To get an SEO job, follow these 7 steps: learn basics, get certifications, master SEO tools, develop specializations, gain experience through internships or freelancing, create portfolios, and apply for jobs. We cover essential SEO job skills, including technical SEO, tools, and WordPress knowledge.
What Are the Important Skills for SEO Jobs?
We explain the most important skills for getting a job in SEO below.
- SEO Fundamentals. Understand how search engines work and rank websites. Learn keyword research, on-page optimization, and content strategy. Study search engine algorithms and ranking factors. Master the basics of HTML, meta tags, and URL structure.
- Technical SEO. Learn how to audit websites for technical issues that affect search rankings. Learn about site speed optimization, mobile responsiveness, and crawlability. Understand XML sitemaps, robots.txt files, and structured data markup. Fix broken links, duplicate content, and indexing problems.
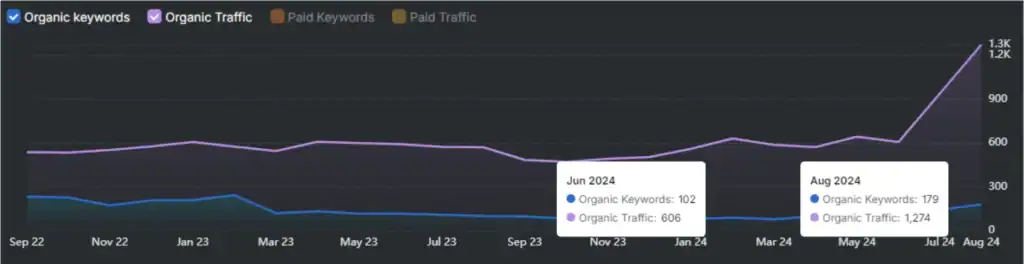
- Google Sheets. You use spreadsheets in SEO work to track keyword rankings, organize content calendars, and analyze data. Learn formulas and data visualization techniques.
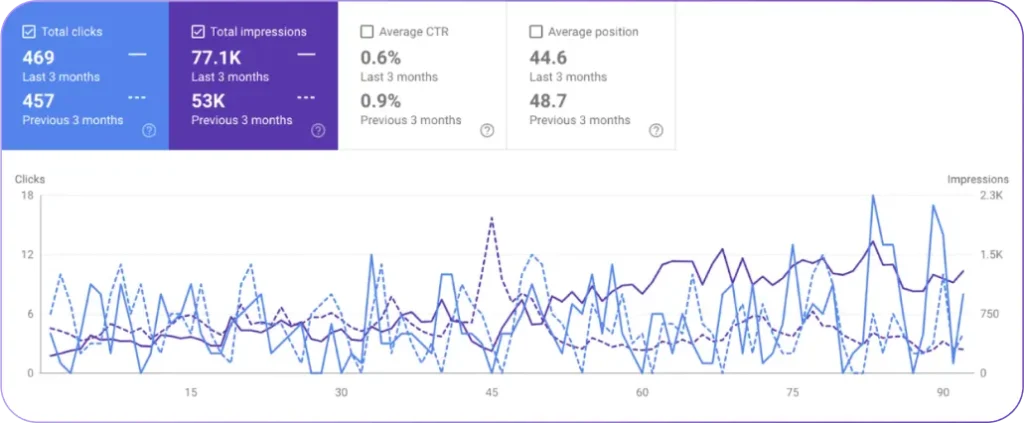
- SEO Tools. You work with various software platforms to research and analyze. Master tools like Search Atlas, Google Analytics (GA4), and Google Search Console (GSC). Learn how to extract insights from data and create actionable recommendations. Understand which metrics matter most for different SEO performance objectives.
- Knowledge of WordPress. You optimize many websites that run on WordPress. Learn how to install and configure SEO plugins like Yoast or RankMath. Understand theme structure, permalink settings, and site architecture. Learn how to make technical changes without breaking websites.
