Blog posts perform well because they align with user interest clusters, allow for entity-driven topical coverage, and adapt flexibly to trending or evergreen themes.
- Video Content. YouTube videos and embedded videos featured directly in the feed. Video receives high engagement rates and supports passive content discovery across categories such as entertainment, education, and product reviews.
- Sports Coverage. Game highlights, athlete profiles, team news, and post-match analysis. Sports content in Discover follows seasonal trends and event-driven interest spikes, particularly during major tournaments or playoffs.
- Entertainment Updates.Coverage of films, TV shows, celebrities, music releases, and digital culture. This category benefits from trending topic detection, visual prominence, and fast update cycles.
Blog posts are the most dominant content type across industries. Blog posts perform well because they consistently match user interest clusters and allow entity-driven topical coverage.
How to Optimize for Google Discover?

Optimizing for Google Discover requires a content strategy designed for interest prediction. Visibility depends on how well a page aligns with a user’s behavioral profile, entity interest clusters, and mobile-first experience expectations. Discover SEO prioritizes visual content, semantic consistency, and engagement signals. It’s not as concerned with keyword targeting.
The 7 Google Discover best practices are listed below.
1. Demonstrate E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. EEAT signals help Google evaluate content quality and determine whether a source should be eligible for content surfaces like Discover.
Google Discover surfaces content from sources that indicate author credentials, cite trustworthy sources, and maintain editorial transparency. Thin content or pages without visible ownership and experience signals are typically excluded.
Tips for optimizing E-E-A-T for Discover are below.
- Include author bylines and profile pages with relevant credentials.
- Add About, Contact, and Editorial Policy pages.
- Use experience-based sentences like “We observed…” or “In our test…”.
- Use schema markup for author, publisher, and reviewedBy entities.
- Maintain accurate publication dates and update timestamps when applicable.
- Include citations and references to authoritative sources that support factual claims and enhance content credibility. People, places, products, and institutions should appear with disambiguated phrasing.
Every article needs to feature a bylined author with a linked profile page containing biographical information, topic specialization details, and publication history. This structured attribution helps Google associate content with recognized experts, strengthening EEAT and topical authority signals.
2. Optimize for Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is the process of structuring content around entities and their contextual relationships, rather than keywords alone. In the context of Google Discover, semantic SEO improves how content is mapped to interest graphs.
Google Discover algorithm selects content based on entity-driven interest modeling. If your content doesn’t clearly relate to known entities, topics, or categories, it won’t align with user behavior profiles.
The best practices for Semantic SEO optimization are listed below.
- Center each page around 1–2 primary named entities (e.g., Google Discover, Semantic SEO, Structured Data).
- Use hierarchical topical structure H1 > H2 > H3 should reflect semantic depth, not formatting convenience.
- Add internal links to related entity-based pages (e.g., from “Semantic SEO” to “Entity-Based Content Strategy”).
- Use structured data to define entity type, such as Person, Organization, Product, or CreativeWork.
- Use descriptive, disambiguated phrases: e.g., say “Google Discover algorithm” instead of just “it”.
- Expand topical coverage using supporting paragraphs with shared anchor segments (Rule 6 & 7).
The Search Atlas SCHOLAR Tool (Semantic Content Heuristics for Objective Language Assessment and Review) evaluates this through Entity Score, Information Gain, and User Intent Matching. Poor semantic structure results in low Search Atlas SCHOLAR Tool scores for entities and user intent, both of which are a must for Google Discover inclusion.
