A messy Google Ads campaign structure wastes budget and limits results. Plus, it can make management a total headache, especially if you have multiple campaigns or accounts. 🤦
But it doesn’t have to be like that.
With just a bit of time, you can learn how to set up campaigns for better control and efficiency.
We’ll show you how to group keywords, structure ad groups, and use PPC tools for easier research and organization.
What is Google Ads Campaign Structure?
Google Ads works like a well-organized filing system. 📂
This is how it works, top to bottom:
- At the top, you have your account, which holds everything.
- Inside that, you have campaigns, which act like big folders for different advertising goals.
- Each campaign contains ad groups, which help keep things sorted into smaller, more focused sections.
- Inside those ad groups are keywords and ads, the real drivers of your campaign’s success.
So here’s what happens at each level.
Account Level
This is the top level where you manage your overall Google Ads settings. This includes defining the account name, payment details, time zone, and linking to external sources like Google Analytics or YouTube.
You’ll also set your account’s conversion tracking and attribution model. These settings are foundational because any changes made here will apply to all campaigns, ad groups, and ads within the account.
For example, if you adjust the time zone at the account level, it will affect how and when all your ads are scheduled to run.
Campaign Level
At the campaign level, you’re setting the broad strategy for your ads. Here, you define your campaign goals—whether it’s to drive traffic, generate leads, or increase sales—and specify parameters like budget, location, and language targeting.
You’ll also choose the type of campaign, such as Search or Shopping, and the bidding strategy (e.g., CPC or CPA). Each campaign can contain multiple ad groups, but each one is focused on a single type of ad. The campaign level is where your broader goals and settings take shape.
Ad Group Level
Ad groups are where you manage your keywords and ads within a campaign. Each ad group contains keywords related to a specific product, service, or theme, and every ad group should have ads that reflect these keywords.
The goal here is to maintain relevance between your ads and the keywords that trigger them.
For example, if your ad group is about “winter jackets,” your ads should be specifically tailored to that. A good ad group structure helps improve your Quality Score by ensuring a strong correlation between keywords, ads, and landing pages.
Keywords
Think of keywords as the trigger that makes your ads appear when people search online. However, you choose the words or phrases you want to target, and you decide how strict you want to be with them (broad, phrase, exact).
And if there are certain words you don’t want your ad to show up for, you can add negative keywords. This way, you avoid spending money on clicks that aren’t likely to convert.
Ad Copy
Finally, the ad level is where you get to bring your campaign to life with the actual advertisements users will see.
This is the last step in your Google Ads structure, and it’s crucial to make your ads compelling and tailored to your audience. Here, you’ll create the actual copy, choose your display URL, and link your ad to a specific landing page.

10 Steps to Structure Your Google Ads Campaign
Setting up a well-structured Google Ads campaign is the key to better performance, easier management, and more efficient spending. A scattered setup can lead to wasted budget and missed opportunities, while an organized structure ensures your ads reach the right audience at the right time.
