Breadcrumbs improve structure and navigation. Breadcrumbs show users where they are and connect related pages.
Breadcrumbs display a path from the homepage to the current page. Breadcrumbs reduce confusion and limit unnecessary clicks. Users return to earlier sections easily if breadcrumbs outline the full webpage trail.
Breadcrumbs clarify webpage relationships. Breadcrumbs help search engines understand how content fits within the website structure. The structured data markup for breadcrumbs increases eligibility for enhanced search results.
Breadcrumbs refer to the Grimm story “Hansel and Gretel”. Breadcrumbs in the story mark a path through the forest. Breadcrumbs on websites serve the same purpose, they lead users back through the webpage path.
What Are Breadcrumbs in SEO?
Breadcrumbs are navigation links that show a user’s position within a website’s structure. Breadcrumbs appear near the top of the page and display a horizontal trail from the homepage to the current page.
The breadcrumb trails reflect the website’s structure, moving from general categories to specific pages. The trail updates automatically as users go deeper into the site. Breadcrumbs usually appear as clickable links separated by symbols like slashes (/), arrows (›), or vertical bars (|).
What Is an Example of a Breadcrumb in SEO?
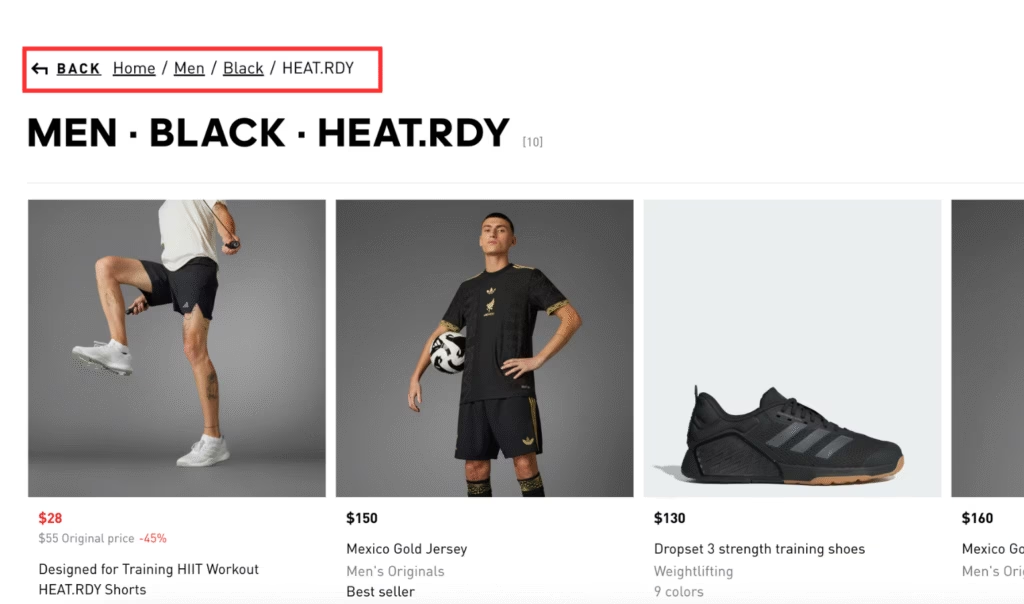
Breadcrumbs show a visitor’s position inside a website’s content hierarchy and provide clickable links to previous sections. Breadcrumbs improve navigation if a site contains many layers, such as categories, subcategories, and individual content pages.
For example, on a travel website, a breadcrumb trail will appear as “Home > Destinations > Europe > Italy > Rome > [Current Page]”. Each part links back to its broader section, which helps visitors move between related pages without relying on browser buttons.
When to Use Breadcrumbs?
Breadcrumbs serve a strategic role if the website follows a multi-level layout and contains deeply nested sections or products. Breadcrumbs guide navigation and support SEO structure only when content depth creates multiple paths between higher-level and lower-level pages.
There are five main situations when breadcrumbs need to be used. These are listed below.
- E-commerce websites. Breadcrumbs help organize navigation across departments, product categories, and item pages.
- Content-heavy blogs. Breadcrumbs show paths through categories, subcategories, and long-form articles.