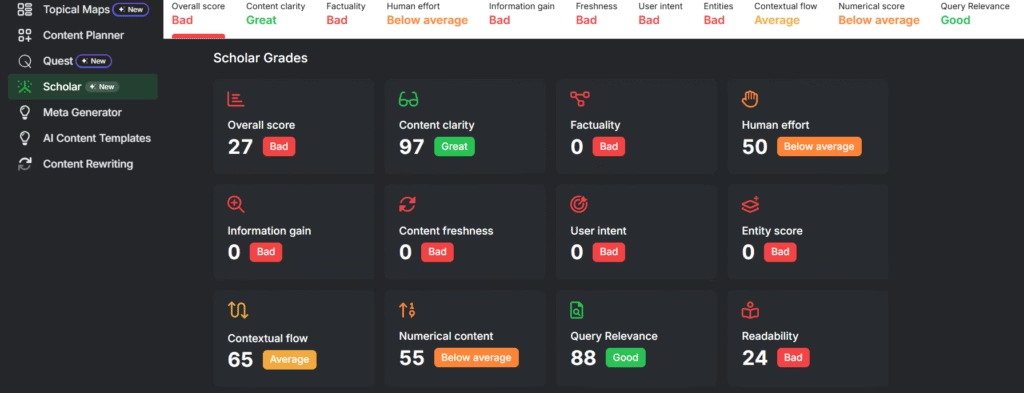
To improve the Entity Score, Search Atlas Scholar expects named entities to be clearly defined, repeated in structured ways, and connected through semantic flow. To increase Information Gain, add original insights, comparisons, or deeper factual layers not found in top-ranking pages.
3. Use High-Quality Images
Using high-quality images is one of the biggest things for Google Discover since visual assets are central to how content appears in the Discover feed. Google Discover prioritizes content with large, clear, and engaging images. Pages that include properly sized, relevant images are significantly more likely to receive impressions.
The Discover algorithm evaluates image SEO quality, file type, aspect ratio, and relevance to the on-page topic. Articles with images smaller than 1200px width or missing Open Graph markup are less likely to be shown. Repeated use of stock or unrelated visuals can also reduce engagement and click-through rates.
The best practices for optimizing image SEO for Google Discover are listed below.
- Use original, high-resolution images with a minimum width of 1200 pixels.
- Set the max-image-preview:large directive using <meta name=”robots” content=”max-image-preview:large”> to allow full image rendering in the feed.
- Define images using Open Graph and Twitter Card metadata, including og:image, og:type, and og:title.
- Use descriptive alt text that reflects the content entity, not generic phrases.
- Avoid using logos, text-overlays, or irrelevant stock photos as the primary image for the article.
The Search Atlas Site Audit Tool simplifies image optimization for Google Discover by identifying critical issues that might prevent content visibility. The Search Atlas Site Audit Tool analyzes missing alt attributes, oversized images (>100KB), outdated formats, and more, providing a “Health Gain” score and suggested fixes to prioritize improvements.
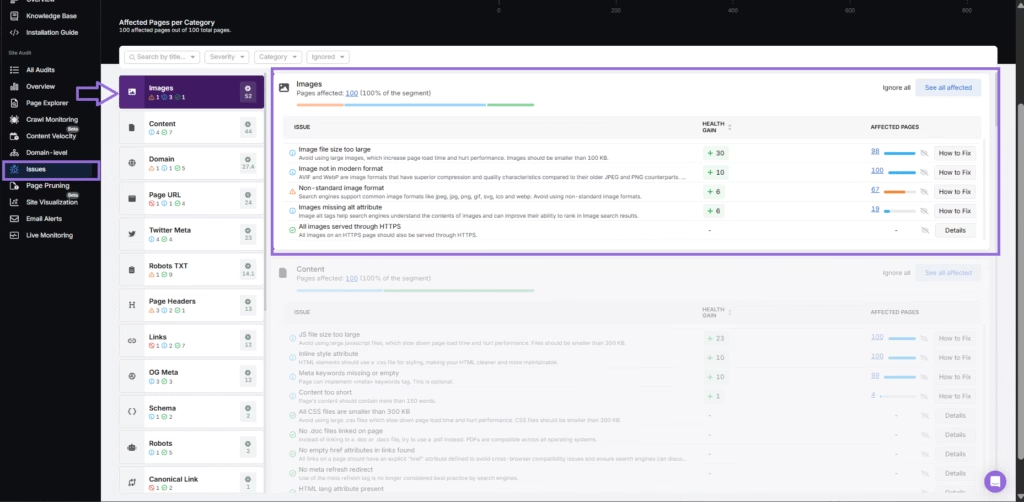
4. Improve Mobile Performance
Improving mobile performance is non-negotiable since Google Discover is accessed almost exclusively on mobile devices. As a result, page speed, mobile responsiveness, and Core Web Vitals are baseline requirements for Discover visibility. Content that loads slowly, shifts on render, or fails Google’s mobile usability criteria will be deprioritized even if it is topically relevant.
