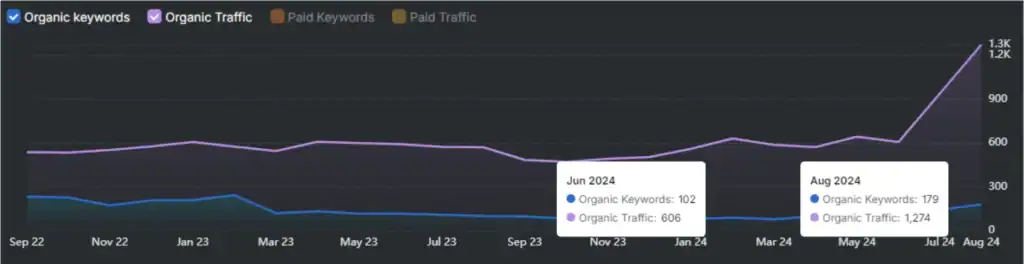
Analyzing SERP competitors’ ranking reveals key insights to improve SEO performance. This analysis identifies keyword gaps, tracks ranking shifts, and studies backlink profiles.
It exposes opportunities that other marketers miss. Using these strategies helps refine content, outrank competitors, and attract targeted traffic. Competitor analysis replaces guesswork with clear data and supports smarter decisions.
Keep reading to learn methods that boost SEO results and grow online presence. 🚀
What Is SERP Competitor Analysis?
SERP competitors ranking analysis is the practice of studying search engine results pages (SERPs) to discover top-ranking pages and what makes them rank.
SEO teams use this data to adjust strategy, close keyword gaps, and match or exceed top results. Marketers inspect title tags, descriptions, structured data, and SERP features that support high rankings. This method focuses on tracking rank shifts, comparing domain strength, and aligning content with user intent.
How Does SERP Analysis Work?
Search engines treat every query as a dynamic contest. Search engines compare content structure, topical authority, page speed, backlinks, and on-page SEO.
The factors that shape this competition are listed below.
- Keyword Types. Short-tail keywords trigger broader competition. Long-tail keywords lead to more specific, often lower-volume SERPs. Each type draws different competitors.
- Audience Behavior. The intent behind the keyword (transactional, informational, navigational) decides which pages rise. Competitors that match intent more closely win higher positions.
- Location. Google localizes results. Users in different regions see different SERPs for the same keyword. Local businesses, service providers, and region-specific content often outrank global pages near the user.
Understanding how competitors win visibility gives you the edge to build better content and claim more clicks.

How to Analyze Your SERP Competitors Ranking
SERP competitor analysis reveals the patterns behind top results and helps shape a smarter SEO strategy. Start with a clear view of who outranks you and why. We will list 6 strategies below.
1. Conduct Keyword Research
Begin by selecting the right keywords. Use the Keyword Research tool in Search Atlas to check search volume, keyword difficulty, and search intent. Depending on your Domain Power, it is easier or harder to rank for the given keyword.
Choose lower-difficulty terms in the short term. For example, target “affordable wedding venues in Austin” instead of just “wedding venues.”
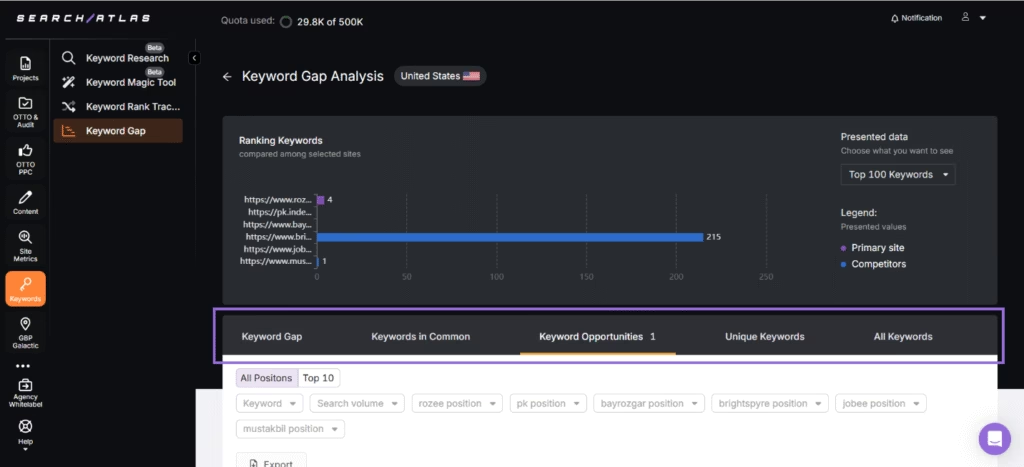
Next, open the Keyword Gap tool. Add your client’s domain and up to five competitors. Find keywords competitors rank for that your client misses. The Keyword Gap Tool shows you the categories listed below.