Additional useful skills differentiate you from the rest of the candidates. Optional skills help SEOs who are just entering the job market land freelancing or small agency jobs.
- Social Media Marketing. Learn how social signals affect search rankings. Study platform-specific best practices and content formats. Practice building audiences that drive traffic to websites.
- Project Management. You coordinate SEO campaigns with multiple team members. Learn planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. Study communication tools and workflow management. Practice managing deadlines and deliverables.
- Content Creation. You write blog posts, landing pages, and marketing copy. Learn how to create content that ranks well and converts visitors. Study content formats like guides, listicles, and case studies. Practice writing engaging and optimized website headings.
- Design Skills. You create visual content that enhances your SEO efforts. Learn Canva, Figma, or Adobe Creative Suite basics. Study graphic design principles like color theory and typography. Practice creating infographics, social media graphics, and featured images.

What are the 7 Steps for Getting a Job in SEO?
We list the steps for getting a job in SEO below.
1. Learn the Basics
You start your SEO journey by understanding fundamental concepts and terminology. Read beginner guides that explain how search engines discover, crawl, and index websites. Study the difference between organic and paid search results. Learn what keywords are and why they matter for website visibility.
Follow a structured SEO learning roadmap that covers essential topics in logical order. Begin with search engine basics, then move to keyword research, on-page optimization, and content strategy. Practice identifying ranking factors and understanding algorithm updates. Complete online courses or certifications that provide comprehensive training.
Your SEO education continues beyond initial training after you feel comfortable with basic terminology. You need to develop practical skills that complement your theoretical knowledge. Apply what you learn to real websites and projects. Stay updated with industry changes and algorithm updates that affect search rankings. It’s easiest to start with an SEO beginner’s guide.
2. Get Certifications
You validate your SEO knowledge through structured certification programs that demonstrate expertise to employers. Enroll in reputable courses that cover comprehensive strategies and practical applications. Complete assessments that test your understanding of core concepts.
Take the Google SEO course and official training programs that search engines provide. Study Google Search Central documentation and complete its SEO fundamentals training. Learn directly from companies that create the algorithms you optimize for.
Consider specialized programs like the Search Atlas SEO course that focus on advanced techniques. Research which certifications employers value most in your target market. Display certificates on professional profiles after you earn them.
3. Learn How to Use SEO Tools
You need specialized software to execute SEO strategies effectively and measure results. Master different tool categories that address specific aspects of search optimization. Practice with both free and premium platforms to understand their capabilities and limitations.
- Link Building Tools. You use these tools to identify link opportunities, manage outreach campaigns, track your backlink profile, and monitor competitor link strategies. These tools also automate prospecting and follow-up communications.
- Site Audit Tools. You use these tools to discover technical issues that prevent search engines from crawling and indexing your website properly. These tools identify broken links, duplicate content, page speed problems, and generate comprehensive reports that prioritize fixes by impact.
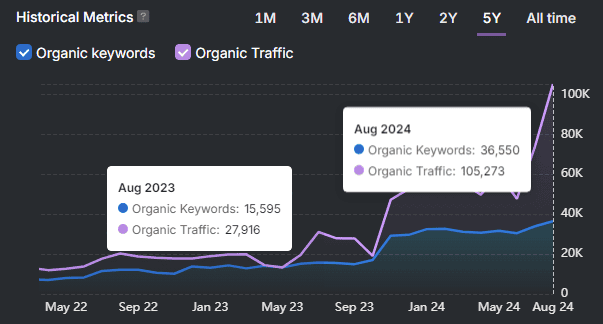
- Online Keyword Research Tools. You use these tools to find search terms that your target audience uses to discover content. These tools analyze search volume, competition levels, keyword difficulty scores, and discover long-tail variations with related phrases.
- Content Analysis Tools. You use these tools to optimize existing content and plan new pieces that rank well. These tools analyze top-performing pages for target keywords, identify content gaps, and measure readability with semantic relevance.