So here’s how to set up your campaigns for success. 🏆
1. Determine Your Account Structure
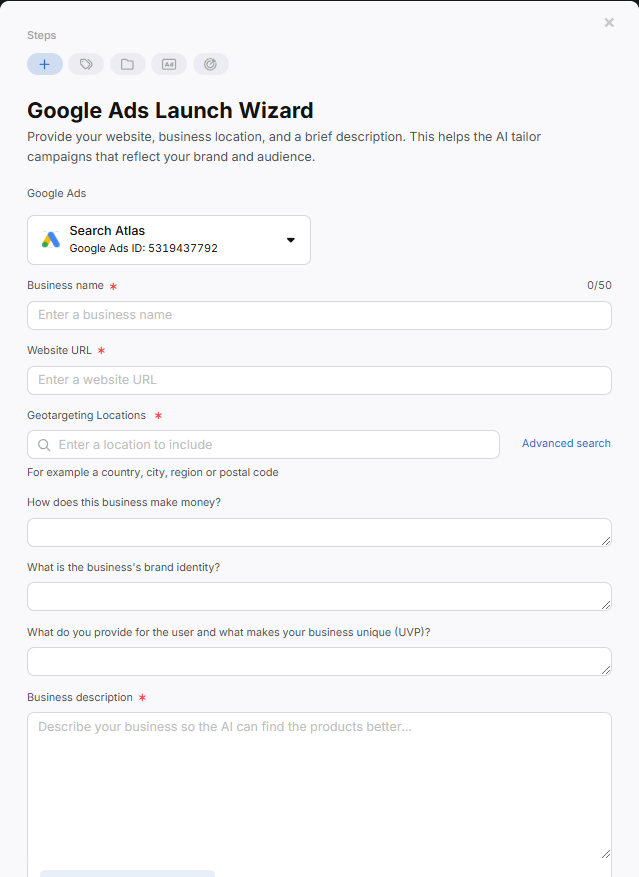
Before launching campaigns, get your account settings in place. Sign in to your Google Ads account and fill out important details like your business name, billing information, time zone, and tracking settings like auto-tagging. These settings help Google track performance and ensure accurate reporting.
Also, consider how you’ll structure your account.
If you run multiple businesses or different brands, you might need separate accounts or a Manager Account. Otherwise, a single account can hold multiple campaigns, each targeting different products, services, or customer segments.
2. Define Your Goals
Before setting up any campaign, be clear on what you want to achieve. Are you looking to drive more website traffic, generate leads, or increase sales? Your goal will determine your campaign type, targeting, and budget.
For example, if you’re running ads for an ecommerce store, your primary goal may be direct sales, so a Shopping campaign could be the best fit. If you’re a local business looking for phone calls, a Search campaign with location targeting may work better. Defining your objectives upfront makes campaign decisions much easier.
3. Choose a Campaign Type
Google Ads offers different campaign types, each suited for specific goals:
- Search Campaigns: Text ads that show on Google search results when users look for your keywords. Best for lead generation and direct sales.
- Display Campaigns: Image ads shown across millions of websites. Great for brand awareness and remarketing.
- Shopping Campaigns: Product listings that appear in Google Shopping results. Ideal for ecommerce businesses.
- Video Campaigns: Ads that run on YouTube. Useful for engagement and awareness.
- Performance Max Campaigns: Automates ad placement across Google’s entire network, optimizing for conversions.
4. Set a Budget and Bidding Strategy
Your budget determines how much you’re willing to spend on your ads. You can set a daily budget per campaign or a monthly total to control costs.
There are also other ways to cap and control your Google Ads budget to avoid overspend.
Start with a manageable budget, track results, and adjust based on performance.
When it comes to bidding strategies, you’ll be able to choose between Smart Bidding, Automated Bidding, and Manual Bidding Strategies. However, the best choice of bidding strategy will depend on your business goals.
5. Target Your Audience
Reaching the right people is just as important as choosing the right keywords. Use these targeting options to refine your audience:
- Location Targeting: Show ads to people in specific cities, regions, or countries.
- Demographics: Filter by age, gender, household income, and more.
- Interests and Behaviors: Target users based on their browsing habits and interests.
- Remarketing: Show ads to people who have previously visited your website.
Setting the right audience ensures your budget is spent on users who are most likely to convert.