- Keyword Gap. Keywords all competitors rank for, but the primary site does not.
- Keywords in Common. Keywords that all sites rank for.
- Keyword Opportunities. Keywords one or more competitors rank for, but the primary site does not.
- Unique Keywords. Keywords primary site ranks for, but competitors do not.
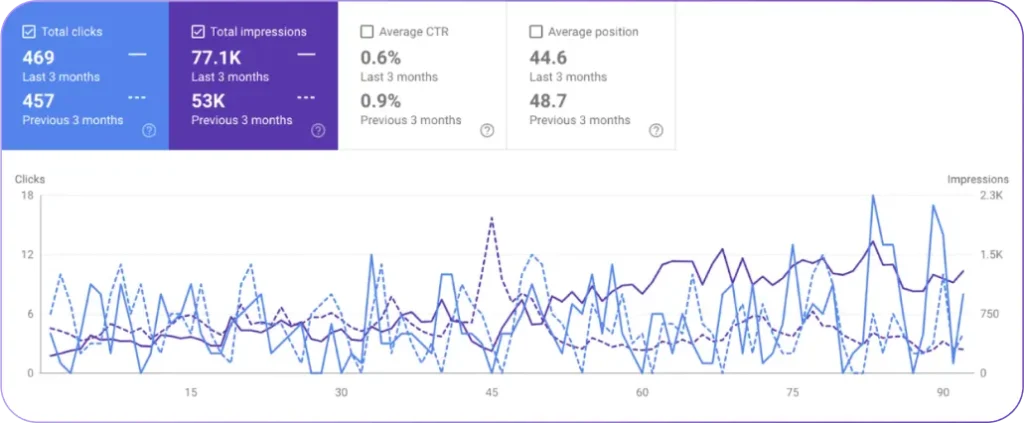
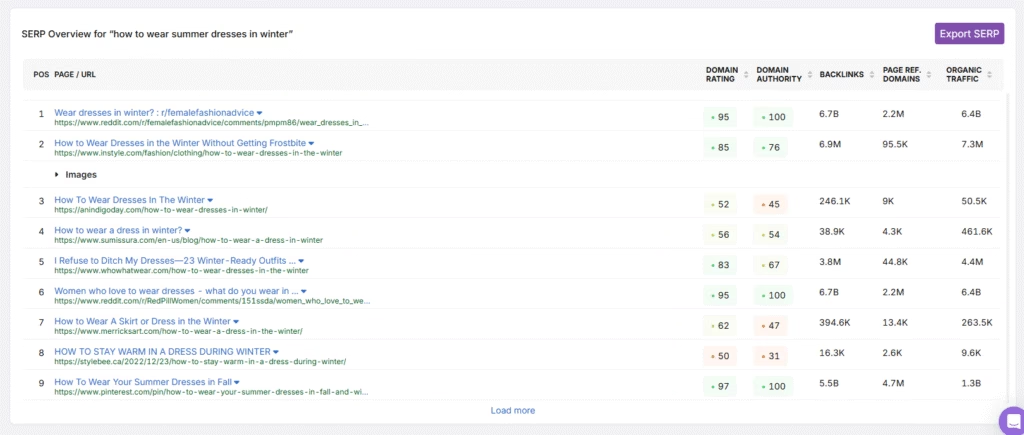
Then, open the SERP data for those keywords. The SERP Overview shows the metrics listed below.
