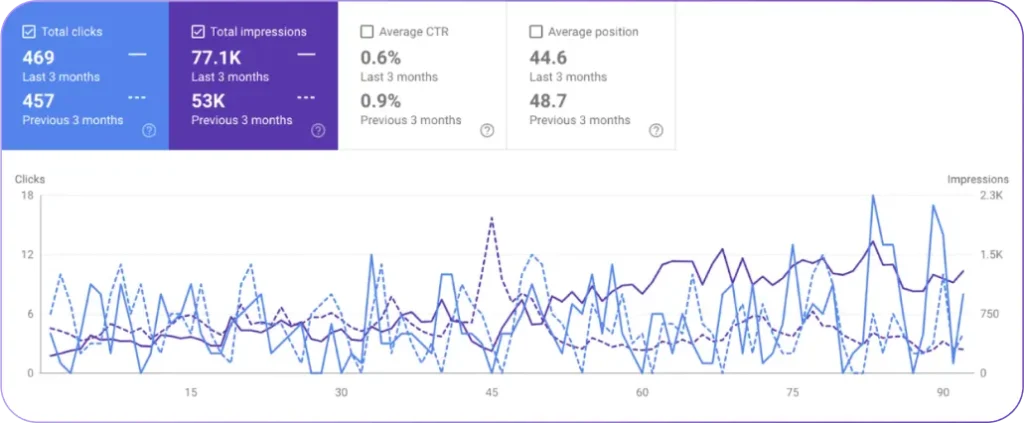
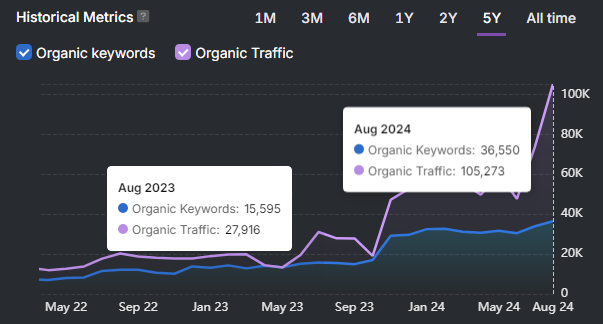
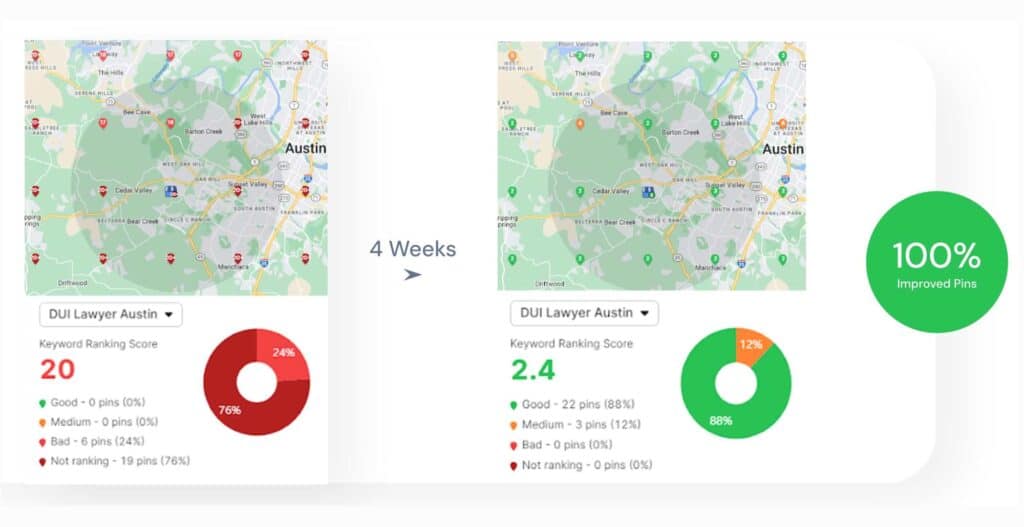
Black hat SEO techniques use manipulative practices that influence rankings without adding user value. Black hat SEO techniques violate search engine guidelines and harm long-term website performance.