- News websites. Breadcrumbs group articles under topics, dates, or editorial series, guiding readers through related stories.
- Documentation portals. Breadcrumbs organize help pages under product lines, features, or use-case categories.
- Educational platforms. Breadcrumbs separate learning tracks, modules, and lesson pages inside structured course flows.
What Is the Importance of Breadcrumbs in SEO?
Breadcrumbs hold importance in SEO because they define structure, support indexing, and guide users through layered content. Breadcrumbs become essential if content depth increases and structured navigation is required across multiple page levels.
Breadcrumbs impact SEO strategy by enhancing user navigation, distributing link equity, and helping search engines interpret site structure. The benefits of using breadcrumbs are outlined below.
- Improve Website Structure. Breadcrumbs reinforce hierarchy and clarify content relationships, helping users and search engines navigate from broad to specific categories.
- Boost Search Engine Clarity. Breadcrumbs communicate webpage context and hierarchy to Google. When enhanced with structured data, they appear as rich snippets in search results.
- Aid Crawlability and Indexing. Breadcrumbs create internal links that support crawlability and indexability by improving the discoverability of deeper webpages, especially on complex websites.
- Strengthen Internal Linking. Breadcrumbs help distribute link equity throughout your site. They reinforce your website hierarchy by linking product pages to subcategories, subcategories to categories, and categories back to the homepage.
- Enhance User Experience. Breadcrumbs reduce confusion by showing where users are within a site. They offer quick access to higher-level pages without relying on the back button.
- Reduce Bounce Rates. Breadcrumbs guide users to related pages, encouraging deeper exploration and increasing on-site engagement.
What Are the 4 Breadcrumb Best Practices to Strengthen Your SEO?
The 4 breadcrumbs best practices to improve UX and rankings are listed below.
1. Choose Which Type of Breadcrumbs to Use
There are 3 main types of breadcrumbs in SEO. Each type supports a different navigation path based on website architecture. These breadcrumbs types are listed below.
Location Breadcrumbs
Location breadcrumbs reflect the webpage’s position within the site structure. These breadcrumbs stay the same for all users, no matter how they arrived. Websites with deep hierarchies or content libraries use this format to support navigation and page discovery.
Home > Blog > SEO > Current Page
Path Breadcrumbs
Path breadcrumbs reflect a user’s unique navigation history. These breadcrumbs track each page visit from the entry point to the current page. The breadcrumb trail changes depending on the user’s path and does not follow the website hierarchy.
Home > Blog > Post > Tag > Current Page
Attribute breadcrumbs
Attribute breadcrumbs reflect selected filters or product traits. These breadcrumbs are common on e-commerce websites and help users retrace filters without leaving the current view. Attribute breadcrumbs often appear alongside location breadcrumbs.
Accessories > Hats > Size. Medium > Color. Black > Style. Fedora
Use location breadcrumbs unless your website includes a product catalog that requires filtering. This format supports both usability and SEO.
2. Add and Test Schema Markup for Breadcrumbs
Schema markup defines structured data for webpages. The schema markup helps search engines understand page content and structure. The schema uses a standard vocabulary called Schema.org. This vocabulary defines elements like products, reviews, and breadcrumbs for web pages.
