Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of structuring content so generative AI systems (ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and Gemini) extract, summarize, and cite it inside AI-generated answers. The GEO definition explains how modern search environments select sources for synthesized responses rather than ranking pages inside link lists.
GEO matters because search behavior now occurs inside systems that generate direct explanations instead of directing users to websites. Generative engines interpret questions, retrieve relevant information, and assemble answers from sources they trust. Brands gain visibility when their content becomes part of those generated answers, which replaces traditional rankings with citation-based exposure.
Generative Engine Optimization creates competitive advantages for brands operating in AI-mediated search environments. GEO increases the likelihood of being cited, strengthens entity recognition, and improves how brands are described inside informational responses. Visibility inside generated answers influences user trust earlier in the decision process, before purchase intent forms.
GEO requires structured information, explicit explanations, and consistent entity signals. Content optimized for generative engines presents clear definitions, organized topic coverage, and verifiable facts that AI systems can reuse across many answer contexts. Generative Engine Optimization aligns content with how AI systems retrieve, interpret, and synthesize information, which defines the current evolution of search visibility.
What Is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a search and content optimization framework that controls how generative AI systems interpret, select, and reference information inside AI-generated answers. GEO connects brand visibility to large language model (LLM) retrieval, which moves optimization away from rankings and toward being cited in AI answers.
GEO governs how conversational engines, AI search interfaces, and answer engines consume structured content, extract entities, and form authoritative responses. Brands use GEO to make sure their facts, definitions, and expertise appear directly inside generated outputs instead of remaining buried inside web pages.
GEO SEO operates across what systems? Generative Engine Optimization operates across conversational AI, AI-powered search, and answer engines. These systems generate responses by combining information from multiple sources and selecting authoritative entities and facts.
What does Generative Engine Optimization optimize in AI driven search? GEO optimizes how content becomes retrievable, citable, and reusable by LLMs during answer generation. GEO focuses on entity clarity, factual accuracy, and semantic alignment so AI systems select a brand as a trusted source.
GEO functions as the control system for brand visibility inside AI-generated answers. Users ask questions and receive synthesized responses, which means GEO determines whether a brand exists inside that response. This control defines what is GEO because modern search now happens inside synthesized responses rather than ranked lists of links.
Why Is GEO Important for Business Reputation Management?
GEO is important for business reputation management because AI-powered search systems summarize brands instead of sending users to websites. These summaries shape how audiences perceive credibility, reliability, and expertise before any direct brand interaction occurs.
The 6 main ways that GEO protects business reputation are listed below.
- Increases authority inside AI-generated answers. Generative Engine Optimization places brand information inside AI-generated summaries, explanations, and citations. This authority appears when users read synthesized answers, which establishes trust even without a website visit.
- Strengthens narrative control across AI systems. Generative Engine Optimization influences how AI systems describe a brand, its products, and its expertise. Consistent entity signals ensure that generated narratives reflect accurate positioning rather than fragmented or misleading interpretations.
- Improves resilience during reputation crises. Generative Engine Optimization reinforces verified sources when negative or incorrect information circulates. Strong authoritative signals reduce the likelihood that AI systems repeat misinformation in generated responses.
- Maintains entity consistency across digital properties. Generative Engine Optimization aligns websites, social profiles, press coverage, and knowledge bases into a single entity profile. This alignment gives AI systems a clear, unified representation of the brand.
- Preserves visibility in zero-click AI environments. Generative Engine Optimization keeps brands visible inside AI-generated answers even when users do not visit external websites. This visibility protects reputation in AI-first and answer-driven search experiences.
- Builds structured trust for AI interpretation. Generative Engine Optimization uses schema, Q and A formats, and factual layouts to provide machine-readable signals. These structures make brand information easier for AI systems to extract and verify.
What Are the Key Benefits of Optimizing a Business for Generative Engines?
The key benefits of optimizing a business for generative engines are stronger authority, broader exposure, and higher-quality demand from optimizing for generative engines. These benefits affect how brands appear inside AI responses, how users evaluate trust, and how demand converts in generative search environments.
The 5 key benefits that businesses gain from optimizing for generative engines are listed below.