- Domain Authority (DA). Estimates a domain’s overall ranking potential based on its backlink profile and trust signals. Higher DA sites often rank more easily.
- Domain Rating (DR). Measures a domain’s backlink strength on a scale from 0 to 100. A higher DR signals stronger link authority across the entire site. Understand Domain Rating vs. Domain Authority.
- Backlinks. Counts the number of inbound links pointing to a specific page or domain. A higher number shows stronger page credibility.
- Referring Domains. Shows how many unique websites link to a page or domain. More unique sources usually indicate better link diversity and authority.
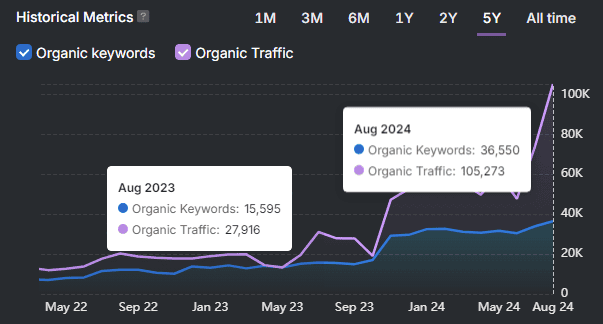
- Organic Traffic. Estimates how many users visit a page or domain through unpaid search results. Higher traffic suggests better visibility and engagement.
2. Determine Search Intent
Search intent is the reason behind a user’s query. It is what the user wants to find, learn, or do after entering a keyword in a search engine.
Common types include informational (looking for answers), navigational (seeking a specific site), transactional (ready to buy), and commercial investigation (researching before a purchase). Understanding search intent helps match content with user needs more precisely.
The Keyword Research Tool in Search Atlas identifies the dominant search intent for each keyword. In the Keyword Overview, you review the search or keyword intent behind top-ranking competitor pages.
This insight shows whether users want blog content, product pages, or service information, so you align your SEO strategy with what searchers expect to find.
3. Identify Your Top Competitors
Top competitors shape the landscape around your target keywords. Identifying them early helps you direct your SEO and PPC strategy where it delivers results.
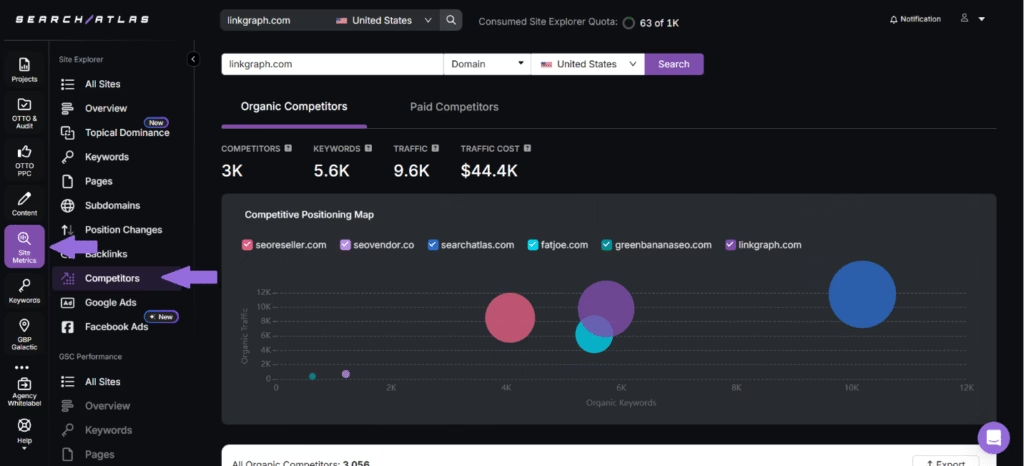
Use the Search Atlas Site Explorer tool to uncover both paid and organic competitors. Open the Competitors tab to compare domains with keyword overlap and visibility.
For organic competitors, the report shows the metrics listed below.
- Competition Level. Scores competition strength based on shared keyword count.
- Common Keywords. Shows how many top 20 organic keywords overlap between both domains.