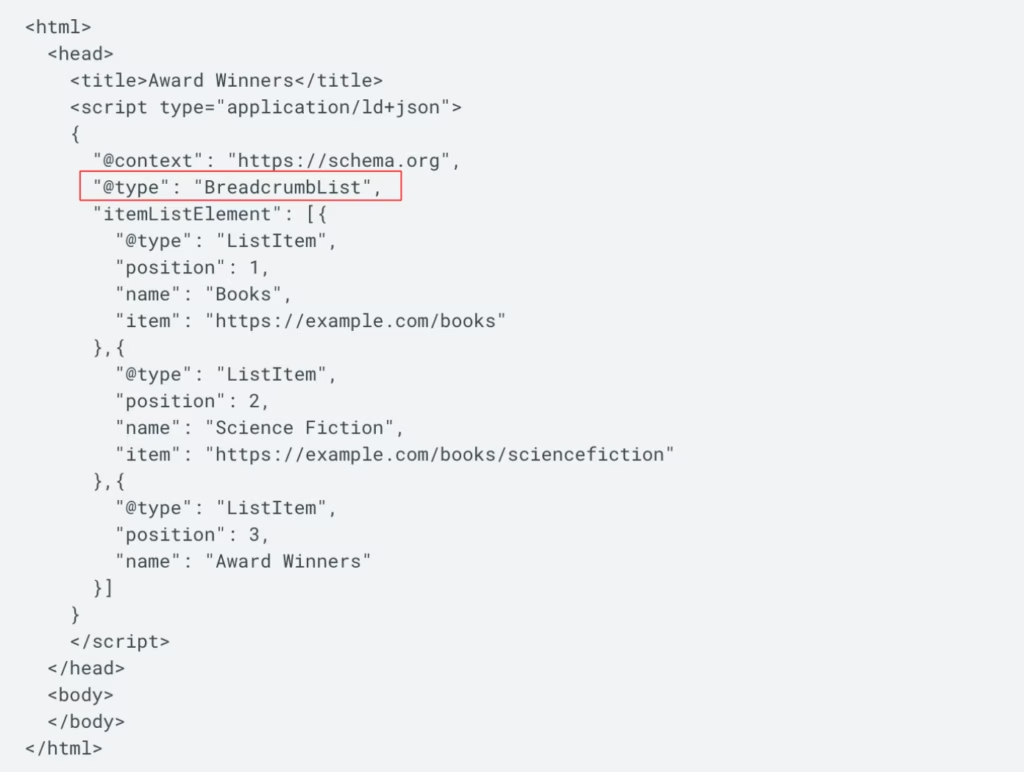
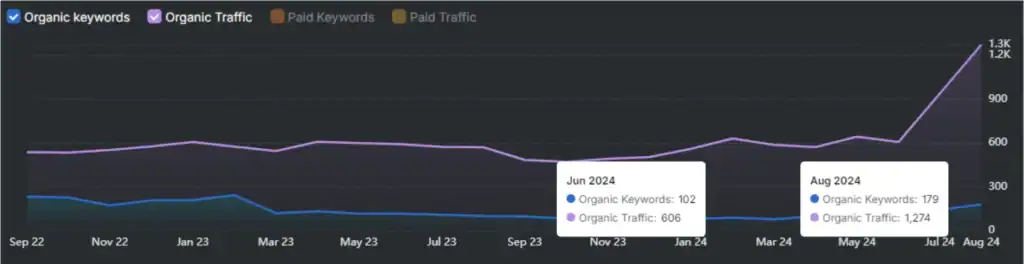
Breadcrumb schema refers to structured data that explains page location in a website. Breadcrumbs use a specific schema type called BreadcrumbList. BreadcrumbList shows a page’s position in the site hierarchy. This schema markup displays the navigation path from the homepage to the current page.
To start implementation, generate the schema code. Use a tool like the Schema Markup Generator or write the JSON-LD manually.
Place the code inside <script type=”application/ld+json”> tags. Add this script to the HTML of each page with breadcrumbs. Position the script in the <head> section or just before the closing </body> tag. The JSON-LD must include four required fields listed below.
- Type
- Position
- Name
- Item
List each breadcrumb level in order, starting with the homepage. Define each step using nested objects and assign the correct field values. See the example below.