1. Strengthens brand authority through AI citations. Generative Engine Optimization places brand information inside AI-generated answers through citations and paraphrased references. This placement confirms expertise at the moment users receive information, which increases trust and perceived credibility.
2. Expands reach across AI platforms. Generative Engine Optimization distributes brand content across ChatGPT, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and similar generative systems. This distribution increases exposure without requiring separate optimization for each platform.
3. Extends the lifespan of content. Generative Engine Optimization converts articles, pages, and data into reference material for AI models. These models reuse reliable sources across many answers, which sustains brand visibility long after initial publication.
4. Improves engagement from high-intent users. Generative Engine Optimization surfaces when users ask direct questions and expect direct solutions. These users arrive with defined needs, which increases the quality of engagement even when raw traffic volume is lower.
5. Preserves visibility in zero-click environments. Generative Engine Optimization keeps brands present inside AI-generated answers where users do not click links. This presence protects visibility as conversational and answer-based search replaces traditional result pages.
These benefits occur because GEO SEO places brands inside AI-generated answers rather than relying on page visits to communicate value. As AI systems summarize information for users, citation, wording, and source trust become more important than traditional rankings.
Is Generative Engine Optimization Different from Traditional SEO?
Yes, Generative Engine Optimization is different from traditional SEO, but GEO extends SEO instead of replacing it. GEO controls how AI systems interpret, summarize, and cite brand information, while SEO controls how web pages rank inside search results.
What is traditional SEO? Traditional SEO organizes web pages so search engines retrieve, rank, and display them in results lists. SEO works through indexing, ranking signals, and competition between pages. Higher-ranked pages receive more exposure because users click the links that appear near the top of the search results. This ranking process defines what is SEO and determines how websites gain visibility and traffic.
How do GEO results differ from SEO results for users? GEO results differ from SEO results for users because SEO presents a list of links to choose from, while GEO presents an AI-generated answer built from multiple sources. In SEO, success depends on whether a page earns a high ranking and receives clicks. In GEO, success depends on whether a brand or domain is selected, cited, and represented inside the generated response. A brand that appears as a trusted source inside an AI answer gains influence even when no website visit occurs.
How do SEO and GEO work together? SEO and GEO work together because SEO makes content discoverable and GEO makes that same content usable inside AI-generated answers. SEO ensures pages are crawled, indexed, and ranked. GEO ensures those pages provide the entities, facts, and context AI systems rely on when describing products, companies, and expertise.
How Does Generative Engine Optimization Actually Work?
Generative Engine Optimization works by shaping content so AI systems understand, trust, and reuse it inside their answers instead of treating it as just another ranked page. GEO turns brand information into structured knowledge that AI models select, summarize, and cite.
There are 6 main ways Generative Engine Optimization works.
1. Intent-driven interpretation. Generative engines analyze what a user wants to know rather than matching keywords. AI queries now average around twenty-three words, which signals deeper intent than short search phrases. GEO aligns content with questions, problems, and goals so AI models match information to the true purpose behind a request.
2. Multi-source synthesis. Generative engines pull data from many documents at once. These systems merge facts, explanations, and examples into one response. GEO structures content so it fits cleanly into this synthesis process. Clear definitions, focused sections, and factual writing increase the chance that AI models select a source for reuse.
3. Concept-level parsing. AI systems break content into entities, relationships, and conclusions. GEO organizes information so machines detect what a brand is, what it does, and why it matters. Content that explains concepts directly gives AI reliable material for answer generation.
4. Structured extraction. Generative engines look for clear blocks of meaning. GEO uses headings, short paragraphs, and schema markup to mark definitions, attributes, and supporting details. This structure reduces ambiguity and increases extraction accuracy.
5. Authority filtering. AI models prefer sources that show expertise and consistency. GEO strengthens topical coverage, aligns facts across pages, and connects information to trusted references. These signals raise the probability that AI systems treat a brand as reliable.
6. Answer readiness. GEO writes content in a format that fits AI outputs. Definitions, explanations, and supporting context appear in a sequence that mirrors how AI answers questions. This alignment makes it easier for generative engines to reuse information without distortion.
How Can Businesses Optimize Their Presence for Generative Engines?