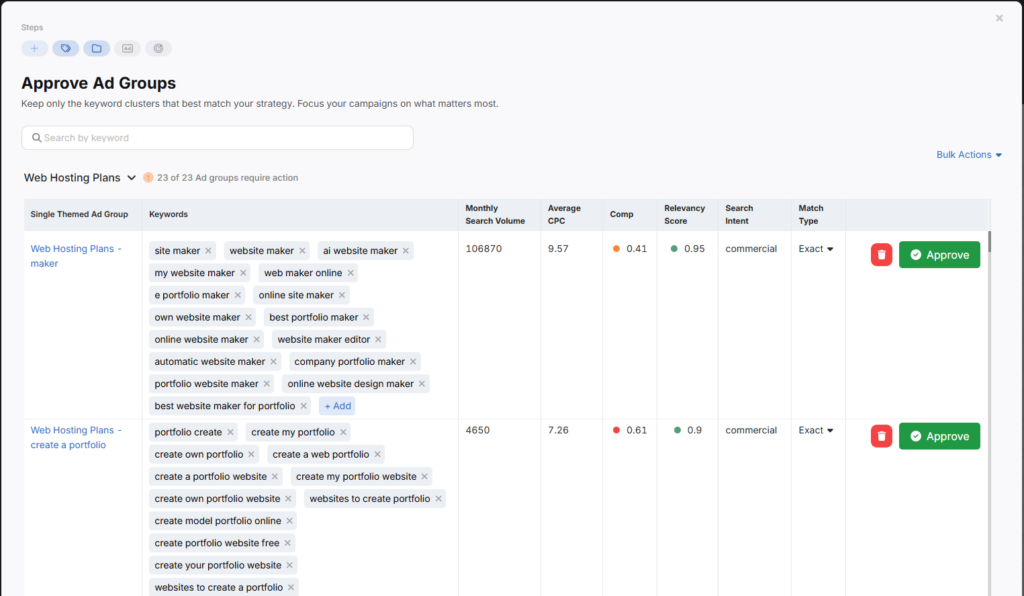
6. Create Relevant Ad Groups
Within each campaign, structure your ad groups around specific themes, products, or services. Each ad group contains its own set of keywords and ads, making them more targeted.
For example, if you run a travel agency, don’t lump all ads under one ad group. Instead, create separate ad groups like:
- Beach vacations
- Adventure tours
- Luxury getaways
This makes your ads more relevant to searchers and improves your Quality Score, which can lower costs.
Aim for 2–3 ads per ad group and keep keyword themes tight. You don’t want your keywords overlapping and competing with one another.
7. Perform Keyword Research
Choosing the right keywords is crucial for Search campaigns. Start with a small, focused list and expand as you gather data.
Use keyword research tools to find relevant search terms, and consider these match types:
- Broad Match: Shows ads on loosely related searches. (e.g., “running shoes” may trigger “best sneakers”)
- Phrase Match: Shows ads for searches containing your keyword in order. (e.g., “best running shoes for men”)
- Exact Match: Shows ads only for that precise term. (e.g., “buy red running shoes”)
A mix of match types helps balance reach and relevance. Start with about 10 keywords per ad group to allow room for testing.
You should also include negative keywords you don;t want to show up for.
Let’s say you have a travel agency and you want to only attract relevant clicks from potential customers. These can be your negative keywords (of course, depending on your services):
- job: To avoid people looking for travel agency jobs
- free:To exclude searches like “free travel packages”
- DIY: If you sell guided tours, not self-planned trips
- map: To prevent people searching for free travel maps
- visa – If you don’t provide visa services
- bus/ train: If you only offer flights and vacation packages
8. Write Compelling Ads
At the ad level, you’ll primarily focus on these elements:
- Headlines and Descriptions: Write clear, engaging headlines that capture attention. These will appear in different combinations if you’re using Responsive Search Ads (RSAs). You can add up to 15 headlines and 4 descriptions, but remember, each headline is limited to 30 characters, and descriptions to 90 characters.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): Every ad should include a strong call-to-action, whether it’s “Shop Now,” “Learn More,” or “Get a Free Quote.” A clear CTA drives user action and conversions.
- Display URL: This is the web address users will see, and it helps reinforce your ad’s relevance. It doesn’t have to be the full URL, but it should reflect the main domain and sometimes the ad’s specific content, like /shoes or /sale.