The Discover feed operates in the Google app and Chrome mobile browser. If a page violates mobile SEO performance thresholds (e.g., slow Largest Contentful Paint or high Cumulative Layout Shift), it will probably be entirely excluded. Discover filters out content with intrusive interstitials or unreadable layouts.
The best practices for mobile SEO in Google Discover are below.
- Pass all Core Web Vitals – Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) within the first 2.5 seconds, Interaction To Next Paint (INP) less than 200 milliseconds, Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) less than 0.1.
- Use a responsive design that adapts fluidly to screen size and avoids horizontal scrolling.
- Avoid layout shifts caused by delayed-loading ads or media.
- Minimize render-blocking scripts and unused CSS.
- Test your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and PageSpeed Insights tools.
Design content for comfortable mobile reading with appropriate font sizes, line heights, and paragraph lengths.
Mobile-optimized content features readable typography (minimum 16px font size), adequate spacing between interactive elements (at least 8mm), and concise paragraphs (3-4 sentences maximum) that prevent cognitive overload on smaller screens.
The Search Atlas Site Audit Tool identifies mobile usability issues that might affect Google Discover performance. The Search Atlas Site Audit Tool analyzes responsive design implementation, mobile rendering problems, and Core Web Vitals metrics to give you actionable recommendations for mobile experience improvement.
5. Publish Around Trends and Entities
Publishing around trends and entities matters because Google Discover reacts to dynamic interest shifts. Google trends and topics that experience a rise in search volume, news mentions, or social engagement are more likely to appear in a user’s feed. The Discover algorithm maps these interest surges to known entities and then evaluates available content against that updated trend graph. If your content matches the entity and the timing, it becomes eligible for exposure, even if it was not previously visible.
Content visibility in Google Discover increases when pages align with active interest patterns, particularly those linked to trending topics and recurring entities. The Discover algorithm prioritizes content that matches short-term spikes in user engagement as well as long-term topical behaviors. Publishing around timely entities improves the probability of inclusion and increases click-through rates during peak demand cycles.
The best practices for trend-based optimization are below.
- Use Google Trends to identify current spikes, regional demand, and breakout queries within your vertical.
- Monitor named entities (e.g., people, products, events) that repeatedly appear in user interest profiles using entity tools and Search Atlas reports.
- Republish or update high-performing content tied to seasonal or cyclical topics to keep it eligible for re-entry into the feed.
- Track Discover clicks in Google Search Console (GSC), filtering by topic cluster or page group to see which entities perform during trend windows.
- Use semantic anchors (e.g., event date, product version, election cycle) in the URL structure or metadata to strengthen relevance.
Google Discover surfaces content that matches rising interest in both behavior and context. Publishing timely, entity-centered content improves freshness scores and shortens the time to visibility.
6. Optimize for the Follow Feature
The Follow feature in Google Discover allows users to subscribe directly to specific websites or topics.
When a user follows a website, Google creates a direct interest signal tied to that domain. This interest signal increases the weight of future content in the Discover algorithm. While not all followers will see every new article, the Follow feature improves initial discovery velocity and repeat exposure.
Google surfaces content from followed sources using publisher feeds (RSS or Atom) and site-level structured data. Publishers that lack proper markup or syndication endpoints will not be eligible for Follow-based distribution.