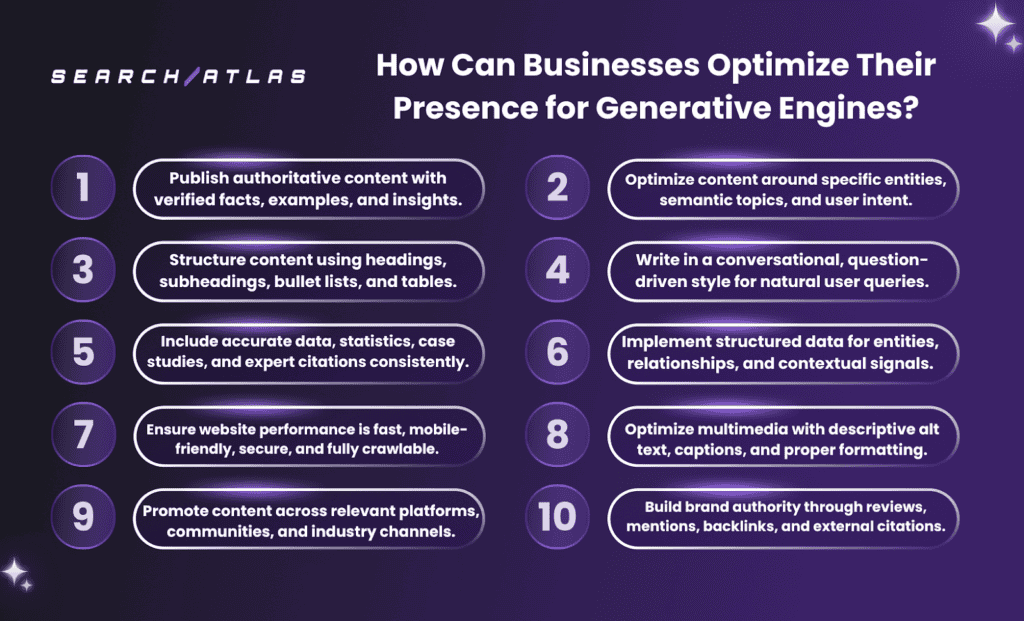
Businesses optimize their presence for generative engines by aligning content creation, information structure, and technical delivery with how generative AI systems interpret, retrieve, and synthesize information. Generative engines select sources based on semantic relevance, entity clarity, and factual consistency. Effective optimization improves inclusion, citation, and reuse inside AI-generated answers rather than rankings in link-based search results.
The 10 methods for businesses to optimize their presence for generative engines are listed below.
- Publish authoritative content with verified facts, examples, and insights.
- Optimize content around specific entities, semantic topics, and user intent.
- Structure content using headings, subheadings, bullet lists, and tables.
- Write in a conversational, question-driven style for natural user queries.
- Include accurate data, statistics, case studies, and expert citations consistently.
- Implement structured data for entities, relationships, and contextual signals.
- Ensure website performance is fast, mobile-friendly, secure, and fully crawlable.
- Optimize multimedia with descriptive alt text, captions, and proper formatting.
- Promote content across relevant platforms, communities, and industry channels.
- Build brand authority through reviews, mentions, backlinks, and external citations.
1. Publish Authoritative Content With Verified Facts, Examples, and Insights
Publishing authoritative content with verified facts, examples, and insights ensures that generative engines treat a brand as a reliable source when producing answers. Generative engines evaluate source reliability by comparing statements across multiple training and retrieval contexts, which makes factual consistency a primary selection factor. Content that contains precise definitions, documented statistics, and real-world examples provides stable reference material that AI systems safely reuse inside generated answers. A practical takeaway involves writing content that resolves questions directly in the opening sentences and supports every claim with information that remains accurate when reused inside an AI-generated answer.
2. Optimize Content Around Specific Entities, Semantic Topics, and User Intent
Optimizing content around specific entities, semantic topics, and user intent ensures that generative engines correctly identify what a brand represents and how its information fits within a broader subject. Generative engines organize knowledge by mapping entities and their relationships, which makes clear entity definition and consistent topic coverage essential for accurate representation. Content that connects products, services, and concepts within well-defined topical clusters provides the semantic depth that AI systems use to generate contextually relevant answers. A functional approach involves structuring content so that each page reinforces a clear entity and one primary topic aligned with a specific user intent.