- Final URL: This is where users are directed when they click your ad. Ensure the landing page is relevant to the ad and provides a seamless experience for users
- Ad Extensions: Enhance your ad with additional information, such as sitelink extensions, callout extensions, and phone numbers. These can make your ad more noticeable and informative.
With Google’s Responsive Search Ads, you can test multiple headlines, and Google will automatically combine them to find the best-performing version. This approach helps improve your ad’s performance without manually adjusting it constantly.
9. Create the Right Landing Page
Your landing page is where users land after clicking your ad, and it plays a big role in conversion rates. A good landing page should:
- Match the ad’s message and keywords.
- Load quickly on desktop and mobile.
- Have a clear CTA (e.g., “Buy Now,” “Get a Free Trial”).
- Be easy to navigate with minimal distractions.
A well-optimized landing page improves user experience, increases conversions, and lowers ad costs by boosting your Quality Score.
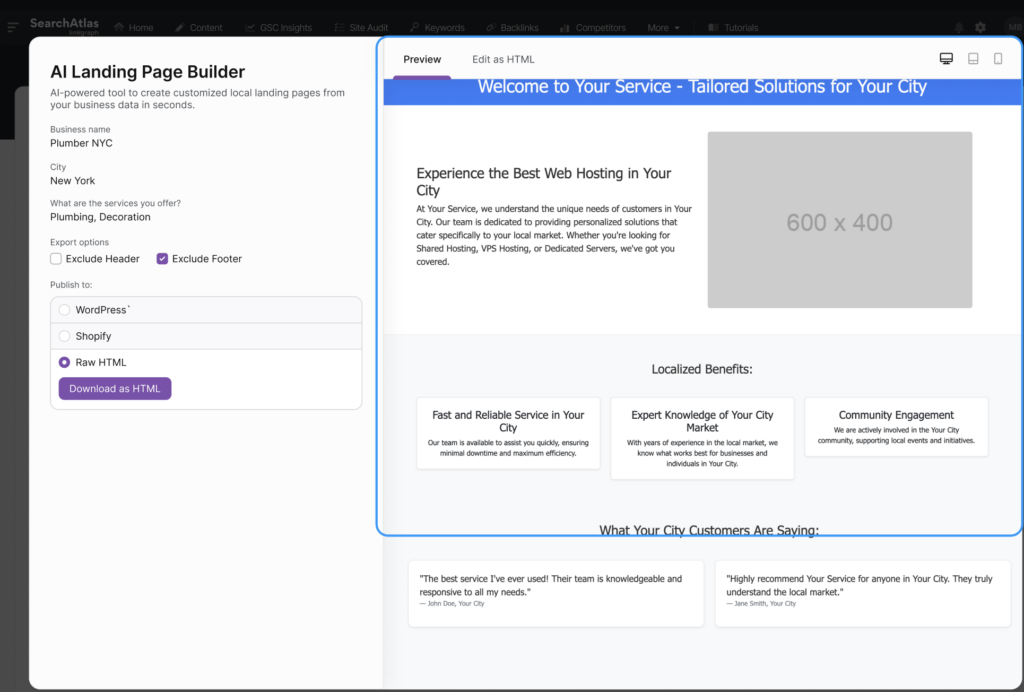
If you have an ecommerce business that requires tons of landing pages, you can create them using specialized AI.
10. Monitor and Optimize Regularly
Once your campaigns are live, don’t just set them and forget them. Regularly track performance and check your Search Report and Auction Insights.
Both tools can help you understand your campaign performance, but they serve different purposes:
- Auction Insights: This report lets you see how your ads perform compared to your competitors. You can check metrics like impression share, overlap rate, and position above rate to understand where you stand. It’s great for gauging your relative performance in the ad auctions.
- Search Terms Report: This report shows the actual search queries that triggered your ads. It helps you identify which keywords are working, discover new keyword opportunities, and add negative keywords to refine your targeting. It’s ideal for optimizing your keyword strategy and ensuring your ads reach the right audience.