Black hat techniques aim to boost visibility using shortcuts that break quality expectations. These shortcuts reduce content trust and distort how search engines evaluate relevance. Search engines improve ranking systems to surface helpful, accurate results. Black hat SEO disrupts this process and often leads to consequences.
What Are Black Hat SEO Techniques?
Black hat SEO techniques are unethical methods used to manipulate search engine rankings. Black hat SEO techniques violate search guidelines and prioritize visibility over user value. Black hat SEO techniques exploit algorithm weaknesses instead of improving relevance or content quality. These manipulations reduce trust and increase the risk of search engine penalties.
What Are the Consequences of Black Hat SEO Techniques?
Black hat SEO techniques lead to serious consequences when detected by search engines. These techniques rely on manipulation, not quality, and violate official ranking guidelines. The main consequences are listed below.
- Negative User Experience. Black hat SEO reduces readability and usability. Disrupted structure increases bounce rates and lowers engagement.
- Search Engine Penalties. Search engines apply algorithmic or manual actions when manipulation is detected. Some pages are removed entirely from results.
- Loss of Ranking and Visibility. Visibility declines across target keywords after a penalty. Traffic drops and rankings collapse.
- Financial Setbacks. Penalties require resource-heavy recovery. The cost of rebuilding outweighs short-term black hat gains.
- Reputation Damage. Deceptive tactics reduce trust. Users who recognize manipulation avoid the brand across all channels.
What Are the 9 Black Hat SEO Techniques That Harm SEO?

The 9 black hat SEO techniques that harm SEO performance and hurt your website are listed below.
1. Abuse of Schema Markup
Abuse of schema markup refers to the use of structured data that misrepresents actual page content. Abuse of schema markup targets rich results by injecting false information into search engines. This tactic changes how search systems interpret and present a page in results.
Schema abuse includes inflated ratings, fake reviews, and incorrect structured types. These signals create a misleading representation of the page. Misleading markup affects trust and trigger rich result removal or algorithmic downgrades.
Use correct schema types for each content category. Match articles, products, and reviews to their official definitions in Schema.org. Avoid injecting fake values. Do not insert inflated ratings, prices, or dates that differ from visible content. Validate structured data regularly. Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test to confirm proper field formatting.
Search Atlas Schema Markup Generator Tool ensures proper schema implementation. The Schema Markup Generator outputs valid JSON-LD using guided inputs. It connects to Google Rich Results Test to confirm setup and prevent markup errors.
2. Paid Link Schemes
Paid link schemes refer to the exchange of money or favors for backlinks placed without editorial oversight. Paid link schemes inflate domain authority using links that do not represent genuine trust. These links appear on unrelated websites and lack contextual alignment.
Backlinks from link farms, low-quality blogs, and spam directories distort search signals. These placements create unnatural link patterns that search engines associate with manipulation. Manual actions and algorithmic filters are applied when these patterns are detected.
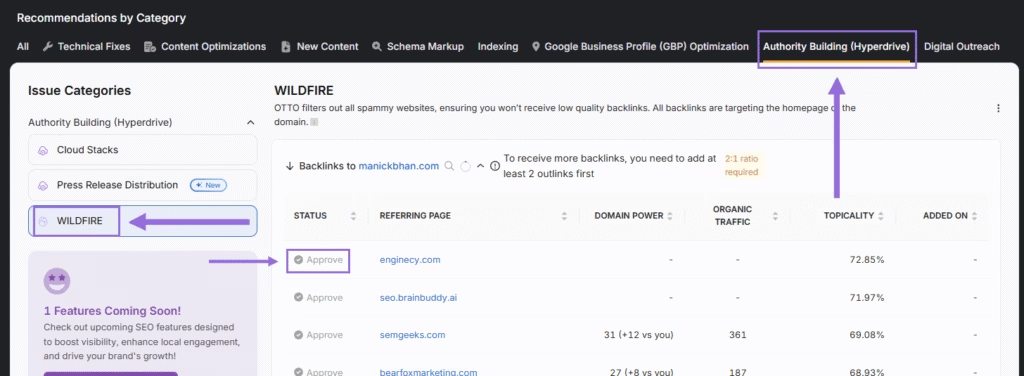
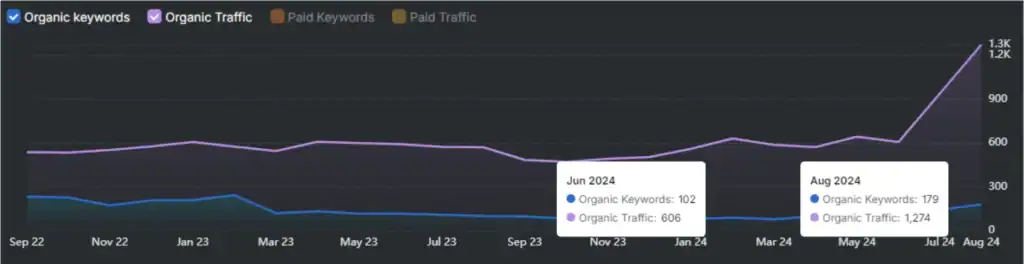
Search Atlas Wildfire Tool solves paid link risks by automating contextual partnerships. The Wildfire Tool suggests partner sites with relevant topics and strong authority. It supports a 2:1 exchange, where two outbound links secure one inbound link from a trusted domain.
3. Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing refers to the repeated use of the same keyword across a page to manipulate rankings. Keyword stuffing ignores natural phrasing and weakens content clarity. Search engines detect the pattern through repetition thresholds and exact-match frequency.
Pages with natural variation avoid keyword stuffing by reflecting how users search. The most common characteristics of high-quality keyword use are listed below.
- Clear phrasing aligned with topic relevance.
- Queries that match user intent and search behavior.
- Long-tail variations that expand topical depth.
- Terms placed where they fit naturally in sentence flow.
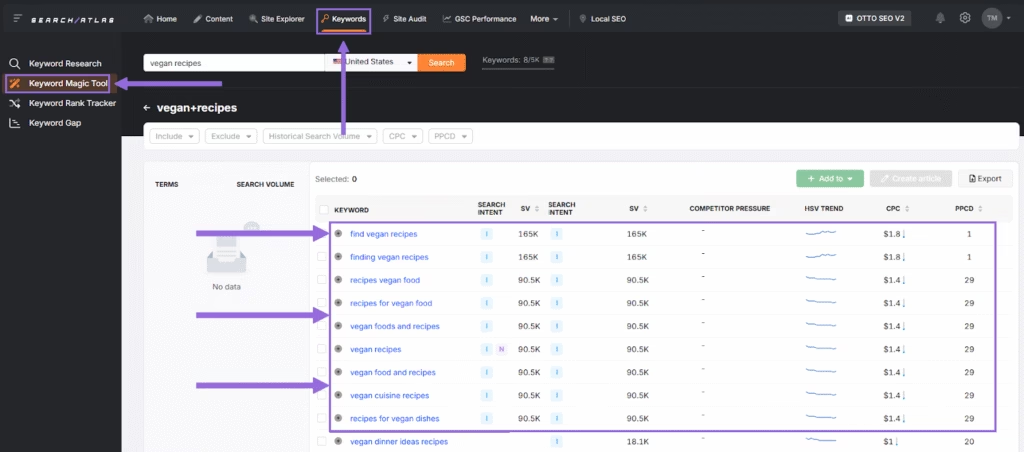
Search Atlas Keyword Magic Tool prevents overuse by expanding keyword coverage with variation. The Keyword Magic Tool includes over 5.2 billion keywords grouped by topic, intent, and difficulty. These variations support relevance while reducing keyword density risks.
4. Copied Content
Copied content refers to blocks of text taken from other websites without attribution. Copied content appears when articles, product descriptions, or blog posts are reused without change. These copies often come from competitors, suppliers, or third-party sources.
Copied content inflates page volume without adding original material. Maintaining quality content requires focus on four safeguards listed below.
- Originality.
- Clarity.
- Attribution.
- Relevance.