- Search Engine Keywords. Shows the total number of keywords bringing users to a given domain via top 100 organic search results.
- Traffic. Estimates monthly search visits through organic search.
- Traffic Cost. Estimates the value of traffic.
For paid competitors, the report shows metrics listed below.
- Competition Level. Measures paid visibility and keyword overlap.
- Common Keywords. Highlights shared paid keywords.
- Traffic. Estimates monthly visits from paid search.
- Traffic Cost. Calculates total ad spend value for that traffic.
- Paid Keywords. Shows total keywords a given domain is buying in Google Ads.
This data helps you understand who ranks, how they rank, and how much their presence influences the SERP.
4. Analyze Their Backlink Profiles and Other Metrics
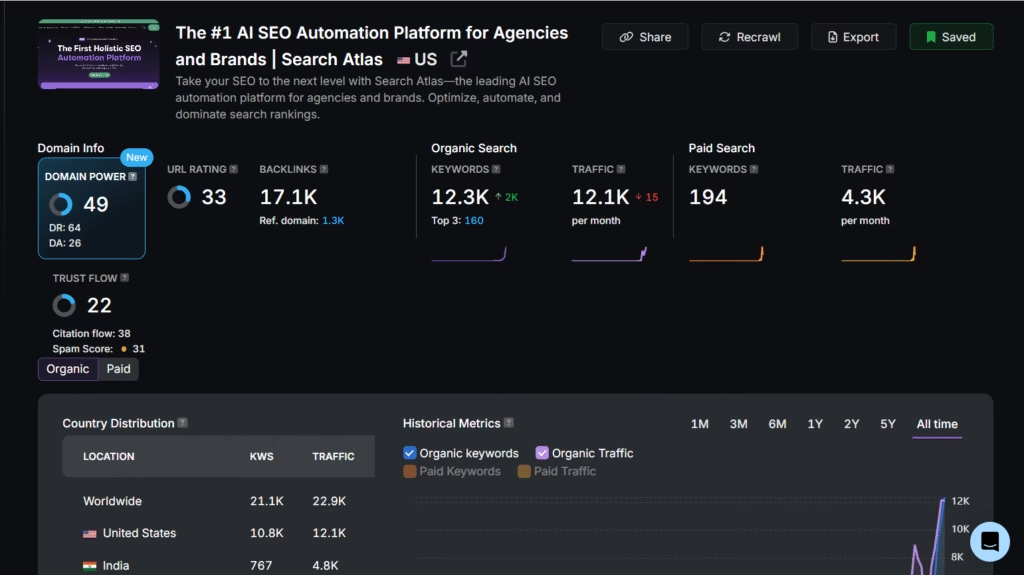
After you identify top competitors, analyze their full SEO profiles to understand what gives them an edge in the SERPs. The Site Explorer tool in Search Atlas provides a detailed view of their organic and paid strategies.
Here are some of the core metrics the tool displays.
- URL Rating. Measures the strength of a specific page based on link data.
- Backlinks. Shows the total number of external links pointing to a domain or page.
- Referring Domains. Unique domains linking to the competitor’s site.
- Trust Flow. Evaluates the quality of backlinks based on source trust.
- Citation Flow. Measures backlink volume, regardless of quality.
- Spam Score. Assesses link profile health and potential penalties.
This data helps you understand the strength and diversity of a competitor’s link profile. A high number of quality backlinks and referring domains usually signals strong authority and trustworthiness.
Competitors with strong authority signals and backlink profiles are typically more difficult to outrank.
Site Explorer shows more organic metrics in detail but these are the key metrics for SERP analysis. Key metrics are listed below.
- Organic Keywords. Keywords delivering traffic through Google’s organic search.
- Top 3 Rankings. Number of keywords ranking in the top 3 positions.
- Organic Traffic. Number of monthly visitors from organic search.
Together, these metrics highlight which keywords attract the most attention and where there are opportunities to compete effectively.
The metrics for paid strategy that show in the quick overview of competitors are listed below.
- Paid Keywords. Number of keywords triggering paid ads.
- Paid Traffic. Visit from PPC campaigns.