Of course, you will have to test and optimize continuously to get the best return on your ad spend, and a Google Ads optimization checklist might help.

7 Best Practices for Structuring Your Google Ads Campaign
The right approach ensures your ads reach the right audience while keeping your budget under control.
Here are some best practices to follow when setting up and managing your campaigns.
1. Start with a Broad Structure and Refine Over Time
When launching your campaigns, begin with a general structure that covers your main products, services, or business goals. Over time, analyze performance data and make refinements.
- Start with a simpler structure to avoid unnecessary complexity.
- Break down campaigns into more specific ad groups as you gather insights.
- Adjust targeting, budgets, and bidding strategies based on performance trends.
By starting broad and fine-tuning as you go, you can adapt to what works best without overwhelming yourself with too many campaigns upfront.
2. Use Highly Focused Keyword Themes
Each ad group should be centered around a tightly related set of keywords. This ensures your ads are more relevant to search queries, which improves engagement and lowers costs.
- Group keywords that share a common intent or topic within a single ad group.
- Avoid mixing unrelated keywords, as doing so weakens ad relevance.
- Keep your keyword lists manageable with 5 to 20 well-targeted keywords max.
The more aligned your keywords are, the better your ads will match search intent, improving your Quality Score and overall campaign performance.
3. Optimize for Quality Score
Google assigns a Quality Score to your keywords based on ad relevance, landing page experience, and expected click-through rate. A higher Quality Score leads to:
- Lower cost-per-click (CPC) 💸
- Better ad placement 🔝
- Higher chances of conversions 🤝
To improve your Quality Score:
- Write highly relevant ad copy that includes targeted keywords.
- Ensure your landing pages match the keywords and ad messaging.
- Continuously test different ad variations to increase engagement.
4. Continuously Test and Optimize
Success in Google Ads comes from constant improvement. Testing different ad elements helps identify what resonates most with your audience.
- Test multiple ad variations with different headlines, descriptions, and calls to action.
- Experiment with different bidding strategies (e.g., Maximize Conversions vs. Target CPA).
- Analyze which keywords drive the best results and pause underperforming ones.
- Try A/B testing on landing pages to improve conversion rates.
Instead of setting up campaigns once and forgetting about them, make data-driven adjustments to keep improving performance.
5. Separate Brand and Non-Brand Search Campaigns
Users searching for your brand already know your business, so brand-related campaigns should be managed separately from non-brand campaigns.
- Brand campaigns: Capture searches for your company name, product names, or branded terms. These typically have high click-through rates and lower costs.
- Non-brand campaigns: Target potential customers searching for general terms related to your business.
Why separate them?
- It gives you better control over budget allocation between brand and non-brand traffic.
- You can analyze performance separately and avoid inflating overall metrics.
- To prevent overlap, add brand keywords as negative keywords in non-brand campaigns.
By structuring them separately, you can track, manage, and optimize each campaign more effectively.
6. Avoid Mixing Search and Display in One Campaign
Google Ads allows you to serve Search ads on the Display Network, but doing so can hurt performance.
- Search campaigns target users actively looking for your product or service.
- Display campaigns focus on visual ads placed on websites, apps, and YouTube.
If you’re running a standard Search campaign, uncheck the option to include the Display Network. This prevents your ads from being shown to users who aren’t actively searching, ensuring better use of your budget.
For newer campaign types like Performance Max, Display, Shopping, and Discovery, Google automatically places ads across multiple networks, so this rule doesn’t apply.
7. Structure Your Campaigns Based on Your Goals
Your campaign structure should align with your business objectives. A well-thought-out structure makes campaign management, reporting, and optimization much easier.
Common ways to organize campaigns include:
- By Sales Funnel Stages: Separate campaigns for awareness, consideration, and conversion.
- By Product or Service Categories: Group campaigns based on different offerings.
- By Location: Create separate campaigns for different cities, regions, or countries.