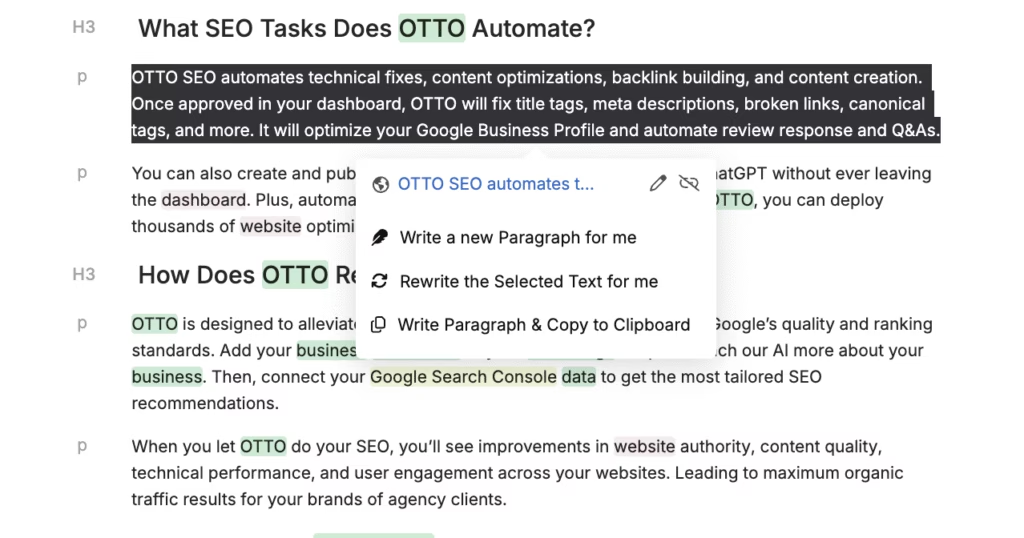
The Content Genius Tool refers to an AI-powered writing assistant in Search Atlas. The Content Genius Tool rewrites selected phrases using original language while keeping meaning intact. This tool replaces duplicated sections to preserve clarity, topic alignment, and search compliance.
5. AI-Powered Content at Scale
AI-powered content at scale refers to generating large volumes of automated text. AI-powered content at scale becomes a black hat SEO technique just when it produces low-quality or unoriginal material.
AI-powered content at scale floods websites with generic phrasing and lacks depth or user intent. Search engines detect AI-powered content at scale by identifying repetitive patterns, unnatural structure, and semantic gaps.
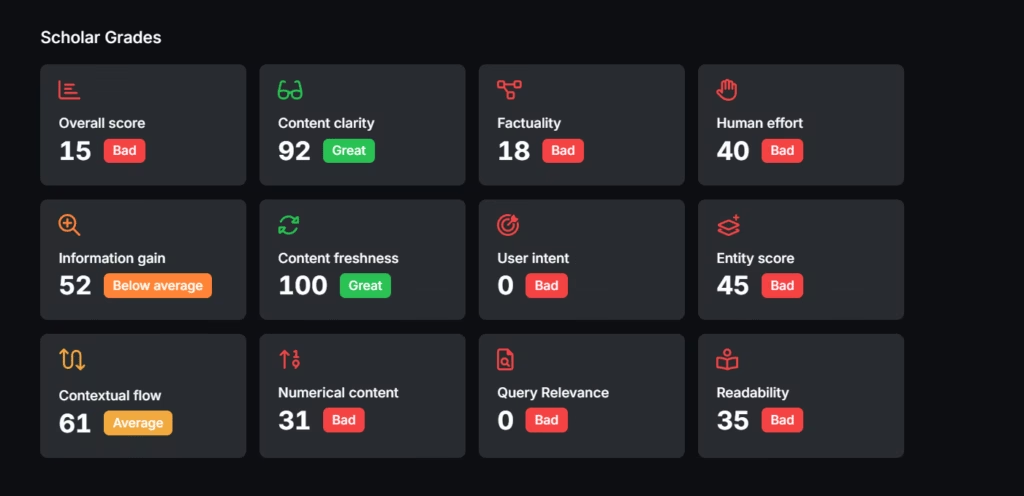
Search Atlas supports AI-powered content at scale with Content Genius and Scholar tools. The Content Genius Tool creates original copy in custom tones aligned with brand voice. The Search Atlas Scholar Tool evaluates content quality against Google PageQuality Algorithm and information retrieval principles. Scholar provides objective metrics to ensure content meets search engine standards.