- Automated Internal Linking Tools. You use these tools to create connections between pages on your website that distribute authority and improve navigation. These tools identify orphaned pages, suggest relevant linking opportunities, and track internal link structure with anchor text distribution.
- SEO Monitoring Tools. You use these tools to create professional reports that communicate results to clients and stakeholders. These tools combine data from multiple sources into dashboards, track key performance indicators, and schedule automated reports that save time.
4. Acquire Specialized Skills
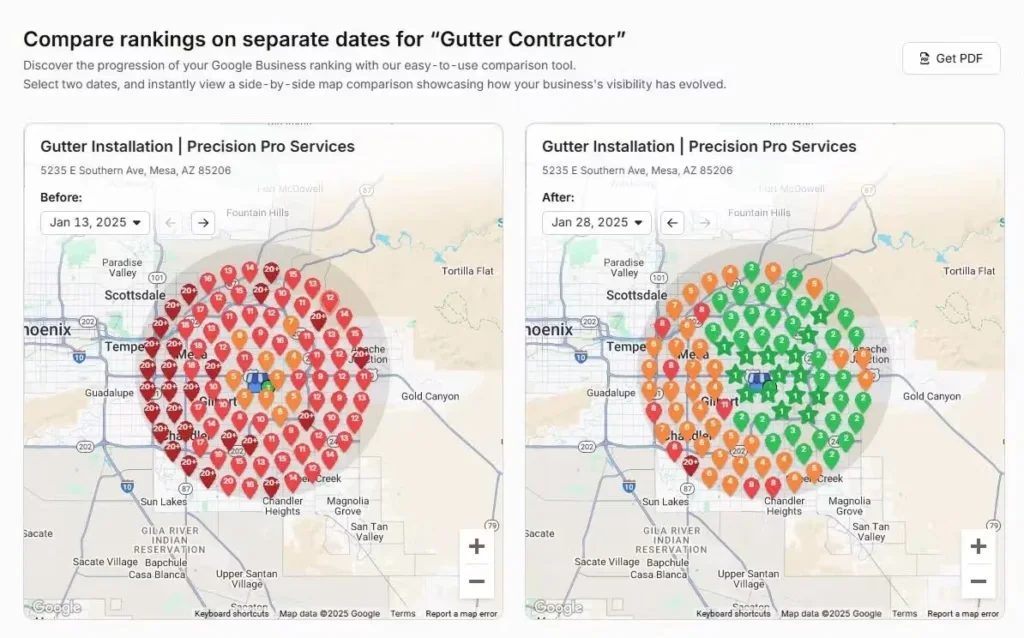
Develop expertise in specific SEO areas that match your career goals and target industries. Focus on specializations that have high demand in the job market. Master one or two areas deeply rather than learning all specializations superficially. Becoming an expert in a specific SEO field increases your job market value. We list some examples below.
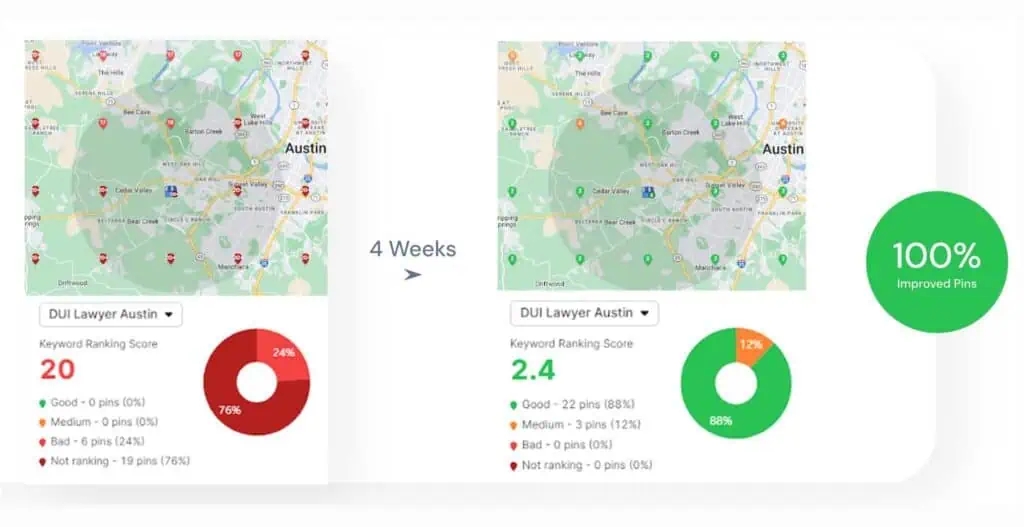
- Local SEO. Local SEO is the practice of optimizing businesses for geographic searches and “near me” queries. You manage Google Business Profiles (GBP), build local citations, collect customer reviews, and target location-specific keywords.