3. Structure Content Using Headings, Subheadings, Bullet Lists, and Tables
Structuring content with headings, subheadings, bullet lists, and tables improves how generative engines locate and extract information from a page. Generative models process text in segments, which makes a hierarchical structure and clearly separated facts easier to identify and reuse. Content that presents definitions, comparisons, and processes in structured formats provides machine-readable patterns that support accurate answer synthesis. A practical takeaway involves organizing each section so that key points remain understandable when extracted independently inside an AI-generated response.
4. Write in Conversational, Question-Driven Style for Natural User Queries
Writing in a conversational, question-driven style means aligning content with how users phrase information requests in natural language. Generative engines process full questions and spoken-style prompts, which makes question-based structure a primary selection signal. Conversational phrasing improves answer extraction because AI systems map user intent to complete explanatory statements. Businesses write in this style by using headings that mirror real search questions and opening sections with direct answers. Clear question framing increases citation likelihood because models associate each question with a specific block of information. A practical takeaway involves structuring headings as natural questions and opening each section with a complete answer before expanding into supporting detail.
5. Include Accurate Data, Statistics, Case Studies, and Expert Citations Consistently
Including accurate data, statistics, case studies, and expert citations means supporting every claim with verifiable evidence. Generative engines evaluate factual confidence by comparing statements across multiple sources, which makes documented proof a core trust signal. Named experts, measured results, and clearly described studies increase reuse because AI systems prefer sources that demonstrate accountability and traceability. Businesses include these elements by publishing author credentials, linking to primary sources, and documenting research methods. Evidence-based content improves answer reliability because models deprioritize unsupported or vague claims. A practical approach involves publishing author credentials, linking to primary sources, and maintaining updated publication dates so AI systems associate the content with expertise and accuracy.
6. Implement Schema.org Structured Data for Entities, Relationships, and Context
Implementing Schema.org structured data for entities, relationships, and context means providing machine-readable definitions that describe what a page represents. Generative engines identify people, products, organizations, and topics by mapping entities and their attributes, which makes explicit markup a key interpretation signal. Structured data defines how entities relate to one another and supplies contextual properties that improve factual grounding during answer generation. Businesses apply structured data by marking articles, authors, products, organizations, and FAQs with standardized types and properties. Explicit entity markup increases answer accuracy because AI systems validate relationships and attributes through structured signals. A functional application involves applying Person, Organization, Product, and FAQ schema to pages that contain definitional or reference information.
7. Ensure Website Performance is Fast, Mobile-Friendly, Secure, and Fully Crawlable
Ensuring that a website is fast, mobile-friendly, secure, and fully crawlable means removing technical barriers that prevent AI systems from accessing content. Generative engines rely on the same crawling, rendering, and indexing pipelines used by search engines, which makes performance and accessibility foundational visibility factors. Pages that load quickly, render correctly on mobile devices, and serve content over secure connections provide stable input for AI extraction and reuse. Businesses maintain website performance by optimizing Core Web Vitals, enabling HTTPS, and allowing crawlers to access all critical resources. A practical application involves monitoring LCP, INP, and CLS metrics and resolving crawl or rendering errors across all devices.
8. Optimize Multimedia With Descriptive Alt-Text, Captions, and Proper Formatting
Optimizing multimedia with descriptive alt text, captions, and proper formatting means providing machine-readable descriptions for visual and audio content. Generative engines interpret images and videos by reading associated text fields, which makes descriptive labeling a primary understanding signal. Alt text and captions supply the context AI systems use to connect visuals to entities, actions, and topics during answer generation. Businesses provide this information by writing concise, specific descriptions that identify subjects, attributes, and intent. Clear media labeling improves answer accuracy because AI systems rely on surrounding text to interpret non-textual content. A functional application involves assigning alt text and captions that describe what appears in each asset rather than generic or empty placeholders.