These metrics reveal competitors’ paid strategy strength, budget focus, and opportunities to optimize your own campaigns. They are essential for all SERP competitor research tools.
6. Analyze Different SERP Features
SERP features are special elements that appear on Google’s search results pages beyond the standard organic listings. SERP features appear above or alongside the usual links. SERP features help your pages get more organic traffic even if they don’t rank #1 in the traditional list.
The most common SERP features SEOs focus on are listed below.
- Featured Snippet. A summary box at the top of search results, showing a direct answer to the query taken from a webpage.
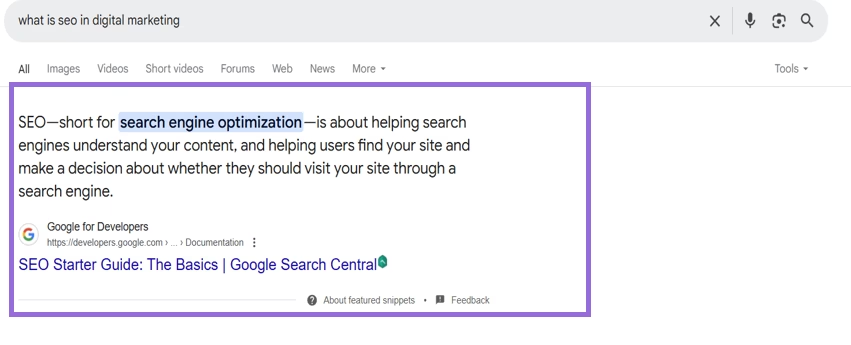
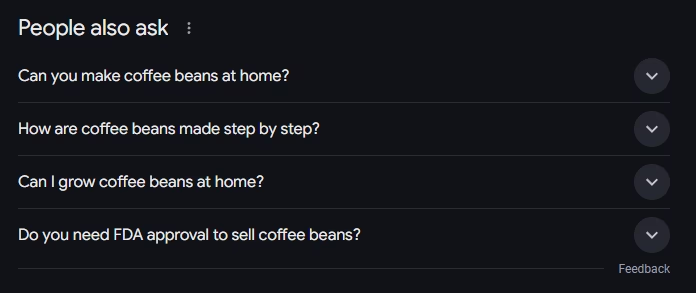
- People Also Ask (PAA). Expandable questions related to the query offering additional quick answers.
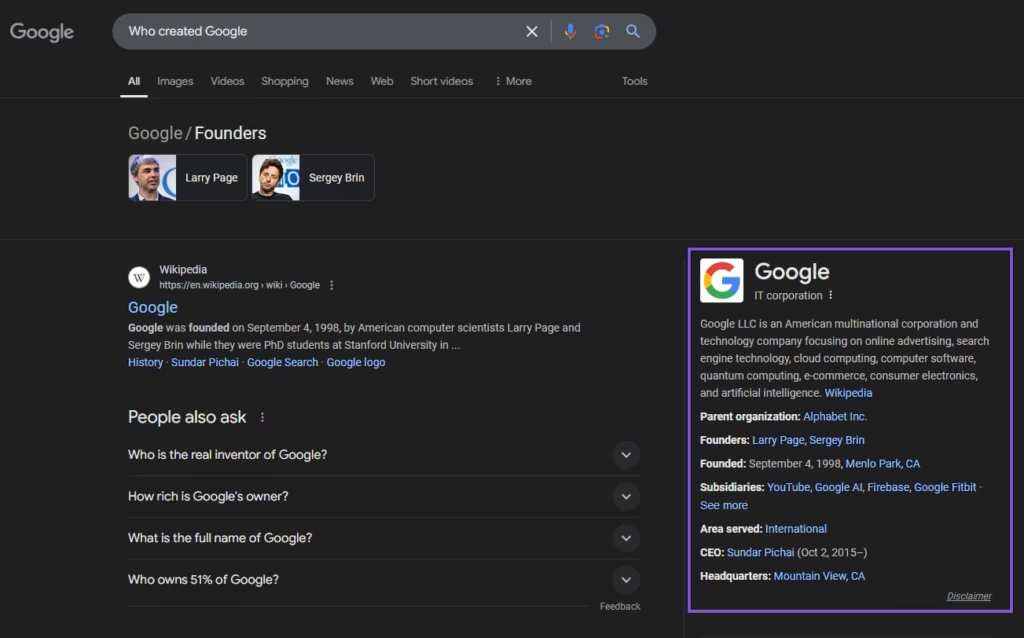
- Knowledge Panel. An information box on the right side with details about businesses, people, or places.