- Position 1 for the homepage
- Position 2 for the category
- Position 3 for the current page
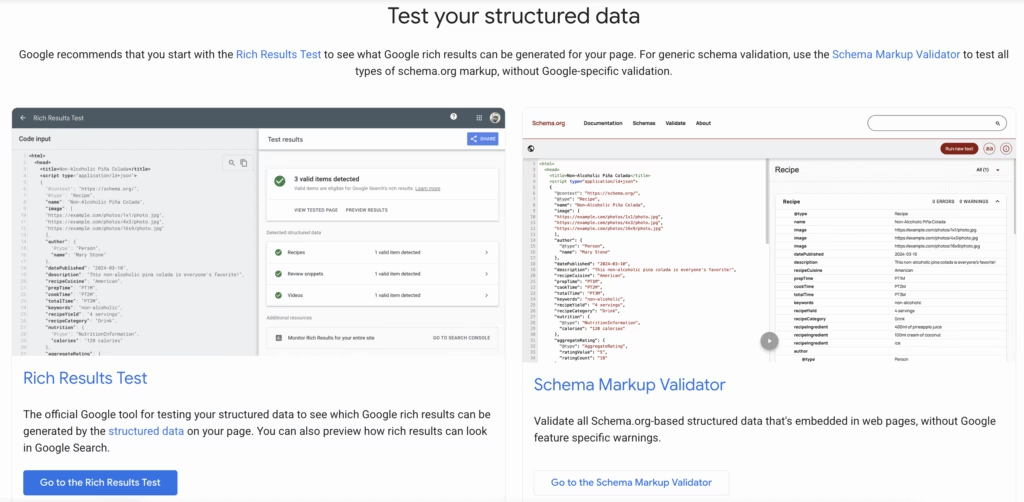
Test the schema markup after adding the code. Use Google Rich Results Test or the Structured Data Testing Tool. Missing fields or syntax errors prevent Google from showing the breadcrumb snippet. These issues block correct structure interpretation.
Manual breadcrumb schema implementation makes teams edit and test code page by page. Breadcrumb errors often appear during site updates or redesigns because manual workflows miss consistency checks.

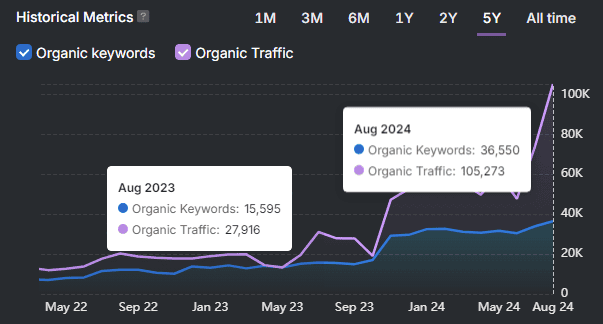
Search Atlas solves this problem using the Search Atlas Schema Markup Generator for BreadcrumbList. The Search Atlas Schema Markup Generator builds valid JSON-LD for blog posts, categories, and product pages. This automation reduces testing time and keeps output consistent across pages.
3. Improve Breadcrumb Design
Improving breadcrumb design refers to optimizing how breadcrumb navigation appears and functions on a website. Breadcrumb design affects both usability and crawlability. Improving breadcrumb design involves visual layout and code-level structure.
To improve breadcrumb SEO design, follow the five best practices below.
- Use Keyword-Relevant Anchor Text. Anchor text in breadcrumb links need to stay short and include focus terms from each webpage. This approach strengthens internal linking structure and adds search engine context.
- Define Start and Destination Clearly. Breadcrumbs must begin with the homepage and end with the current page. The final breadcrumb stays non-clickable and uses styling that signals the user’s location.
- Choose Hierarchy-Friendly Separators. The greater-than symbol (>) communicates progression and hierarchy. Avoid separators like slashes (/), pipes (|), or bulky arrows (» or →) because these create visual clutter.
- Balance Simplicity and Accessibility. Use a small, unobtrusive font size that matches link styles across the site. Remove labels like “You are here” and maintain a clean breadcrumb line. Ensure tap targets remain large enough for mobile users.
- Design for Mobile-First Indexing. Display breadcrumbs in a single line using horizontal overflow. Shorten breadcrumb terms if the trail becomes long.

4. Monitor and Maintain SEO Breadcrumbs
Monitor and maintain breadcrumbs is the ongoing process of keeping breadcrumb navigation accurate, functional, and aligned with site structure. Breadcrumb maintenance ensures that navigation reflects current page hierarchies, URLs, and content relationships.
The breadcrumb trails require updates if site changes affect the structure or internal links. To monitor and maintain breadcrumbs effectively, focus on the four factors below.
- Clarity
- Conciseness
- Consistency
- Accessibility
Breadcrumbs need ongoing checks to remain functional and visible in search results. Broken breadcrumb paths or mismatches between visible trails and structured data happen if sites change URLs, categories, or internal links.