9. Promote Content Strategically Across Platforms, Communities, and Industry Channels
Promoting content across platforms, communities, and industry channels means expanding where and how brand information appears online. Generative engines evaluate topical authority by measuring how frequently and consistently content appears across relevant digital environments. Distribution through industry-aligned channels reinforces semantic relevance and increases the number of signals that connect a brand to a subject area. Businesses achieve this by sharing content in professional communities, media outlets, and platforms that match their industry focus. Broad distribution increases citation likelihood because AI systems recognize widely referenced material as more authoritative. A practical application involves publishing and syndicating content within domain-specific networks rather than relying on a single website.
10. Build Brand Authority With Reviews, Mentions, Backlinks, and External Citations
Building brand authority with reviews, mentions, backlinks, and external citations increases how often generative engines recognize a brand as a credible source. Generative engines evaluate brand authority by measuring references across media, social platforms, and business databases, which makes third-party validation a primary trust signal. Editorial coverage, social discussion, and directory profiles provide the signals AI systems use to select brands for inclusion in generated answers. A working application involves targeting commercial editorial teams, maintaining an active platform presence, and securing reviews and listings on authoritative business directories.
Do Generative Engines Function the Same Way as Traditional Search Engines?
No, GEO search does not function the same way as traditional search engines. Traditional search engines show a list of web pages based on keywords and links, while generative engines create answers by pulling information from many sources.
Generative engines read a user question, find relevant information across the web, and combine that information into one written response. Traditional search engines instead show links and require users to open and compare pages themselves.
Generative engines focus on selecting the best answer rather than ranking pages. GEO search visibility depends on whether the content explains a topic clearly and accurately to be used inside an AI-generated answer. Traditional search visibility depends on where a page appears in the results list.
How Does GEO Optimization Differ From Large Language Model Optimization?
GEO Optimization and Large Language Model Optimization perform different functions inside AI systems. GEO controls how public AI search platforms cite and summarize brand information, while Large Language Model Optimization controls how a specific model ingests and applies data. This distinction separates visibility inside AI answers from accuracy inside an individual AI system.
What does GEO optimize inside generative search platforms? GEO optimizes structured, factual, and authoritative content so public AI systems (Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity) select and cite it when generating answers. These citations determine how brands appear inside AI-generated summaries and how often they are used to explain topics.
What does Large Language Model Optimization optimize? Large Language Model Optimization structures data so that one controlled model retrieves and uses information correctly. This process relies on grounding files, embeddings, JSON-LD, and private datasets that guide how a model produces responses inside closed environments.
GEO exists to influence how AI explains a brand to the public, while Large Language Model Optimization exists to ensure an AI system uses a company’s data correctly. GEO applies LLM optimization principles to generative search visibility, which makes it the public-facing layer of model-focused optimization.
How Can Generative Engine Optimization Be Integrated With Traditional SEO Strategies?
Generative Engine Optimization integrates with traditional SEO by aligning content, structure, and authority signals so the same pages perform in ranked search results and AI-generated answers. Integration requires semantically complete explanations, a clear information hierarchy, and factual signals that both search engines and generative systems evaluate during retrieval and synthesis.
Successful integration appears when ages that contain clear entity definitions, explicit explanations, and consistent facts remain usable by both systems. Search engines retrieve and rank those pages. Generative engines extract and reuse the same information to construct answers. Both systems depend on the same content assets, but they apply different retrieval and synthesis processes to determine visibility and presentation.
How Long Does It Typically Take for a Business to Optimize for Generative Engines?
A business typically sees early GEO visibility within 2 to 4 weeks, while stable generative authority forms over 6 to 12 months. Early visibility reflects initial citation eligibility, while long-term visibility reflects repeated reuse across many AI answers.
What happens during the first 2 to 4 weeks of GEO? The first two to four weeks produce initial AI citations because generative engines detect new structured and authoritative sources. These early references confirm that content entered the generative retrieval layer.
What happens during the next 3 to 6 months of GEO? The next three to six months increase source reuse across related prompts because generative engines test consistency and reliability. Repeated reuse raises citation frequency and strengthens brand presence inside AI answers.
Why does GEO require sustained time rather than instant results? GEO requires sustained time because generative engines validate accuracy through repetition and cross-source agreement. Authority grows only after the same sources appear across many independent answer contexts.