Understanding which SERP features your competitors rank for reveals how Google highlights their content. The benefits of examining competitor SERP features are listed below.
- Untapped Opportunities. Areas where your site compete to appear in valuable SERP features like featured snippets or People Also Ask boxes.
- Content Gaps. Missing or underdeveloped content types based on the answers and formats Google prefers for specific keywords.
- SEO Strategy Adaptation. Adjusting your approach to focus on the most influential SERP features to increase visibility and drive more traffic.
- User Intent Insight. Better understanding of what users want by analyzing which formats and information Google prioritizes for each search query.
Site Explorer reveals which SERP features your competitors rank for and how those features spread across their keywords. This insight helps you discover new content opportunities, such as targeting featured snippets or local packs.
Rank Tracker shows your own keyword rankings and indicates which SERP features your pages appear in. This is a feature in most modern rank tracking tools. It gives you a clear understanding of how your content is presented in search results.
[You can see all SERP features a keyword rank for in the Search Atlas Rank Tracker. You can also filter by individual feature.]
7. Compare Content Structure and Optimization
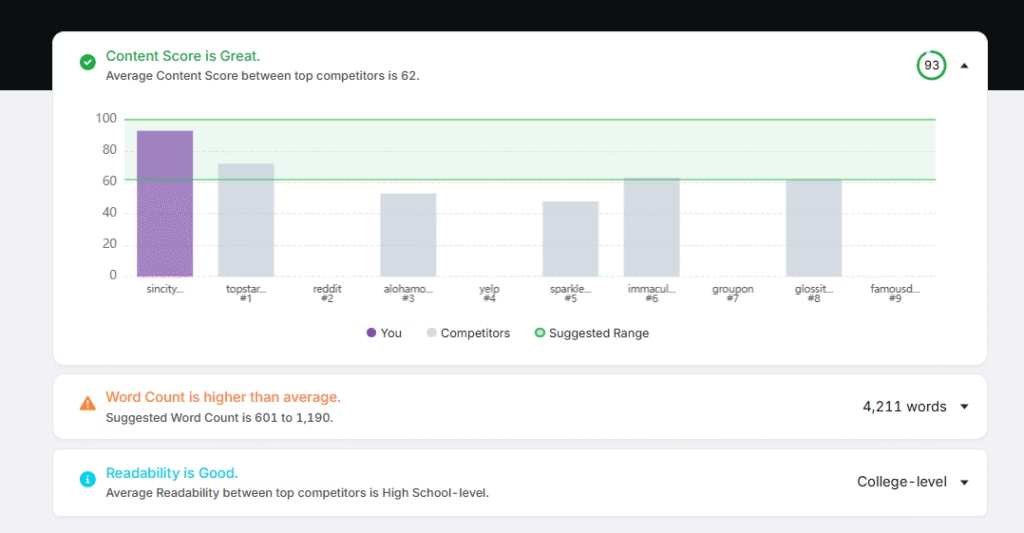
Examining how SERP competitors structure content reveals what Google values for a given search intent. You identify what is missing or needs improvement on your pages to better match or exceed those standards.
Search Atlas automates the process with the Onpage Audit Tool. The Onpage Audit tool uses AI to analyze your page and compare it against SEO best practices and competitor strategies. It highlights where your content and on-page elements fall short or excel. It gives you clear guidance on what to improve.
The Onpage Audit Tool gives you insights that are listed below.
- Content Score. Compare your score to top competitors to assess overall content quality.
- Word Count. Match the suggested word range based on top-ranking pages for the target query.
- Readability. Evaluate how easy the content is to read based on standard readability metrics.