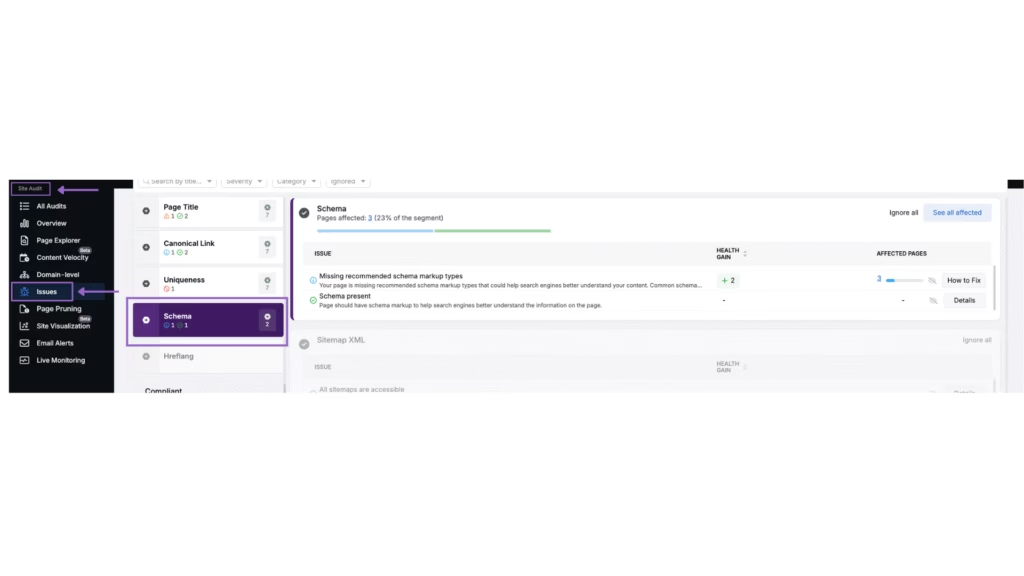
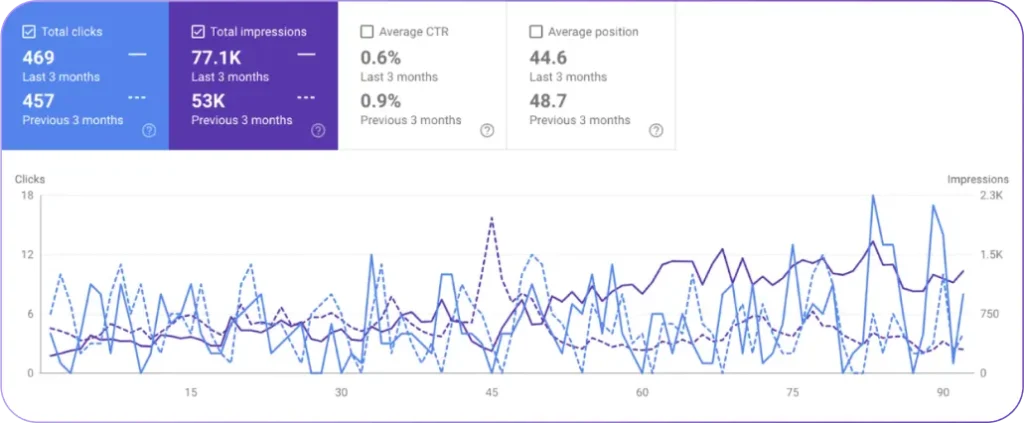
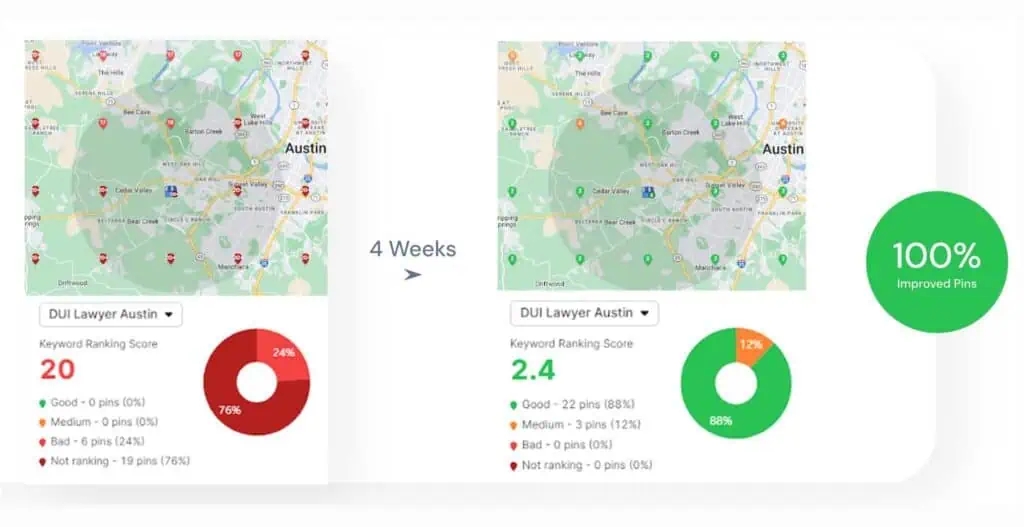
The Site Auditor in Search Atlas detects breadcrumb issues that affect visibility in search results. The Site Auditor flags missing or incorrect breadcrumb markup, inconsistent page paths, and crawl issues that disrupt breadcrumb structure. The Site Auditor checks for broken links where the anchor text no longer points to valid URLs.
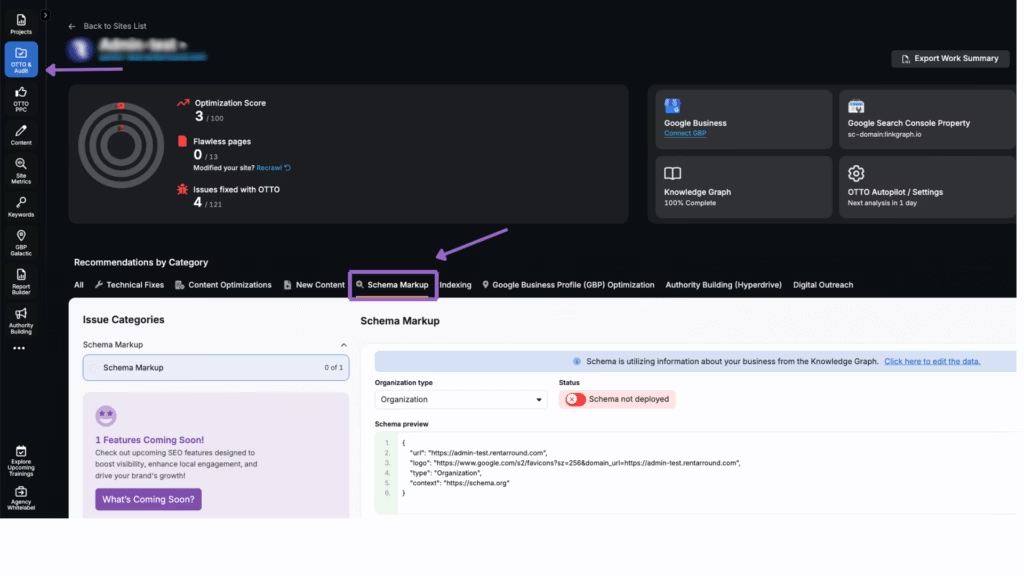
Search Atlas OTTO SEO automatically implements missing schema types like BreadcrumbList during key page audits. OTTO applies structured data updates to help search engines understand content and improve visibility in search results.
Why Breadcrumbs Don’t Work on Every Website?
Breadcrumbs fail on some websites because the structure is too simple to justify layered navigation. The reasons below explain why breadcrumbs don’t work on every website.
Breadcrumbs don’t help if the website lacks a clear content hierarchy
Breadcrumbs provide no value if the website has no structured navigation. Single-page layouts or ungrouped pages lack defined categories. These websites often scroll vertically and don’t separate content into distinct URLs. A floating scroll-to-top button replaces the need for navigational context.