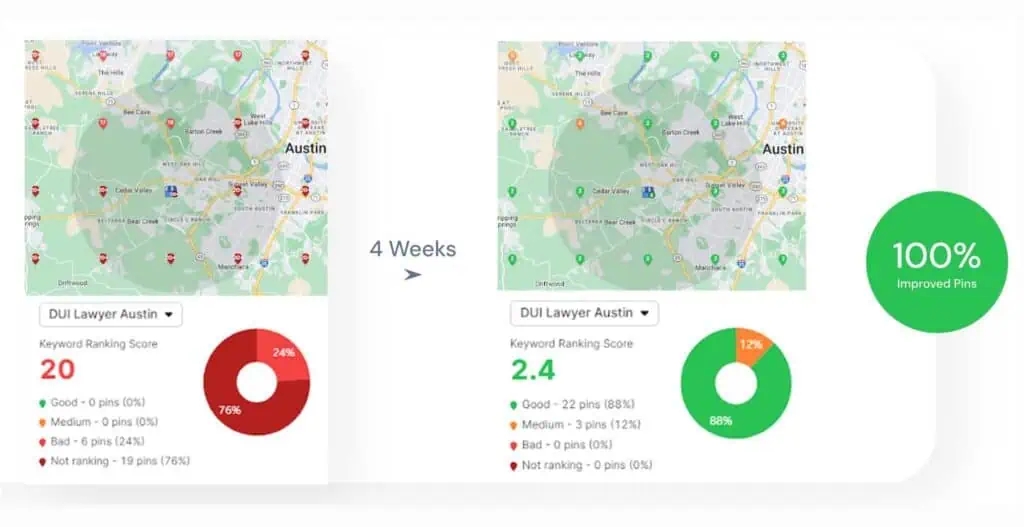
What Common Pitfalls Should Businesses Avoid That Reduce GEO Visibility?
The most common GEO visibility pitfalls are incomplete Google Business Profiles, inconsistent business data, incorrect category selection, weak reviews, and thin location content. Common pitfalls reduce GEO visibility because inaccurate business data, weak local optimization, and poor engagement signals confuse search engines and suppress local rankings.
How does an incomplete Google Business Profile reduce GEO visibility? An incomplete or unverified profile limits map pack exposure and AI location trust because missing hours, services, categories, and images prevent platforms from confirming business legitimacy.
Why does inconsistent Name, Address, and Phone data reduce GEO visibility? Inconsistent NAP fragments entity recognition across directories and platforms, which causes Google Maps and LLMs to treat one business as multiple entities and lower ranking confidence.
How do incorrect business categories reduce GEO visibility? Incorrect or overly broad categories break relevance between a business and local search intent, which prevents geo-based matching even when location and services are correct.
Why do weak reviews and engagement reduce GEO visibility? Low review volume, negative sentiment, and missing responses weaken prominence signals that both Google and AI systems use to rank and recommend local businesses.
How does thin or generic location content reduce GEO visibility? Pages that do not connect services to cities and neighborhoods fail to rank for geo-modified searches and fail to qualify for AI-driven local answers.
How Often Should Businesses Update Content for GEO Effectiveness?
Businesses need to update GEO content continuously based on real-world changes, search performance, and industry activity rather than on a fixed calendar. Generative Engine Optimization depends on freshness, accuracy, and location alignment, so content must evolve whenever services, competitors, or user intent change.
How often should evergreen GEO content be updated? Evergreen pages require updates every 6 to 12 months because service details, examples, competitors, and local search behavior shift even when the topic stays stable.
How often should trend-based or time-sensitive GEO content be updated? News, events, and seasonal content require monthly or weekly updates because AI systems and local SERPs prioritize the most recent information for geo-based queries.
How often should product and service pages be updated for GEO? Product and service pages require immediate updates whenever pricing, features, locations, or availability change because outdated information breaks trust signals for Google Maps and AI retrieval.
How often should statistical and research-based GEO content be updated? Data-driven content requires updates whenever new research or metrics appear because LLMs evaluate factual freshness before selecting sources for answers.