- Page Structure. Check how you rank for keyword usage in text body, title, and headings, and the use of bold or strong tags.
- Meta Tags. Compare your title, meta description, canonical, and robots tags optimization.
- Rich Media Elements. Check the optimization of images, videos, iframes, links, schema markup, social sources, and Javascript files.
8. Compare Content Quality
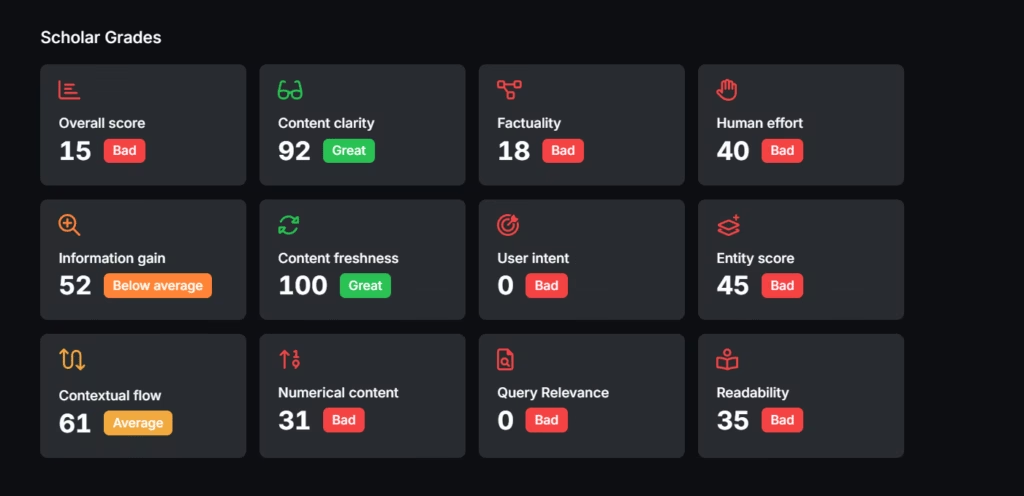
Study how competing pages cover the topic to understand how they satisfy search intent. Look at which angles they prioritize, how they structure information, and what formats they use. These choices reveal what Google favors for the keyword. To outrank them, deliver more complete, better-structured, and more relevant content.
Use Search Atlas Scholar to quantify these differences. Scholar evaluates content against hidden search factors and compares your page to top performers.
The metrics in Scholar are listed below.
- Content Clarity. Analyze sentence structure, reading level, and message flow to measure how clearly your page communicates ideas.
- Factuality. Check how well the language and concepts fit with the topic.
- Human Effort. Review signs of human input across the content, such as images, schema markup, and more.
- Information Gain. Identify whether the page offers unique insight or simply repeats what already exists.
- Content Freshness. Detect outdated material by reviewing dates, references, and publication cues.
- User Intent Alignment. Compare your content format and depth to what searchers want based on SERP signals.
- Entities. Evaluate whether the content mentions key concepts that connect to the topic in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
- Contextual Flow. Inspect the order and relationship of subtopics to confirm that the structure makes logical sense.
- Numerical Score. Measure the use and accuracy of statistics, figures, and data points within the content.
- Query Relevance. Check alignment between target keyword, URL, title, and headings to confirm topical focus.
- Readability. Rate the clarity and complexity of your writing for search and user experience.