Minimal navigation websites reduce clutter by skipping breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs compete with clean design elements on minimalist websites. Portfolios and landing pages often favor icon menus or static anchor links. These interfaces prioritize focus and simplicity. Adding breadcrumbs creates visual noise and distracts users from the main call to action or featured content.
Flat website structures make breadcrumbs redundant
Breadcrumbs lose function if every webpage is directly linked from the homepage. Flat websites contain no parent categories or nested URLs. A search bar or a top-level navigation menu handles orientation instead. Without a layered hierarchy, breadcrumb paths become repetitive or irrelevant for visitors.
Lack of content hierarchy creates inconsistent breadcrumb paths
Breadcrumbs confuse users if navigation does not follow a consistent logic. Pages without defined relationships result in breadcrumbs that skip or repeat levels. The inconsistent structures cause breadcrumb trails to break or mislead. Breadcrumbs depend on predictable webpage order to support user orientation.
How to Avoid Common Breadcrumbs Mistakes in SEO

Breadcrumb issues affect usability, crawlability, and rankings when structure, markup, or navigation roles are mismanaged. To avoid common breadcrumb mistakes in SEO, follow the steps listed below.
- Match Site Hierarchy. Breadcrumb paths must match the site’s structure. Each level needs to reflect a real content relationship. Avoid misplacing unrelated categories in the trail.
- Keep Design Simple. Breadcrumbs must stay readable and usable across devices. Use clear fonts and high-contrast colors. Prevent text overlap or squishing on mobile. Ensure clickable areas stay large enough for mobile tap targets.
- Use Correct Structured Data. Breadcrumbs need valid structured data. Use the BreadcrumbList schema with all required fields. Avoid missing fields, incorrect types, or duplicate breadcrumb paths on different pages.
- Limit Path Depth. The breadcrumb trails work best when short and clear. Limit the breadcrumb path to essential levels. Avoid excessive nesting or unnecessary subcategories that reduce clarity and clutter the webpage layout.
- Avoid Navigation Duplication. Breadcrumbs need to complement, not copy, the main navigation menu. Skip full menu repetition. Focus on showing the page’s location within the site hierarchy. Breadcrumbs help users orient, not navigate the full site structure.
- Show Hierarchy, Not History. Breadcrumbs must reflect site hierarchy, not individual browsing paths. Avoid mimicking the browser’s back button. Always show the shortest logical path from the homepage to the current page.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing. Breadcrumb text must stay descriptive and relevant. Overusing keywords makes breadcrumbs look spammy and trigger SEO penalties. Keep language natural and user-friendly.
- Fix Broken or Incorrect Links. Breadcrumbs must show accurate paths. Incorrect or outdated breadcrumb links confuse users and reduce SEO value. Regularly audit breadcrumbs and structured data to match the current site structure.
What is the difference between breadcrumbs and a sitemap?
Breadcrumbs and sitemaps both support navigation but operate in different areas of a website. Breadcrumbs display a user’s location within the content hierarchy using page-level paths like Home > Blog > Article. Sitemaps show the website’s full structure. They exist as XML for crawlers or HTML for user navigation. Use breadcrumbs for local orientation and sitemaps to list all key URLs in one place.
Where should breadcrumbs be placed on a page?
Place breadcrumbs just below the main navigation at the top of the page. This position keeps breadcrumbs visible and easy to access during browsing. Avoid placing them below the fold or inside secondary elements because visibility and usability decreases.
How many levels breadcrumbs need to show?
Breadcrumbs need to display 2 to 4 levels to reflect a clear path without cluttering the layout. Use the homepage as the first level only when there’s enough space. Shorten longer trails using an ellipsis to keep the design simple and focused.
What is the difference between breadcrumbs and faceted navigation?
Breadcrumbs show static navigation paths based on page hierarchy. Faceted navigation filters content based on selectable attributes. Breadcrumbs help search engines understand structure and improve internal linking. Faceted navigation creates custom views that cause indexing issues if left unmanaged. Use breadcrumbs to organize and facets to refine selections.