UGC (User-Generated Content) links are links that use the rel=”ugc” attribute to tell Google that users, not website owners, created the content containing these links. Google introduced this attribute in 2019 to better understand linking patterns. UGC links don’t pass significant link equity or boost SEO rankings, functioning similarly to nofollow links. Website owners should apply UGC attributes to links in comments, forum posts, reviews, and user profiles to distinguish user-generated content from editorial content and prevent spam-related penalties.
What Are UGC Links?
UGC (User-Generated Content) links are links marked with the rel=”ugc” attribute. This attribute tells Google that users created the content containing the link. Google introduced this attribute in 2019 along with rel=”sponsored” after changing how the nofollow attribute works. The company wanted to better understand linking patterns across the web.
The UGC attribute applies to user-generated content like comments, forum posts, and other areas where website visitors add content. Search engines use this signal to identify content that comes from users rather than site owners. Most websites don’t use rel=”ugc” as a standard practice. The attribute remains optional for webmasters who want to clearly mark user-generated links for search engines.

What Is the Difference Between UGC and Other Link Attributes?
UGC links differ from other link attributes (nofollow, sponsored) primarily in their purpose and who places them. The UGC attribute specifically tells Google that users created the content containing the link, not the website owner. This contrasts with the nofollow attribute, which website owners use for any link they choose not to endorse or want to prevent from passing link equity. While nofollow is applied to any link based on the site owner’s preference, UGC applies only when users generate the content.
The sponsored attribute serves a different purpose entirely, marking paid or commercial links rather than user-generated ones. All three attributes work together to give search engines clearer signals about link origins and intentions. UGC links function as nofollow links by default, meaning they don’t pass link equity or influence search rankings.
Google introduced this system in September 2019 after the original nofollow attribute became too broad and unclear. Before this change, nofollow covered advertisements, user-generated content, and untrusted links without distinction. The company split nofollow into three specific attributes to help search engines better understand link context, fight spam more effectively, and improve the accuracy of link evaluation across the web.
How Do UGC Links Affect SEO?
UGC links have minimal direct impact on SEO rankings. These links don’t pass significant link equity or authority to the linked pages, similar to nofollow links. Google treats UGC links primarily as signals rather than ranking factors.
Website owners use the UGC attribute on links within user-generated content like comments, reviews, and forum posts. This practice helps Google understand why these links exist and whether to include them in PageRank calculations. The attribute signals that users, not the site owner, placed these links.
Using UGC attributes provides protection against potential penalties. Comment sections often attract spammy links from people trying to manipulate search rankings through black hat SEO tactics. The UGC attribute helps distinguish legitimate user content from spam attempts. Google analyzes these attributes to detect patterns of unnatural linking behavior.
Google now treats link attributes as hints rather than absolute directives. This means the search engines still consider UGC links within its ranking systems in some cases. However, the primary benefit comes from proper categorization rather than direct SEO value. Sites use the standard nofollow attribute for user-generated links, which achieves similar results in most situations.
When Should You Use the UGC Attribute?
Use the UGC attribute on all links within user-generated content to help search engines understand that users, not the website owner, placed these links. This practice provides clarity about link origins and helps prevent potential spam-related penalties.
- Blog Comments. Add rel=”ugc” to any links users include in comment sections. This distinguishes user-added links from editorial links the site owner places within the main content.
- Forum Posts. Apply the UGC attribute to links within forum discussions, replies, and user signatures. Forums generate large volumes of user content that often contains links to external sites.
- Product Reviews. Use UGC attributes on links customers include in product reviews and testimonials. Users often link to related products, competitors, or their own experiences.
- User Profiles. Add the attribute to links users include in their profile pages, biographical sections, or personal information areas on social platforms and community sites.
- Guest Book Entries. Apply UGC to links visitors add to guest books, visitor logs, or similar interactive features where users leave messages.
- Community Submissions. Use the attribute for links within user-submitted articles, stories, photos, or other content contributions on community-driven websites.
How to Add A UGC Link Attribute
To add a UGC link attribute, edit the HTML code of your webpage. Insert the rel=”ugc” attribute directly into the link’s anchor tag. The steps for adding the attribute are listed below.
1. Locate the Target Link. Find the specific link in your user-generated content that needs the UGC attribute. This is linked in comments, reviews, or forum posts.
2. Access the HTML Code. Open your webpage’s HTML editor or content management system’s HTML view to see the underlying code structure.
3. Find the Link’s HTML. Look for the anchor tag that creates your link. It will appear as <a href="URL">Link Text</a> in the code.
4. Insert the UGC Attribute. Add rel=”ugc” inside the opening anchor tag, placing it after the href attribute but before the closing bracket.
We provide an example below.
- The code before adding UGC.
<a href="http://example.com">Link Text</a> - The code after adding UGC.
<a href="http://example.com" rel="ugc">Link Text</a>
5. Save Your Changes. Save the HTML file or publish your changes through your content management system.
The UGC attribute now tells search engines that users created this link rather than the website owner. The link functions normally for visitors but carries the proper signal for search engine crawlers.
How to Find UGC Links on a Website?
To find UGC links on yours or any other website, there are two methods. The first method is to examine the HTML code of the page using CTRL + F. UGC links have the rel=”ugc” attribute within its <a> tag. The second is to use SEO tools like the Search Atlas Site Explorer.