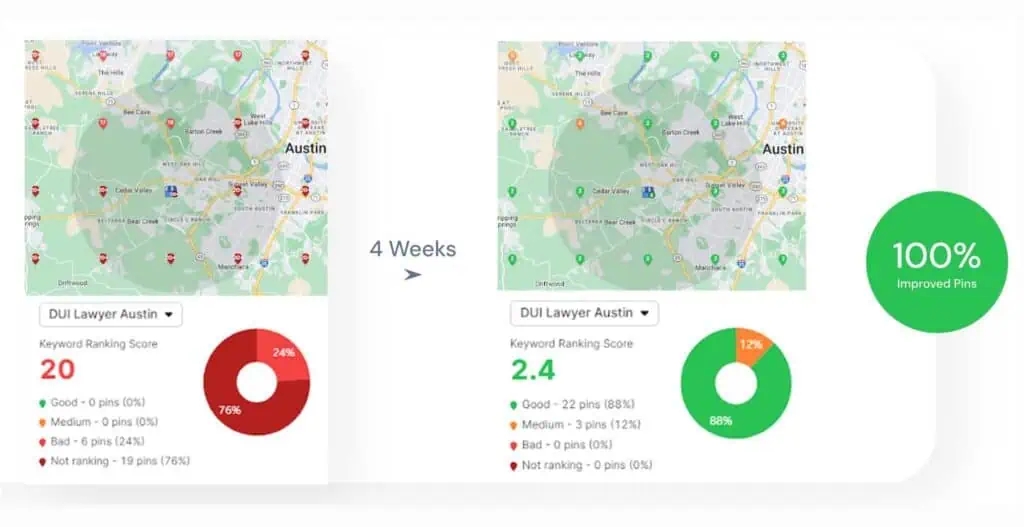
9. Examine Local SERPs
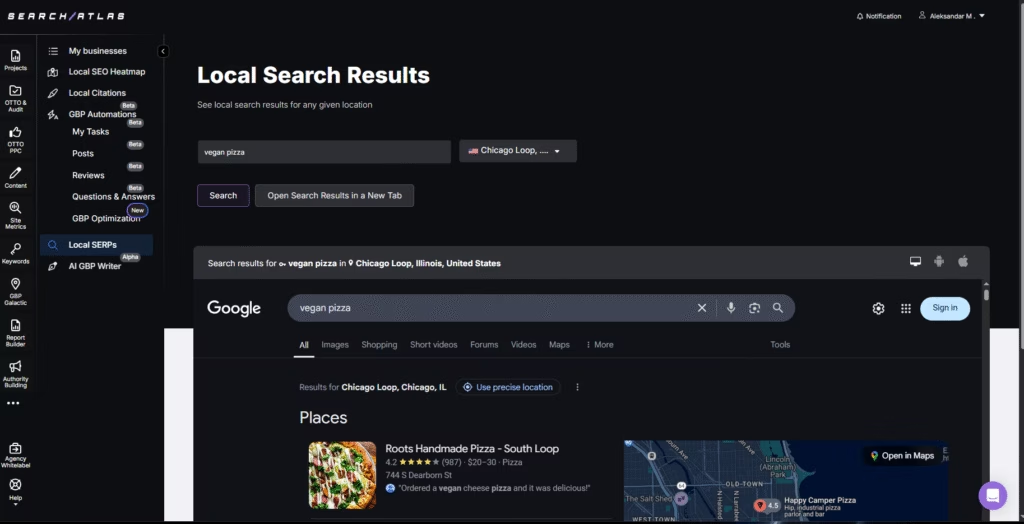
Search results change based on geographic context. Google adjusts rankings, business listings, and SERP features. These changes reflect the physical location of the searcher.
Review local SERPs to track which competitors appear in each region. Measure how well each result matches the search intent for that area. Find variations between cities or zip codes. Evaluate which domains dominate across different locations.
Use the Local Search Results Tool inside the local SEO toolkit. Enter specific neighborhoods or city names. View SERPs that reflect actual results from that location.
The benefits of checking local SERPs are listed below.
- Identifying top competitors in each region. Check which websites hold strong positions.
- Tracking local pack placement. Verify business visibility inside Google Maps listings.
- Reviewing SERP features. Detect the presence of reviews, People Also Ask boxes, or local snippets.
- Adjusting SEO strategy per region. Focus on areas that lack visibility. Build targeted content or update local business data.
Analyze SERP Competitors Ranking With Search Atlas
Studying SERP competitor rankings reveals how top pages meet user intent, earn visibility, and secure premium search features. These insights uncover exactly where your content underperforms and what improvements lead to higher rankings.
However, manual checks miss patterns, while automation reveals them.
Search Atlas is an SEO automation platform that tracks SERP features, scores content, and compares results across any market.
Try Search Atlas FREE for 7 days and use real data to refine your SEO. No commitment, cancel anytime.