Why does update frequency affect GEO performance? AI search engines and local ranking systems use freshness and accuracy to confirm business reliability, which determines whether a brand appears in geo-based search and AI-generated responses.
Can AI Tools Effectively Help Businesses Optimize for Generative Engines?
Yes, AI tools effectively help Generative Engine Optimization by analyzing language patterns, entities, and semantic relationships that generative engines use to select sources. Generative engines evaluate topic coverage, factual accuracy, intent alignment, and entity consistency rather than keyword frequency.
AI tools improve GEO by generating structured drafts that cover topics, subtopics, and user questions in formats that generative engines extract during answer synthesis. These drafts reflect the patterns that AI systems prefer when building responses.
AI tools improve intent modeling by clustering related queries and mapping how questions appear inside ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. AI tools align content with real user prompts instead of keyword fragments.
Automation improves GEO by applying schema, refreshing internal links, and correcting technical gaps that prevent AI retrieval. Generative engines select sources that remain structured, accurate, and machine-readable.
Which AI Tools Are Best for Optimizing and Tracking Visibility Across Generative Engines?
The best AI tools for optimizing and tracking visibility across generative engines measure citation frequency, brand presence, and competitive exposure inside AI-generated answers. The 5 best AI tools for GEO are Search Atlas, Writesonic, Profound, Peec AI, and LLMrefs.
1. Search Atlas. Search Atlas tracks brand visibility across generative AI platforms (ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and Claude). Search Atlas measures how often a brand appears, how it is described, and which competitors displace it inside AI-generated answers. Search Atlas connects GEO with content, SEO, and technical optimization workflows, which enables execution from one system. This execution focus makes Search Atlas the most complete platform for Generative Engine Optimization.
2. Writesonic. Writesonic tracks visibility across major generative engines and provides an Action Center focused on content fixes. Writesonic emphasizes cross-engine tracking, AI crawler analytics, and an integrated SEO toolkit that supports GEO execution after visibility changes appear. Writesonic fits teams that want monitoring plus guided remediation in one workflow.
3. Profound. Profound monitors brand citations across multiple AI systems and identifies which queries and topics trigger visibility. Profound surfaces where brands appear, how often brands are referenced, and which competitors displace them inside generative answers. Profound emphasizes large-scale monitoring and prompt-level analysis, which fits organizations focused on coverage and diagnostics.
4. Peec AI. Peec AI tracks brand and competitor mentions, sentiment, and visibility across major generative models (ChatGPT and Gemini). Peec AI provides prompt analytics, benchmarking, and customizable reporting via Looker Studio. Peec AI fits teams that prioritize dashboards and competitive reporting over execution tooling.
5. LLMrefs. LLMrefs tracks GEO visibility with a keyword-first methodology and multi-model share of voice reporting. LLMrefs adds AI crawlability checks and API access, which supports teams that want structured reporting, technical validation, and integration into internal analytics stacks. LLMrefs fits teams that manage GEO measurement through keyword sets and repeatable reporting.
Among available GEO tools, Search Atlas LLM visibility feature provides the most complete GEO workflow because it combines multi-engine visibility tracking with execution pathways that connect insights to content and technical updates.
How Much Does It Cost For Businesses To Optimize For a Generative Engine?
Businesses typically spend $2,000 to $5,000 per month for small GEO programs and $10,000 or more for enterprise programs because generative engines require continuous content validation and entity coverage. Lower-cost GEO options range from $150 to $1,000 for freelancers or small projects that focus on prompt testing, limited schema, and content updates.
Search Atlas offers a lower-cost way for businesses to optimize for GEO. Businesses start optimizing for both traditional SEO and GEO through Search Atlas plans starting at $99 per month, or test the full platform through a 7-day free trial. Search Atlas pricing model allows brands to enter GEO search without the overhead of agency retainers or custom AI engineering.