The tips for optimizing the Follow feature are outlined below.
- Implement valid RSS or Atom feeds that reflect your most recent articles. Place them in your <head> or robots.txt for easy discovery.
- Use schema.org/Organization and schema.org/WebSite markup to define publisher identity. These structured data types help Google associate content with a consistent brand entity.
- Add the data-nosnippet tag to exclude parts of your page from appearing in Discover if needed (e.g., author disclaimers or legal content).
- Maintain a consistent publishing cadence so followers receive new content regularly. Irregular activity or infrequent updates may reduce visibility.
Discover uses the Follow feature to reinforce publisher relevance. Brands with active feeds and schema are more likely to benefit from persistent user interest over time.
7. Meet Google Discover Content Policies
Google Discover Content Policies are a separate set of content quality and compliance policies distinct from traditional Search. Google Discover content policies act as a pre-filter, which means even technically optimized or semantically rich content will not appear in Discover if it violates any of these standards.
Before Google considers behavioral or entity relevance, it screens content for policy compliance. Content that contains misleading headlines, lacks editorial transparency, or uses manipulative engagement tactics is excluded from the Discover index. Repeated violations can suppress an entire domain’s visibility across Discover surfaces.
The key Google Discover content policies are listed below.
- No clickbait or misleading titles. Headlines must accurately reflect the article’s content.
- No sensationalism or emotionally manipulative language. Content should maintain a professional tone and avoid exaggerated claims.
- No harmful, hateful, or dangerous content. Pages that promote violence, discrimination, or conspiracy theories are not eligible.
- High editorial transparency required. Every article must clearly show who wrote it and provide context for the publishing source.
- Avoid spammy design and ad overload. Excessive ads, deceptive UI elements, or aggressive interstitials will reduce eligibility.
Discover policies are applied before the algorithmic ranking. Failing this layer means zero visibility, regardless of performance elsewhere.
How Does Google Discover Traffic Differ from Keyword-Driven Traffic?
Google Discover traffic is interest-based and unpredictable, while keyword-driven traffic is intent-based and more stable. In Google Discover, visibility depends on how well your content aligns with a user’s behavioral profile, including search history, YouTube activity, location signals, and entity engagement. There is no query, no search results page, and no ranking position to target.
In contrast, traditional keyword-driven traffic comes from typed or spoken queries, matched through search intent, keyword relevance, and SERP competition. Traditional keyword-driven visits are easier to forecast and control via structured content targeting.
If you’ve seen a sudden Google Discover traffic drop, it most likely reflects changes in user behavior modeling, entity interest shifts, or a loss of eligibility due to content freshness or policy issues. It’s not a drop in keyword rankings as in keyword-driven traffic.
How to Monitor Performance on Google Discover?
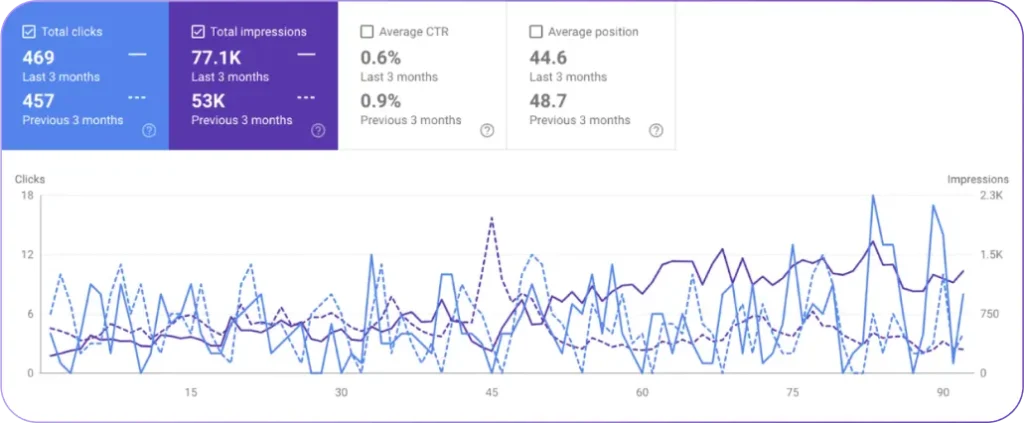
Monitoring performance on Google Discover requires using Google Search Console’s dedicated Discover report, which provides impression and click data for Google Discover traffic. GSC’s dedicated Discover report shows performance trends over time and allows you to identify which content types and topics generate the strongest Discover engagement. The data will give you insights into content characteristics that resonate with Discover audiences so you can make future content strategy decisions.