- Content Marketing. Content marketing is the strategy of creating and promoting content that attracts organic traffic and builds brand authority. You develop content strategies, create editorial calendars, conduct topic research, and distribute content across multiple channels.
- Ecommerce SEO. Ecommerce SEO is the optimization of online stores to increase product visibility and sales through search engines. You optimize product pages, structure categories, implement schema markup, and manage large-scale websites with thousands of pages.
- International SEO. International SEO is the process of helping websites rank in multiple countries and languages through technical implementations. You implement hreflang tags, manage country-specific domains, adapt content culturally, and handle complex site architectures.
5. Get Experience
Gain practical SEO experience through various opportunities that build your skills and create resume content. We list some suggestions below.
- Internship. Internships provide structured learning environments where you work alongside experienced SEO professionals. You handle real client projects, learn industry workflows, and build professional networks that lead to full-time opportunities.
- Freelancing. Freelancing allows you to work with multiple clients while building a diverse portfolio of results. You set your own rates, choose projects that interest you, and develop business skills alongside technical expertise.
- Launching Your Own Website. Launching your own website gives you complete control over SEO experiments and strategy implementation. You test different SEO techniques, track long-term results, and demonstrate your ability to grow organic traffic from zero.
- Helping Friends and Family Helping friends and family provides low-pressure opportunities to practice your skills on real businesses. You optimize local businesses, personal blogs, or small e-commerce sites while building case studies.
- Volunteering. Volunteering for nonprofits or community organizations creates meaningful portfolio pieces while supporting good causes. You help organizations increase their online visibility and impact while gaining experience with different industries.
5. Create a Resume With a Portfolio
Showcase your SEO skills and experience through professional documentation that attracts employers. Build materials that demonstrate your practical knowledge and results. Present your qualifications in formats that hiring managers expect.
- SEO-Focused Resume. An SEO-focused resume highlights your technical skills, certifications, and measurable achievements. List specific tools you mastered and campaigns you managed.
- Case Study Portfolio. A case study portfolio documents real projects with before-and-after results. You explain your strategy, implementation steps, and measurable outcomes like ranking improvements or traffic growth.
- Professional Website. A professional website serves as your online presence and demonstrates your SEO abilities. You optimize your own site to rank for relevant keywords while showcasing your expertise.
7. Look for a Job In the Right Places
Target entry-level roles that match your skill level and specialization areas. Look for an SEO job in ways listed below.
- Job Boards. Job boards list current openings at companies actively hiring SEO specialists. You search platforms like Indeed, LinkedIn, and specialized marketing job sites for relevant positions.
- Networking. Networking connects you with professionals who share job opportunities and provide referrals. You attend industry events, join SEO communities, and engage with experts on social media platforms.
- Direct Applications. Direct applications involve reaching out to companies you want to work for even without posted openings. You research target companies, find hiring managers, and pitch your value proposition directly.
Learn More About SEO With Search Atlas
Getting your first SEO job requires dedication and consistent practice. You build foundational skills, gain certifications, master essential tools, and create compelling portfolios that demonstrate results. Test Search Atlas tools for free for 7 days since they provide everything you need for SEO work in one comprehensive platform. Cancel anytime.