Together, these tools enable scalable AI content that remains clear, relevant, and compliant with SEO best practices.
6. Hidden Links
Hidden links refer to anchor elements placed in the page code that remain invisible to users but are still accessible to search engines. Hidden links distort SEO signals by inflating backlink references without contributing to content clarity or user navigation.
Hidden links manipulate how search engines interpret internal structure. The crawlers detect a link as valid, even though no user interaction is possible. This disconnect sends misleading signals about content relationships, authority, or intent.
Improve link transparency by removing deceptive formatting as listed below.
- Identify invisible anchors. Check the DOM for 1-pixel fonts or non-clickable elements.
- Audit buttons and images. Look for links hidden behind visual layers.
- Place links with user intent. Embed them in content or menus where they offer navigation or context.
- Avoid identical color pairings. Make sure anchor text visibly contrasts with the page background.
7. Cloaking
Cloaking refers to showing one version of a webpage to search engines and another to users. Cloaking becomes a black hat SEO technique when it alters content visibility to influence rankings. Cloaking presents keyword-heavy HTML to crawlers while users see unrelated visuals, ads, or scripts. Cloaking often changes based on the browser, device, or user agent.
Cloaking creates mismatches between crawled and visible content. These mismatches produce misleading signals about topic coverage, structure, and page quality. Search engines evaluate page content based on the version they crawl. Cloaked versions disrupt this evaluation and violate ranking expectations.
To avoid cloaking penalties, maintain consistent content for both users and crawlers. Do not serve alternate layouts or inject hidden keyword blocks based on user agent or device.
8. Clickbait Manipulation
Clickbait manipulation refers to using exaggerated or misleading headlines to drive traffic to unrelated or low-value content. Clickbait headlines trigger curiosity or urgency but lead to shallow or off-topic pages.
This black hat SEO technique distorts performance signals by creating a gap between user expectation and actual content. Clickbait manipulation includes the traits below.
- Promising content not delivered on the page.
- Prioritizing sensationalism over relevance or quality.
- Combining clickbait with other deceptive black hat techniques.
- Creating titles that misalign with search intent or topic coverage.
Avoid clickbait manipulation using descriptive headlines that match on-page content. Remove vague promises or emotional triggers that mislead users. Use AI SEO tools to rewrite weak titles with clear intent, aligned keywords, and content consistency.
9. Doorway Pages
Doorway pages refer to low-value pages created to rank for narrow search queries and redirect users elsewhere. Doorway pages exist to attract clicks without satisfying user intent or offering complete content.
These pages target specific terms but provide limited value. Visitors land on a doorway page, then move to a different URL, often without knowing. Use structured publishing if your aim is to reach different regions, services, or user groups
- Make sure each page answers a unique question or intent.
- Include real value on every page, not just keyword variations.
- Use internal linking strategies to connect content based on topic relevance.
- Group pages into clusters, not keyword-stuffed silos.