For deeper insights, use Google Analytics (GA4) to create segments that isolate traffic from the “google” referral path. GA4 analyzes engagement metrics like bounce rate, session duration, and conversion rates. Combining GSC and GA4 sources into custom dashboards enables tracking different content types performance on Discover, giving you substantial info for optimization strategies.
What are the Best Google Discover SEO Tools?
The best Google Discover SEO tools combine data collection capabilities with actionable insights and optimization features. Google’s native tools provide direct performance data, while third-party platforms like the Search Atlas SEO platform offer expanded analysis and implementation support for Google Discover optimization.
Free Google tools include Google Search Console‘s Discover report for performance tracking, Google Analytics 4 for user behavior analysis, and Google PageSpeed Insights (PSI) for mobile experience evaluation.
For comprehensive optimization, use the advanced Search Atlas SEO tools. The Search Atlas SEO tools include specialized features like AI-powered OTTO SEO, content analysis for engagement potential assessment, the Search Atlas Schema Markup Generator for proper structured data implementation, and the Search Atlas Site Audit Tool, which identifies structural and mobile usability issues that might affect Google Discover inclusion. The platform offers Search Atlas OTTO SEO, which can deploy all these site-wide fixes with a single click.
Combining Google’s free native tools and AI-powered advanced tools like the Search Atlas SEO platform creates a complete Discover system for maximizing visibility in Google’s personalized feed.
Is It Hard to Get on Google Discover?
Yes, getting into Google Discover is challenging. Google sets high standards for content quality since Google Discover proactively recommends content to users. Websites need strong E-E-A-T signals, excellent mobile performance, and compelling images to be considered.
But if you consistently publish high-quality content that users engage with, use proper technical setup, and include striking visuals, you can gain and keep visibility in Google Discover.
What is the Difference Between Google Discover and Google News?
Google Discover shows personalized content based on your interests and past behavior across Google services. Discover content includes many content types like articles, videos, and blog posts on any topic you might like. Google News focuses only on current events and timely reporting from established news publishers. For example, an article about “summer gardening tips” might appear in your Discover feed if you’re interested in gardening, but it wouldn’t show up in Google News unless it was breaking news. Optimizing for Google News SEO requires different technical approaches than Discover optimization.
What is the Difference Between Google Discover and Google Search?
Google Discover pushes content to you without you asking for it, based on what Google thinks you’ll like based on your past activity. Discover shows you topics you might not have thought to search for. Google Search only responds when you actively type in a query looking for specific information. While Google Search ranks content based on how well it matches your query, Google Discover picks content based on your interests and how engaging the content is, without needing specific keywords. This fundamental difference shapes how you should approach optimization for each platform.
What is the Relation Between Google Discover and SEO Content?
Google Discover builds on basic SEO content principles but needs extra elements to drive engagement. Both Google Discover and traditional SEO content value thorough topic coverage and good user experience, but Google Discover puts more emphasis on eye-catching images and content that creates an emotional connection. The best content for Discover follows SEO best practices for structure and relevance and adds compelling visuals and emotional hooks. Start with solid SEO content, then enhance it with elements that make people want to engage with and share it.