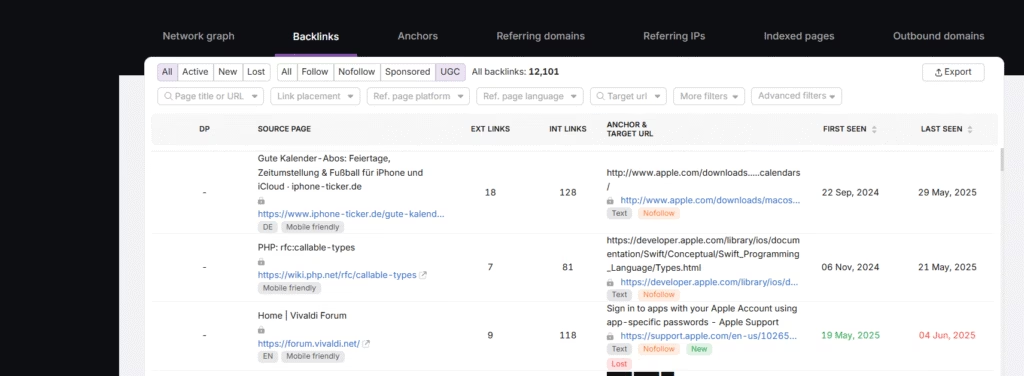
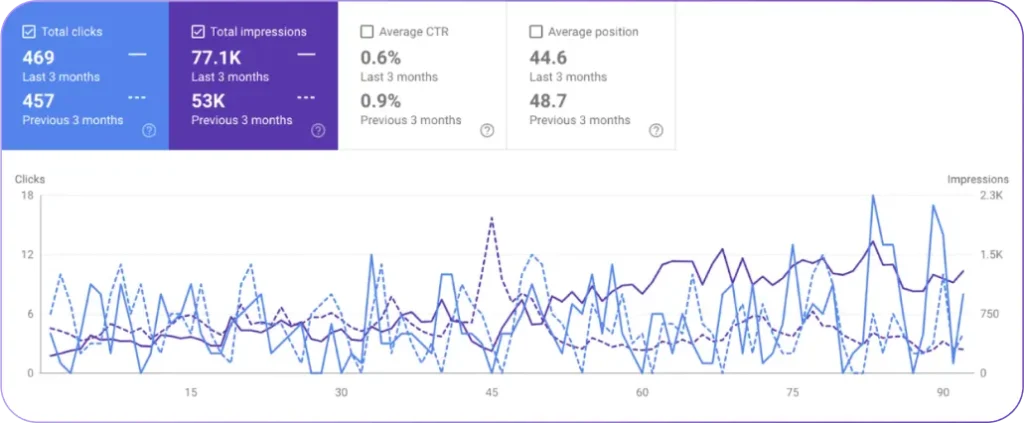
The Site Explorer displays all backlinks present on a site. It filters the links by nofollow, sponsored, and UGC attributes. It shows anchor text, target pages, and other relevant backlink information.
Optimize Your Link Strategy With Advanced SEO Tools
The strategic use of UGC attributes, combined with proper monitoring of your overall link profile, creates a foundation for sustainable SEO growth. UGC links themselves don’t directly boost rankings, but they’re a part of a transparent linking strategy that search engines appreciate.
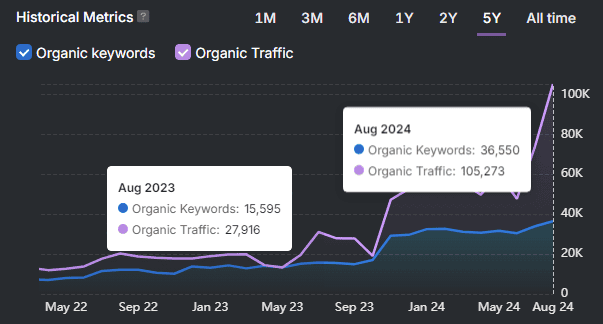
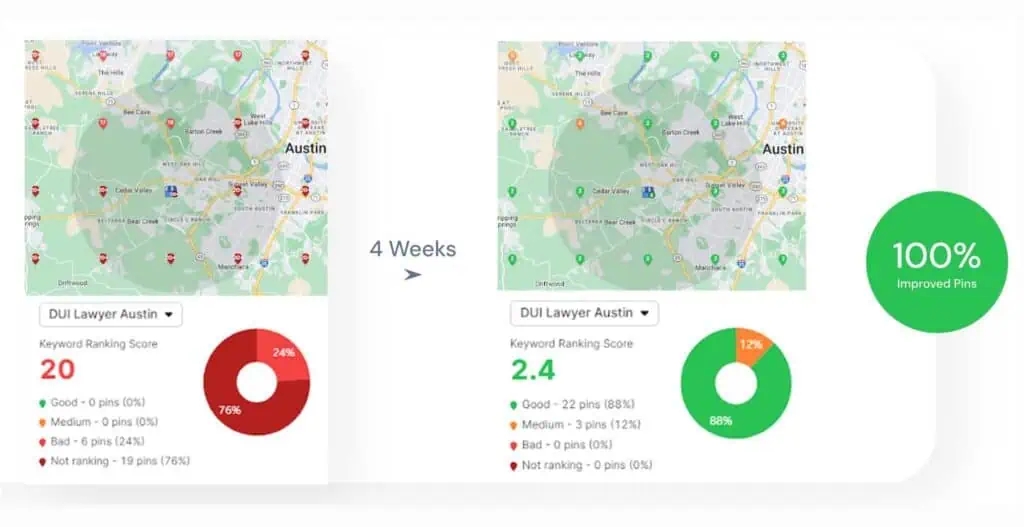
Professional SEO tools like Search Atlas provide comprehensive backlink analysis and management capabilities to elevate your link-building efforts beyond basic UGC implementation. Monitor your complete link profile, identify high-value linking opportunities, and build authoritative connections that drive real results. Start your free trial today and transform your approach to link management.