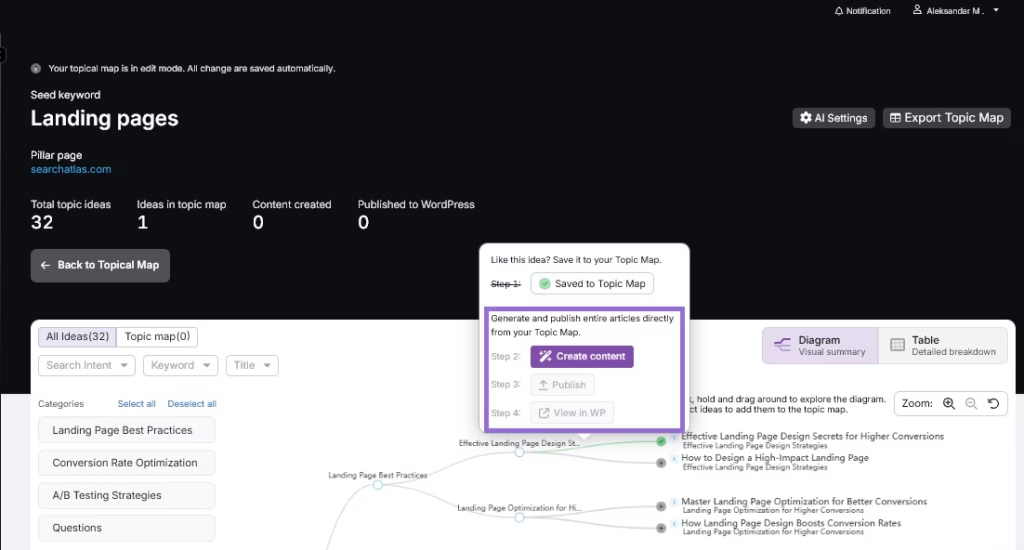
Search Atlas prevents doorway page issues using the Topical Map Generator Tool. The Topical Map Generator Tool involves organizing content around a central theme, with each page targeting a specific subtopic, question, or user intent. This replaces doorways pages with a unified strategy that supports ranking without manipulation.
How to Identify Black Hat SEO on Your Site
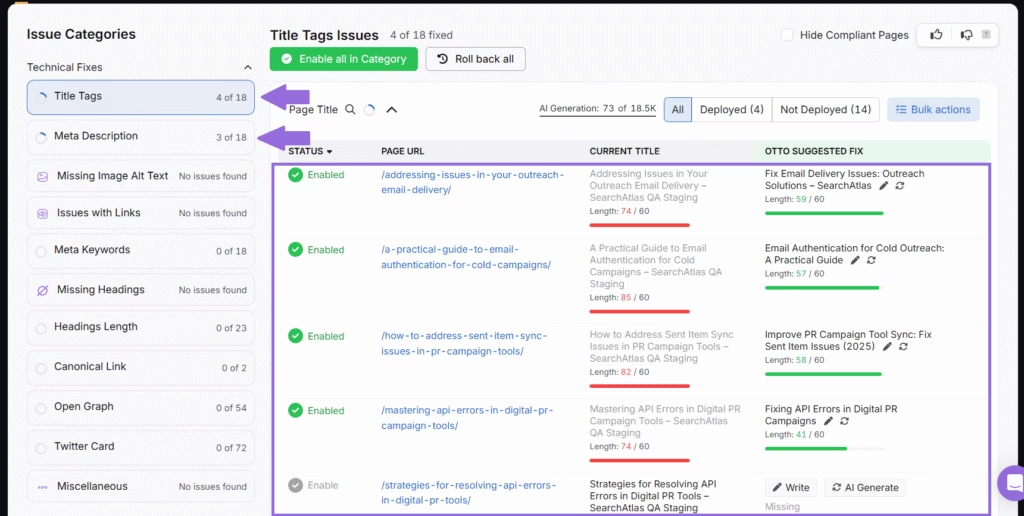
Run a full audit using trusted SEO tools to uncover black hat SEO techniques.Catch risks early and correct issues before they trigger penalties. The Search Atlas Site Auditor Tool flags these issues automatically, highlighting elements that violate search engine guidelines and disrupt content integrity.
Can I recover from a Black Hat SEO penalty?
Yes. Recovery happens if you identify the source of the penalty and remove manipulative tactics. Fix issues like toxic backlinks, cloaked content, and keyword stuffing.
How Long Does Black Hat SEO Recovery Take?
Recovery time depends on the scope of violations. Most cases require several weeks or months. Results come faster if fixes are implemented quickly and content follows clear, ethical guidelines.
What to Use Instead of Black Hat SEO?
Use methods that follow search engine guidelines like white hat SEO techniques. Publish original content, earn backlinks through relevance, and keep site structure crawlable. These practices build authority over time and reduce ranking volatility.
How Black Hat, White Hat, and Gray Hat SEO Compare?
White hat SEO uses approved techniques that prioritize users and meet search engine expectations. Black hat SEO manipulates systems using tactics like cloaking, hidden links, and duplicate pages. Gray hat SEO uses risky or borderline tactics that shift into black hat territory as guidelines change.