- By Conversion Type: If your business has multiple goals (e.g., lead generation vs. online purchases), structure campaigns accordingly.
Use AI Tools to Simplify and Optimize Structuring
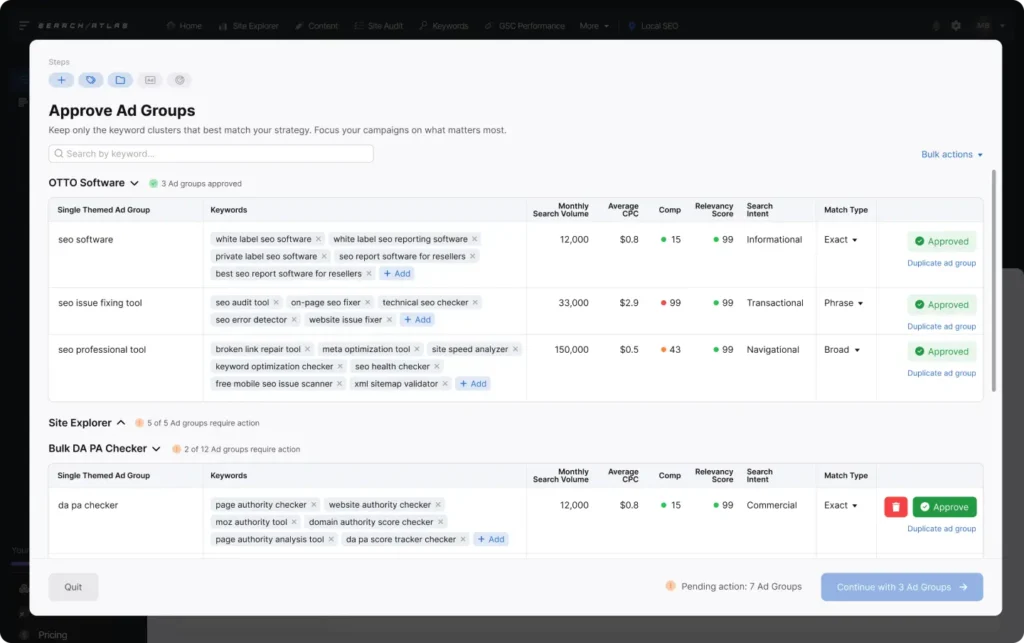
Optimizing your Google Ads campaigns and ad groups can be a time-consuming and complex process, often requiring constant adjustments and trial and error. With OTTO Google Ads, all that effort is streamlined.

OTTO Google Ads fully automates campaign structuring while giving you total control over your campaigns. 🎮
It lets you create large, single-theme ad groups in minutes, with keywords and ad copy super-aligned to the keyword cluster and search intent.
This gives even small businesses the precision of ad management that would otherwise take days and require professional assistance.
These are all the tasks he can complete in minutes, instead of days:
- Creating Campaigns
- Organizing Ad Groups
- Finding the Best Keywords
- Writing Engaging Ad Copy
- Simplified A/B Testing
- Automated Geotargeting
- Performance-Driven Campaign Setup
Your ad portfolio becomes neatly packaged and easy to manage with the help of AI. What’s fantastic is that it works even with low budgets, plus it saves time and money on human effort.
Also, OTTO Google Ads is a part of Search Atlas, a platform that gives you a full search solution: SEO, PPC, content, and digital PR.
No matter your business size, OTTO Google Ads scales to meet your needs. It has been tested by freelancers, marketing agencies, and enterprises with excellent reviews.
Simplifying Google Ads Campaign Structure
By understanding the roles of the account, campaign, ad group, keywords, and ads, you can create a strategy that’s both organized and optimized for success. But as you grow, automation can make a huge difference in efficiency and results.
OTTO Google Ads makes automating your campaigns a breeze, allowing you to focus on growing your business. 🌱
Why not give it a try? No commitments, no hassle, and you can cancel anytime—just like that! Sign up for a free trial today!