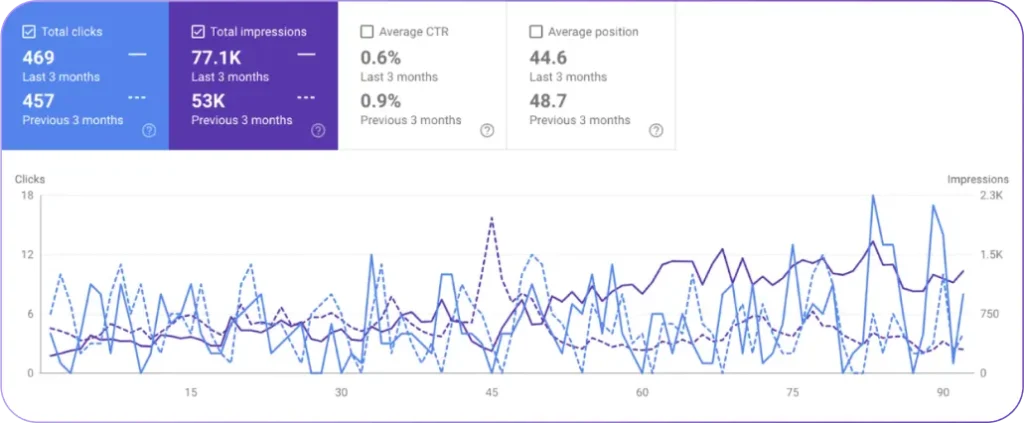
What Metrics Should Be Tracked to Evaluate GEO Effectiveness?
The most important GEO metrics of generative search performance are AI share of voice, sentiment, and competitive visibility because generative engines select brands based on presence, perception, and relative authority inside AI-generated answers.
AI share of voice measures how often a brand appears across large language models for a specific topic or query. Higher appearance frequency indicates stronger discoverability inside generative search results.
Sentiment measures how AI systems describe a brand when it appears in answers. Positive, neutral, or negative language influences whether users trust and select a brand from AI-generated recommendations.
Competitive visibility compares how often a brand appears against rivals for the same intent clusters over time. Trend data shows which brands dominate affordability, feature, or enterprise queries, which reveals shifts in authority inside generative engines.
These 3 metrics define GEO performance by showing whether a brand appears, how it is described, and how it compares to competitors inside AI-generated answers.
How Do Brand Authority and External Citations Affect GEO Results?
Brand authority and external citations affect GEO results because generative engines select and cite businesses they recognize as reliable and widely referenced. AI systems evaluate whether a brand appears consistent, relevant, and trusted before using it in AI-generated answers.
Brand authority increases GEO visibility through repeated mentions across websites, media, reviews, and industry sources. These signals strengthen entity recognition, which makes a brand safer for AI systems to reference.
External citations confirm business identity by repeating the same name, location, and service context across the web. These references allow AI systems to verify that a business exists and operates in a specific market.
Strong and consistent citations raise the likelihood of appearing inside ChatGPT, Gemini, and AI Overviews. Weak or fragmented citations reduce GEO performance by creating uncertainty around brand legitimacy.
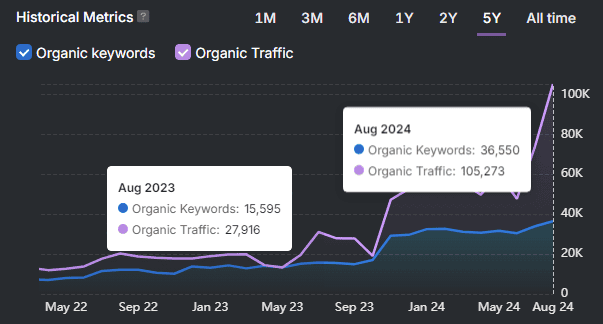
What Are Emerging Trends in GEO That Businesses Should Prepare For?
The main emerging GEO centers on entity clarity, real-time validation, multimodal visibility, and AI-driven authority scoring. Generative engines increasingly select brands based on how clearly they understand who a business is, what it offers, and how trustworthy it appears across text, images, and structured data.
Current patterns show that structured and succinct content now drives retrieval inside generative search. AI systems favor pages that present information in clearly defined sections, factual statements, and machine-readable formats that allow accurate summarization and citation.
Generative engines are expanding beyond text to integrate visual signals, live data, and cross-platform references. Brands that maintain consistent entity definitions and update-ready content across formats gain stronger and more durable visibility as AI-generated answers replace traditional ranking-based discovery.